

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 107-118.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025076
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
魏孔涛1,2,3( ), 张春平1,2,3, 俞旸1,2,3, 张正社4, 周泽1,2,3, 张雪1,2,3, 王鑫鑫1,2,3, 岳思玉1,2,3, 曹铨1,2,3(
), 张春平1,2,3, 俞旸1,2,3, 张正社4, 周泽1,2,3, 张雪1,2,3, 王鑫鑫1,2,3, 岳思玉1,2,3, 曹铨1,2,3( ), 董全民1,2,3(
), 董全民1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-11
修回日期:2025-04-15
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2025-11-13
通讯作者:
曹铨,董全民
作者简介:qmdong@qhu.edu.cn基金资助:
Kong-tao WEI1,2,3( ), Chun-ping ZHANG1,2,3, Yang YU1,2,3, Zheng-she ZHANG4, Ze ZHOU1,2,3, Xue ZHANG1,2,3, Xin-xin WANG1,2,3, Si-yu YUE1,2,3, Quan CAO1,2,3(
), Chun-ping ZHANG1,2,3, Yang YU1,2,3, Zheng-she ZHANG4, Ze ZHOU1,2,3, Xue ZHANG1,2,3, Xin-xin WANG1,2,3, Si-yu YUE1,2,3, Quan CAO1,2,3( ), Quan-min DONG1,2,3(
), Quan-min DONG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-03-11
Revised:2025-04-15
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2025-11-13
Contact:
Quan CAO,Quan-min DONG
摘要:
针对高寒生态区饲草生产需求,本研究系统评估了10个燕麦品种在产量、营养品质及土壤改良方面的综合表现。通过方差分析、结构方程模型和TOPSIS(technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution)模型综合评价方法揭示品种适应性以及与土壤的互作机制,为环青海湖共和盆地草牧业发展提供科学依据。结果表明:美达、福瑞至和黑玫克表现出显著产量优势,鲜草产量50.20~54.78 t·hm-2,干草产量18.68~21.48 t·hm-2;其中艾斯克鲜干比最低(1.67),而爱沃茎叶比最低(2.19)。营养价值呈现品种特异性,楷模和爱沃粗蛋白含量8.23%~8.45%,美达和艾斯克粗脂肪含量突出(4.94%和4.85%);贝勒2纤维组分表现突出,其粗纤维、中性洗涤纤维和酸性洗涤纤维含量均表现较低,且相对饲喂价值和总可消化养分显著领先,饲用价值较优。贝勒2和福星种植区土壤磷含量表现出较高水平;楷模种植区土壤全氮和全碳含量表现出较高水平。相关性分析提示了高产燕麦品种通常伴随优质营养价值和良好的土壤生态反馈。结构方程模型显示,品种通过直接效应(路径系数0.4088~0.4368)和土壤介导的间接效应(0.0725~0.6885)共同调控产量与营养品质。TOPSIS综合评价表明,楷模综合得分最高(0.580),兼具高产特性、优质营养及良好的土壤反馈能力,可作为环青海湖共和盆地退化草地修复与草牧业发展的优选品种。
魏孔涛, 张春平, 俞旸, 张正社, 周泽, 张雪, 王鑫鑫, 岳思玉, 曹铨, 董全民. 环青海湖共和盆地不同燕麦品种的产量、营养价值及对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 107-118.
Kong-tao WEI, Chun-ping ZHANG, Yang YU, Zheng-she ZHANG, Ze ZHOU, Xue ZHANG, Xin-xin WANG, Si-yu YUE, Quan CAO, Quan-min DONG. Yield performance, nutritional quality, and soil physicochemical responses of oat (Avena sativa) cultivars in the Qinghai Lake-Gonghe Basin region[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(1): 107-118.
编号 Number | 品种名称 Varieties name | 类型 Type | 产地 Producing area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 楷模Model | 早熟Early maturity | 加拿大Canada |
| Y2 | 贝勒Baler | 中熟Mid maturity | 加拿大Canada |
| Y3 | 艾斯克Esker | 中熟Mid maturity | 美国America |
| Y4 | 贝勒2 Baler 2 | 晚熟Late maturity | 加拿大Canada |
| Y5 | 爱沃Everleaf | 超晚熟Ultra-late maturity | 美国America |
| Y6 | 黑玫克Haymaker | 晚熟Late maturity | 中国China |
| Y7 | 福瑞至Forage | 中晚熟Mid-late maturity | 美国America |
| Y8 | 美达Monida | 中早熟Mid-early maturity | 美国America |
| Y9 | 速锐Souris | 早熟Early maturity | 加拿大Canada |
| Y10 | 福星Fuxing | 中晚熟Mid-late maturity | 美国America |
表1 供试燕麦品种基本特征
Table 1 The basic characteristics of tested oat varieties
编号 Number | 品种名称 Varieties name | 类型 Type | 产地 Producing area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 楷模Model | 早熟Early maturity | 加拿大Canada |
| Y2 | 贝勒Baler | 中熟Mid maturity | 加拿大Canada |
| Y3 | 艾斯克Esker | 中熟Mid maturity | 美国America |
| Y4 | 贝勒2 Baler 2 | 晚熟Late maturity | 加拿大Canada |
| Y5 | 爱沃Everleaf | 超晚熟Ultra-late maturity | 美国America |
| Y6 | 黑玫克Haymaker | 晚熟Late maturity | 中国China |
| Y7 | 福瑞至Forage | 中晚熟Mid-late maturity | 美国America |
| Y8 | 美达Monida | 中早熟Mid-early maturity | 美国America |
| Y9 | 速锐Souris | 早熟Early maturity | 加拿大Canada |
| Y10 | 福星Fuxing | 中晚熟Mid-late maturity | 美国