

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 184-195.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024106
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
汪欣瑶1,3( ), 彭亚萍1,3, 姚立蓉1,3, 汪军成1,3, 司二静1,3, 张宏1,3, 杨轲1,3, 马小乐1,3, 孟亚雄1,3, 王化俊1,3(
), 彭亚萍1,3, 姚立蓉1,3, 汪军成1,3, 司二静1,3, 张宏1,3, 杨轲1,3, 马小乐1,3, 孟亚雄1,3, 王化俊1,3( ), 李葆春1,2
), 李葆春1,2
收稿日期:2024-04-02
修回日期:2024-06-04
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
王化俊
作者简介:E-mail: huajunwang@sina.com基金资助:
Xin-yao WANG1,3( ), Ya-ping PENG1,3, Li-rong YAO1,3, Jun-cheng WANG1,3, Er-jing SI1,3, Hong ZHANG1,3, Ke YANG1,3, Xiao-le MA1,3, Ya-xiong MENG1,3, Hua-jun WANG1,3(
), Ya-ping PENG1,3, Li-rong YAO1,3, Jun-cheng WANG1,3, Er-jing SI1,3, Hong ZHANG1,3, Ke YANG1,3, Xiao-le MA1,3, Ya-xiong MENG1,3, Hua-jun WANG1,3( ), Bao-chun LI1,2
), Bao-chun LI1,2
Received:2024-04-02
Revised:2024-06-04
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Hua-jun WANG
摘要:
为应对日益严峻的干旱环境问题,发掘植物体内的抗旱基因具有重要意义。基于前期盐生草转录组测序数据分析结果,盐胁迫后HgS5基因的表达量与差异倍数最高,故选其为研究对象,对目的基因编码的蛋白进行生物信息学分析并进行亚细胞定位;通过qRT-PCR检测目的基因在拟南芥植株叶片和根系的相对表达量,并利用农杆菌完成拟南芥异源表达,以验证目的基因的抗旱能力。结果表明,HgS5基因中碱基对的数量为1738,编码370个氨基酸,编码蛋白为酸性亲水性蛋白且没有跨膜区;具有116个启动子顺式作用元件;HgS5基因和巨人柱、苋菜和甜菜相关同源基因拥有相同的A_thal_3526保守结构域;亚细胞定位显示HgS5基因主要在细胞膜上表达; 荧光定量结果显示HgS5基因主要在拟南芥根系表达,处理第6天表达量与其他组别差异显著(P<0.05);抗旱鉴定结果显示过表达拟南芥的抗旱性明显增强,具体表现为植株枯萎程度减缓;基因HgS5通过影响酶活性来对抗干旱环境,过表达拟南芥根系超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性在干旱胁迫后期整体高于野生型。综上所述,基因HgS5在抗旱过程中起到了积极的调控作用。研究结果旨在为进一步探索HgS5基因应对干旱胁迫的分子响应机制提供理论依据。
汪欣瑶, 彭亚萍, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草HgS5基因的克隆与抗旱性鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 184-195.
Xin-yao WANG, Ya-ping PENG, Li-rong YAO, Jun-cheng WANG, Er-jing SI, Hong ZHANG, Ke YANG, Xiao-le MA, Ya-xiong MENG, Hua-jun WANG, Bao-chun LI. Gene cloning and drought resistance identification of the gene HgS5 in Halogeton glomeratus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 184-195.
| 引物名称Name of primers | 引物序列Sequence of primers (5′-3′) | 用途Function |
|---|---|---|
| HgS5-F1 | CGTTGTTTCCAGCCCACTTC | 克隆基因 Gene cloning |
| HgS5-R1 | AATGTTAAACACTTTACAATAC | |
HgS5-F1 HgS5-R1 | GG CG | 表达载体 Expression vector |
35s-F HgS5-R | GACGCACAATCCCACTATCC CGGGATCCAGAATGTTAAACACTTTACAATAC | 鉴定引物 Identification primer |
| HgS5-F1 | GCTCTAGAGACGTTGTTTCCAGCCCACT | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| HgS5-R1 | GGGGTACCAGAATGTTAAACACTTTACAATAC | |
| HgS5-F1 | ACCCTGTCCTACAACCACCT | 荧光定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| HgS5-R1 | TGGGAGCAGGGACTCCATTA | |
| Actin-F1 | GGTGATGGTGTGTCTCACACTG | |
| Actin-R1 | GAGGTTTCCATCTCCTGCTCGTAG | |
| Actin-F2 | ACACAAGGTCTATGTCGGAAAT | |
| Actin-R2 | TAACACTCTCGTGCTTACGATT |
表1 试验所用引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequence used in the experiment
| 引物名称Name of primers | 引物序列Sequence of primers (5′-3′) | 用途Function |
|---|---|---|
| HgS5-F1 | CGTTGTTTCCAGCCCACTTC | 克隆基因 Gene cloning |
| HgS5-R1 | AATGTTAAACACTTTACAATAC | |
HgS5-F1 HgS5-R1 | GG CG | 表达载体 Expression vector |
35s-F HgS5-R | GACGCACAATCCCACTATCC CGGGATCCAGAATGTTAAACACTTTACAATAC | 鉴定引物 Identification primer |
| HgS5-F1 | GCTCTAGAGACGTTGTTTCCAGCCCACT | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| HgS5-R1 | GGGGTACCAGAATGTTAAACACTTTACAATAC | |
| HgS5-F1 | ACCCTGTCCTACAACCACCT | 荧光定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| HgS5-R1 | TGGGAGCAGGGACTCCATTA | |
| Actin-F1 | GGTGATGGTGTGTCTCACACTG | |
| Actin-R1 | GAGGTTTCCATCTCCTGCTCGTAG | |
| Actin-F2 | ACACAAGGTCTATGTCGGAAAT | |
| Actin-R2 | TAACACTCTCGTGCTTACGATT |

图1 HgS5基因生物信息学分析A: PCR扩增;泳道1~4为HgS5基因的PCR扩增产物电泳图(Marker为2000 bp);B: 蛋白跨膜区分析图; C: 蛋白亲疏水性预测; D: 蛋白二级结构预测图; E : 蛋白质三级结构预测。A: PCR amplification; Lane 1-4 is the PCR product amplification electrophoresis image of gene HgS5 (M: DL 2000 DNA Marker); B: Analysis diagram of protein transmembrane region; C: Protein hydrophobicity prediction; D: Protein secondary structure prediction diagram; E: Protein tertiary structure prediction.
Fig.1 Bioinformatics analysis and prediction of HgS5
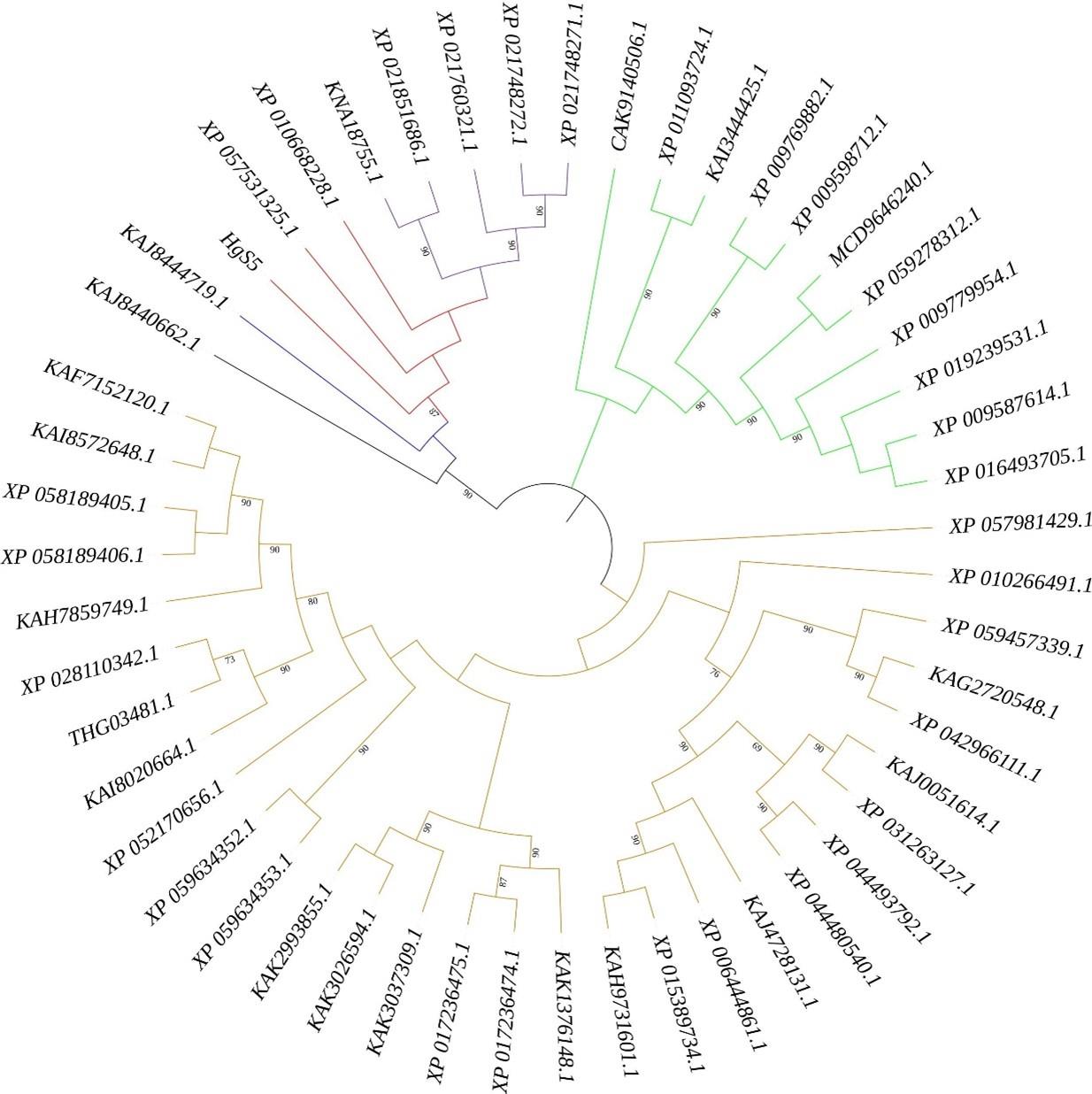
图2 HgS5基因的系统进化树选取同源性依次递减的前50个基因。The first 50 genes with decreasing homology were selected. HgS5 (Halogeton glomeratus)、XP_021851686.1 (Spinacia oleracea)、KNA18755.1 (Spinacia oleracea)、XP_010668228.1 (Beta vulgaris subsp.)、XP_021760321.1 (Chenopodium quinoa)、XP_057531325.1 (Amaranthus tricolor)、XP_021748271.1 (Chenopodium quinoa)、KAJ8444719.1 (Carnegiea gigantea)、XP_059634352.1 (Cornus florida)、XP_016493705.1 (Nicotiana tabacum)、XP_021748272.1 (Chenopodium quinoa)、XP_009587614.1 (Nicotiana tomentosiformis)、XP_028110342.1 (Camellia sinensis)、XP_057981429.1 (Malania oleifera)、XP_059634353.1 (Cornus florida)、THG03481.1 (Camellia sinensis var.)、KAJ4728131.1 (Melia azedarach)、KAI8020664.1 (Camellia lanceoleosa)、KAF7152120.1 (Rhododendron simsii)、XP_009779954.1 (Nicotiana sylvestris)、XP_058189405.1 (Rhododendron vialii)、XP_019239531.1 (Nicotiana attenuate)、KAJ8440662.1 (Carnegiea gigantea)、XP_006444861.1 (Citrus x clementina)、XP_058189406.1 (Rhododendron vialii)、KAK2993855.1 (Escallonia rubra)、XP_042966111.1 (Carya illinoinensis)、CAK9140506.1 (Ilex paraguariensis)、KAK3026594.1 (Escallonia herrerae)、KAG2720548.1 (Carya illinoinensis)、KAI3444425.1 (Paulownia fortune)、KAH7859749.1 (Vaccinium darrowii)、KAH9731601.1 (Citrus sinensis)、KAK3037309.1 (Escallonia herrerae)、XP_009598712.1 (Nicotiana tomentosiformis)、XP_044480540.1 (Mangifera indica)、XP_015389734.1 (Citrus sinensis)、XP_044493792.1 (Mangifera indica)、XP_009769882.1 (Nicotiana sylvestris)、KAI8572648.1 (Rhododendron molle)、KAK1376148.1 (Heracleum sosnowskyi)、XP_010266491.1 (Nelumbo nucifera)、XP_031263127.1 (Pistacia vera)、XP_017236475.1 (Daucus carota subsp.)、XP_017236474.1 (Daucus carota subsp.)、XP_059278312.1 (Lycium ferocissimum)、KAJ0051614.1 (Pistacia integerrima)、XP_011093724.1 (Sesamum indicum)、MCD9646240.1 (Datura stramonium)、XP_059457339.1 (Corylus avellana) and XP_052170656.1 (Diospyros lotus).
Fig.2 Phylogenetic tree of the gene HgS5
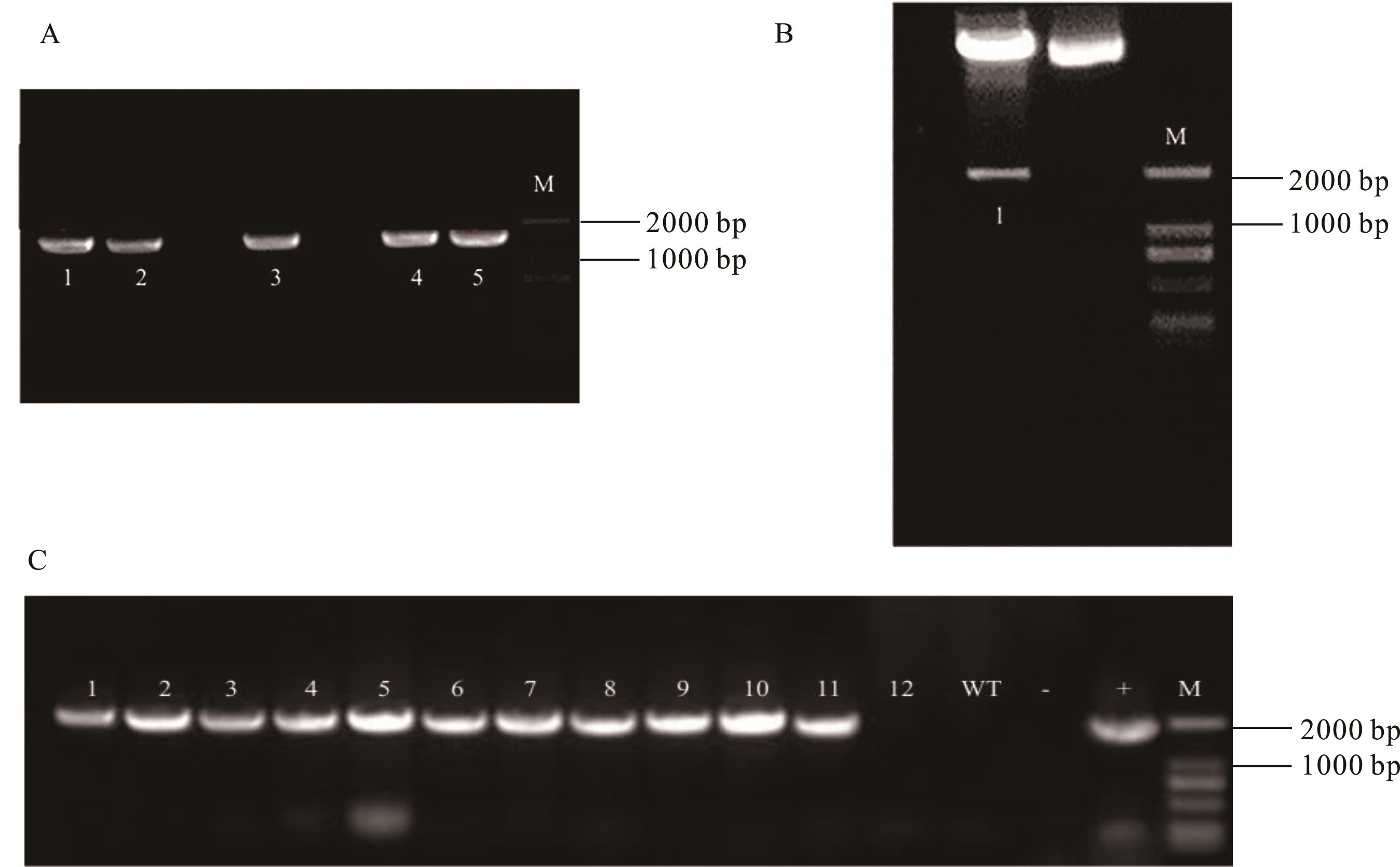
图5 遗传转化拟南芥PCR胶图汇总A: pCambia2301-HgS5表达载体PCR验证,M为Marker,泳道1~5为HgS5基因的单克隆PCR验证;B:pCambia2301-HgS5表达载体双酶切验证,M为Marker,泳道1为HgS5基因的单克隆PCR验证;C:T0代阳性株检验,M为Marker,泳道1~12为HgS5基因的单克隆PCR验证,“WT”为野生型,“-”为ddH2O,“+”为质粒。Marker为2000 bp。A: pCambia2301-HgS5 expression vector PCR verification, M as Marker, lanes 1-5 as HgS5 gene monoclonal PCR verification; B:pCambia2301-HgS5 expression vector was verified by double restriction enzyme digestion, M was the Marker, and lane 1 was the monoclonal PCR verification of HgS5 gene; C: T0 generation positive plant test, M is Marker, lanes 1-12 are confirmed by monoclonal PCR of HgS5 gene, “WT” is wild type, “-” is ddH2O, and “+” is plasmid. Marker is 2000 bp.
Fig.5 Summary of PCR gel map of genetic transformation A. thaliana
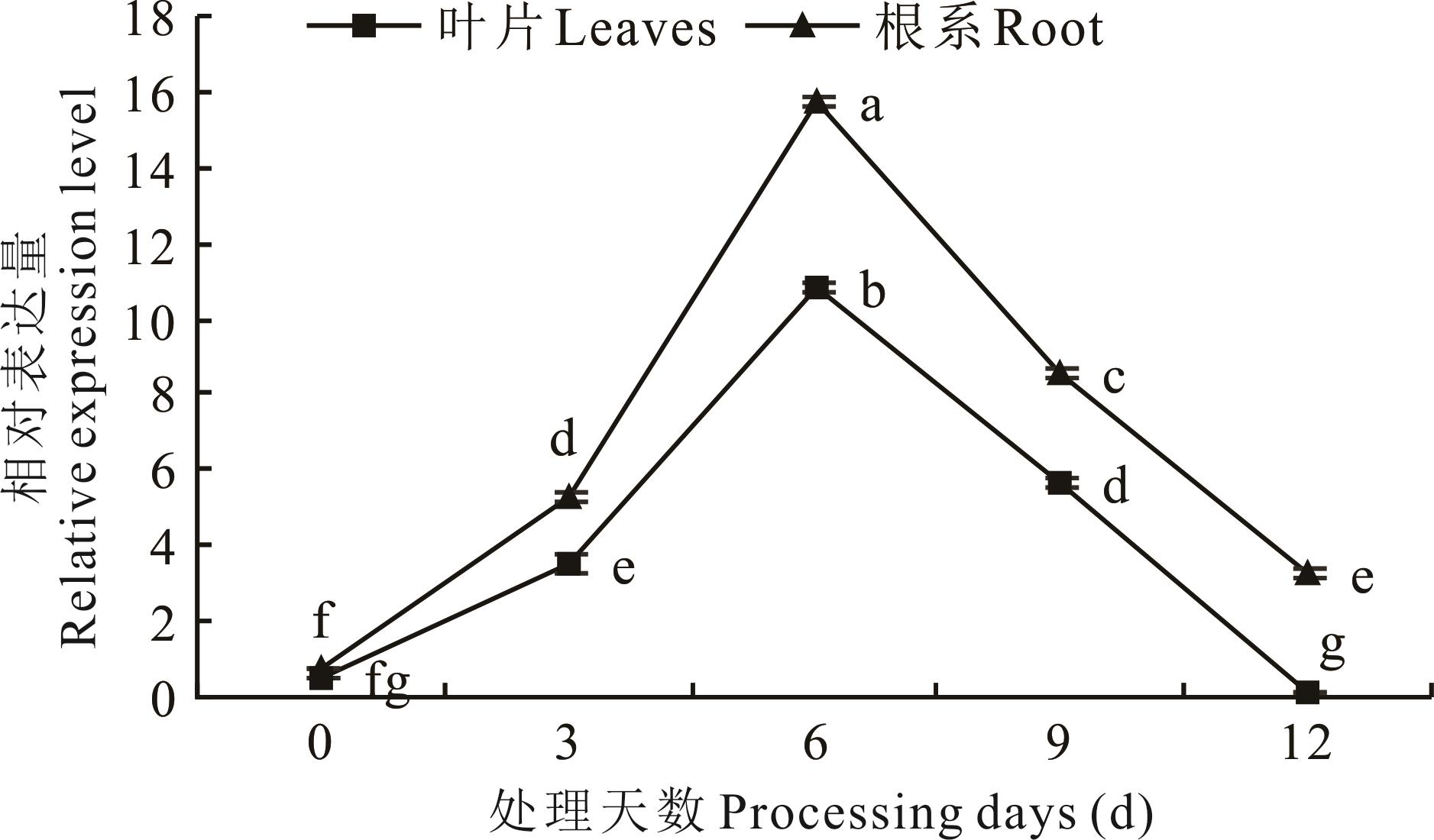
图6 基因相对表达量分析不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.6 Gene relative expression analysis
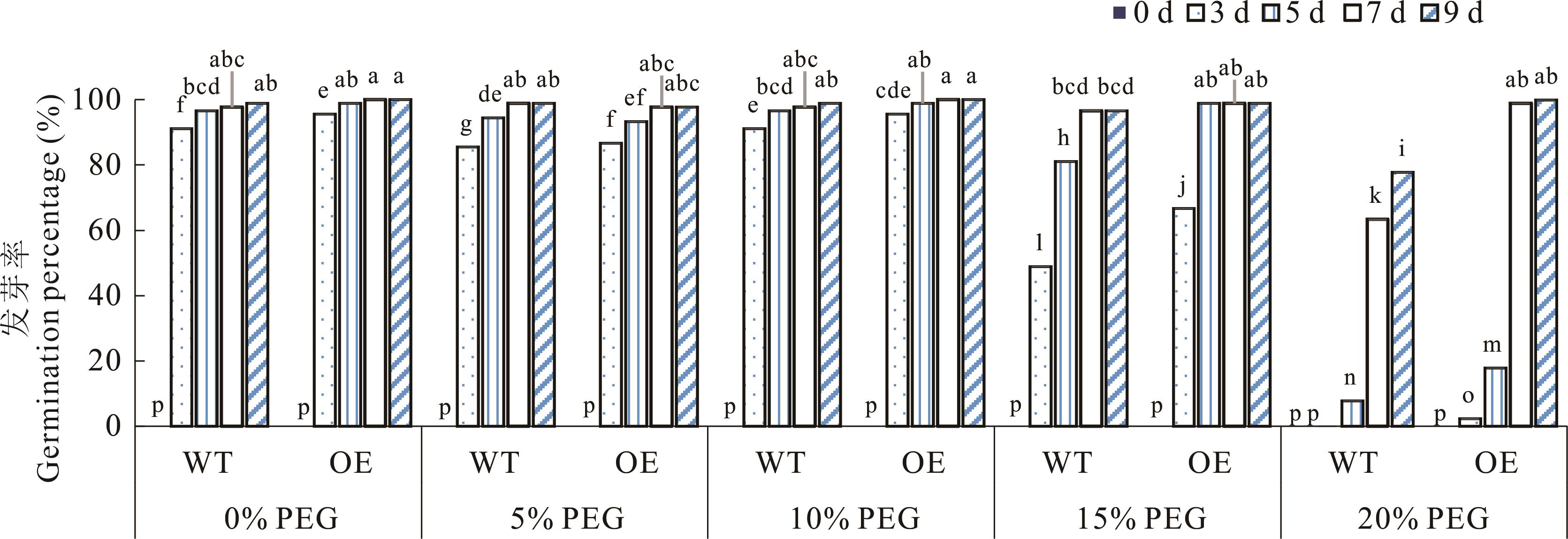
图7 PEG胁迫处理下种子萌发情况WT:野生型;OE:过表达株系;PEG:聚乙二醇;下同。WT: Wild type; OE: Overexpression plants; PEG: Polyethylene glycol; The same below.
Fig.7 Seed germination under different PEG stress treatments
| 项目 Item | 0 d | 3 d | 6 d | 9 d | 12 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT-1 | 50.52 | 45.99 | 30.22 | 7.13 | 5.98 |
| WT-2 | 50.94 | 43.08 | 30.98 | 7.15 | 5.87 |
| WT-3 | 50.99 | 44.44 | 30.45 | 7.12 | 5.88 |
| OE-1 | 50.87 | 45.35 | 30.45 | 7.14 | 5.56 |
| OE-2 | 50.83 | 44.42 | 30.35 | 7.33 | 5.78 |
| OE-3 | 50.76 | 43.55 | 30.57 | 7.25 | 5.88 |
表2 干旱处理下的土壤含水量
Table 2 Soil moisture content under drought stress (%)
| 项目 Item | 0 d | 3 d | 6 d | 9 d | 12 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT-1 | 50.52 | 45.99 | 30.22 | 7.13 | 5.98 |
| WT-2 | 50.94 | 43.08 | 30.98 | 7.15 | 5.87 |
| WT-3 | 50.99 | 44.44 | 30.45 | 7.12 | 5.88 |
| OE-1 | 50.87 | 45.35 | 30.45 | 7.14 | 5.56 |
| OE-2 | 50.83 | 44.42 | 30.35 | 7.33 | 5.78 |
| OE-3 | 50.76 | 43.55 | 30.57 | 7.25 | 5.88 |
| 1 | Tian L X, Yang Y, Song Y H, et al. Rehydration under extreme drought conditions affected rhizosphere microorganisms more than bulk soil in broomcorn millet farmland. Agricultural Water Management, 2024, 295(1): 108781-108794. |
| 2 | Corwin D L. Climate change impacts on soil salinity in agricultural areas. European Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 72(2): 842-862. |
| 3 | Sun M, Peng F, Xiao Y, et al. Exogenous phosphatidylcholine treatment alleviates drought stress and maintains the integrity of root cell membranes in peach. Scientia Horticulturae, 2020, 259(6): 108821-108829. |
| 4 | Zhang H O. An analysis of the distribution and evolutionary characteristics of saline soils in China. Agriculture and Technology, 2022, 42(5): 104-107. |
| 5 | Yang S S, Gao J F. Influence of active oxygen and free radicals on plant senescence. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2001, 21(2): 36-41. |
| 杨淑慎, 高俊凤. 活性氧、自由基与植物的衰老. 西北植物学报, 2001, 21(2): 36-41. | |
| 6 | Zhang J, Mao C L, khan A, et al. Enhanced methane production by using phytoremediated Halogeton glomeratus as substrate via anaerobic digestion. Renewable Energy, 2022, 194(1): 28-39. |
| 7 | Wang J C, Yang K, Yao L R, et al. Metabolomics analyses provide insights into nutritional value and abiotic stress tolerance in halophyte Halogeton glomeratus. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021(12): 703255-703264. |
| 8 | Eggers E J, Burgt A, Heusden S, et al. Neofunctionalisation of the Sli gene leads to self-compatibility and facilitates precision breeding in potato. Nature Communications, 2021(12): 4141-4151. |
| 9 | Cheng Q, Gan Z, Wang Y, et al. The soybean gene J contributes to salt stress tolerance by up-regulating salt-responsive genes. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020(11): 272-281. |
| 10 | Gálvez R L. The application of metabolomics for the study of cereal corn (Zea mays L.). Metabolites, 2020(10): 300-308. |
| 11 | Ren X M, Hu Z R, Jiang X Z, et al. Analysis of physiological characteristics and related gene expression in response to low-temperature stress in different tobacco varieties. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2024(1): 10-15. |
| 任晓敏, 户正荣, 姜习振, 等. 低温胁迫对不同烟草品种的生理特性及相关基因表达分析. 分子植物育种, 2024(1): 10-15. | |
| 12 | Wang Q, Tang J, Han B, et al. Advances in genome-wide association studies of complex traits in rice. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2020, 133(1): 1415-1425. |
| 13 | Zafar M M, Rehman A, Razzaq A, et al. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of Erf gene family in cotton. BMC Plant Biology, 2022, 134(1): 22-43. |
| 14 | Patel J, Mishra A. Plant aquaporins alleviate drought tolerance in plants by modulating cellular biochemistry, root-architecture, and photosynthesis. Physiologia Plantarum, 2021, 172(2): 1030-1044. |
| 15 | Xu X L. Cloning of tonoplast and plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene and isolating of 5′ flanking sequence of HgNHX1 from Halogeton glomeratus. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2014. |
| 徐先良. 盐生草Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因的克隆及HgNHX1基因5′端侧翼序列的分离. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2014. | |
| 16 | Zhang Y, Li B C, Hu Y L, et al. Functional verification of HgNHX1 gene derived from Halogeton glomeratus in barley. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2018, 38(8): 929-934. |
| 张燕, 李葆春, 胡有良, 等. 盐生草HgNHX1基因在大麦株系中的功能验证. 麦类作物学报, 2018, 38(8): 929-934. | |
| 17 | Zou L, Yang K, Xu X L, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of halophyte Halogeton glomeratus HgNHX1 promoter. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(11): 57-68. |
| 邹兰, 杨轲, 徐先良, 等. 盐生草HgNHX1基因启动子的克隆及功能验证. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 57-68. | |
| 18 | Ma Y H, Xu X L, Wang J C, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of Actin gene fragment from halophyte Halogeton glomeratus. Pratacultural Science, 2015, 32(9): 1432-1437. |
| 马艳红, 徐先良, 汪军成, 等. 盐生草Actin基因片段的克隆及表达. 草业科学, 2015, 32(9): 1432-1437. | |
| 19 | Hu S Q, Wang J C, Yao L R, et al. Cloning and preliminary functional analysis of the root gene HgAKR6C of Halogeton glomeratus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(1): 61-74. |
| 胡尚钦, 汪军成, 姚立蓉, 等. 盐生草根系基因HgAKR6C的克隆与初步功能分析. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 61-74. | |
| 20 | Wang J C, Li B C, Meng Y X, et al. Transcriptomic profiling of the salt-stress response in the halophyte Halogeton glomeratus. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16(1):169. |
| 21 | Wang J C, Wang H J, Yao L R, et al. Salt-tolerant gene HgS3 of Halogeton glomeratus and its application: CN107287212B. 2020-10-30. |
| 汪军成, 王化俊, 姚立蓉, 等. 盐生草耐盐基因HgS3及其应用: CN107287212B. 2020-10-30. | |
| 22 | Zhou M. Effects of exogenous calcium on physiological characteristics of Rhododendron ovatum Planch seed germination under drought stress. Beijing Agriculture, 2014(21): 11-12. |
| 周敏. 干旱胁迫下外源钙对马缨杜鹃种子萌发生理特性的影响. 北京农业, 2014(21): 11-12. | |
| 23 | Ma J W, Ma Z K, Yao L R, et al. Regulating effect of exogenous melatonin on root growth of barley seedling under phosphorus stress. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2023, 43(8): 1020-1028. |
| 马静玮, 马增科, 姚立蓉, 等. 低磷胁迫下外源褪黑素对大麦幼苗根系发育的调控作用. 麦类作物学报, 2023, 43(8): 1020-1028. | |
| 24 | Yao H. Cloning of DFR, FLS promoters and RNAi vector construction of LYCE and LYCB in Narcissus tazetta var. chinensis. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2024. |
| 姚红. 中国水仙DFR和FLS启动子克隆及LYCE和LYCB RNAi表达载体的构建. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2024. | |
| 25 | Li G, Bai Y, Jia Z Y, et al. Phosphorus altered the response of ionomics and metabolomics to drought stress in wheat seedlings. Scientia Agricultural Sinica, 2022, 55(2): 280-294. |
| 李刚, 白阳, 贾子颖, 等.两种磷素水平下小麦苗期对干旱胁迫的离子组和代谢组响应. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(2): 280-294. | |
| 26 | Zeng F L, Li Y F. Generation of active oxygen free radicals and its injury to microsome membranes in wheat leaves under drought stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 1997, 39(12): 1105-1109. |
| 曾福礼, 李玉峰.干旱胁迫下小麦叶片微粒体活性氧自由基的产生及其对膜的伤害. 植物学报, 1997, 39(12): 1105-1109. | |
| 27 | Li D, Peng S, Chen S, et al. Identification and characterization of 5 walnut MYB genes in response to drought stress involved in ABA signaling. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2021, 27(6): 1323-1335. |
| 28 | Yang Y Y, Ren Y P, Su Y M, et al. Cloning and analysis of two promoters of stress-related genes in Medicago varia Xinmu-1. Pratacultural Science, 2012, 29(12): 1887-1893. |
| 杨云尧, 任燕萍, 苏豫梅, 等. 新牧1号苜蓿两个抗逆相关基因启动子的克隆及分析. 草业科学, 2012, 29(12): 1887-1893. | |
| 29 | Wang K, Nan L L, Guo Q E, et al. Effects of drought stress on root architecture of different root-type alfalfa. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(20): 8365-8373. |
| 汪堃, 南丽丽, 郭全恩, 等. 干旱胁迫对不同根型苜蓿根系构型的影响. 生态学报, 2022, 42(20): 8365-8373. | |
| 30 | Chen Q, Xu X Y, Wang J C, et al. Identification of a WRKY gene family based on full-length transcriptome sequences and analysis of response patterns under salt stress in Halogeton glomeratus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 146-157. |
| 陈倩, 徐晓芸, 汪军成, 等. 基于全长转录组的盐生草WRKY基因家族的鉴定及其盐胁迫响应模式分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 146-157. | |
| 31 | Wu Y H, Liu W H, Liu K Q, et al. Effects of drought stress on leaf senescence and the active oxygen scavenging system of oat seedlings. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 75-86. |
| 吴雨涵, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 等. 干旱胁迫对燕麦幼苗叶片光合特性及活性氧清除系统的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31 (10): 75-86. | |
| 32 | Bogati K, Walczak M. The impact of drought stress on soil microbial community, enzyme activities and plants. Agronomy, 2022(12): 189-199. |
| 33 | Wang W B, Kim Y H, Lee H S, et al. Analysis of antioxidant enzyme activity during germination of alfalfa under salt and drought stresses. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 47(7): 570-577. |
| 34 | Han G, Dang Q, Zhao Z, et al. Responses of antioxidation protective system of Caragana korshinskii Kom. to drought stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(4): 528-532. |
| 韩刚, 党青, 赵忠, 等. 柠条抗氧化保护系统对干旱胁迫的响应. 草地学报, 2010, 18(4): 528-532. | |
| 35 | Jia H T, Hu X J, Qiu F T, et al. The effects of compound anti-drought seed soaking agent and seed coating agent on SOD, POD and CAT isozyme expression in wheat seedlings. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2016, 36(5): 647-652. |
| 贾洪涛, 胡晓君, 邱奉同, 等. 小麦专用复方抗旱型浸种剂和包衣剂对小麦幼苗SOD、POD和CAT同工酶表达的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2016, 36(5): 647-652. |
| [1] | 贺龙义, 谭萌萌, 车海涛, 张红鹰, 朱雨欣, 张彦妮. 细叶百合LpDREB9基因克隆及耐旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 161-173. |
| [2] | 崔红丽, 孙明哲, 贾博为, 孙晓丽. 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族鉴定及低温逆境表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 111-125. |
| [3] | 王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93. |
| [4] | 马圆, 刘欢, 赵桂琴, 王敬龙, 张然, 姚瑞瑞. 燕麦sHSP基因家族的鉴定及其响应高温及老化的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 145-158. |
| [5] | 吴毅, 冯雅岚, 王添宁, 琚吉浩, 肖慧淑, 马超, 张均. 小麦及其祖先物种Hsp70基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 53-67. |
| [6] | 张震欢, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草AKR基因家族成员的鉴定及根系盐胁迫响应基因HgAKR42639的耐盐分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 68-83. |
| [7] | 孔海明, 宋家兴, 杨静, 李倩, 杨培志, 曹玉曼. 紫花苜蓿CAMTA基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [8] | 黎泽斌, 邱永争, 刘延杰, 喻金秋, 王柏吉, 刘千宁, 王月, 崔国文. 紫花苜蓿BZR基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 106-122. |
| [9] | 周昕越, 蒋庆雪, 贾会丽, 马琳, 樊璐, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX20基因克隆及耐盐功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 55-73. |
| [10] | 胡尚钦, 汪军成, 姚立蓉, 司二静, 马小乐, 杨轲, 张宏, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草根系基因HgAKR6C的克隆与初步功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 61-74. |
| [11] | 史先飞, 高宇, 黄旭升, 周雅莉, 蔡桂萍, 李昕儒, 李润植, 薛金爱. 油莎豆CeWRKY转录因子响应非生物胁迫的功能表征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 186-201. |
| [12] | 张振粉, 黄荣, 李向阳, 姚博, 赵桂琴. 基于Illumina MiSeq高通量测序的燕麦种带细菌多样性及功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 96-108. |
| [13] | 王园, 王晶, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX24基因的克隆及耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 107-117. |
| [14] | 李雯, 赵丽蓉, 张建平, 刘自刚, 齐燕妮, 李闻娟, 谢亚萍. 亚麻DMP基因家族的全基因组鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 91-106. |
| [15] | 刘福, 陈诚, 张凯旋, 周美亮, 张新全. 日本百脉根LjbHLH34基因克隆及耐旱功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 178-191. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||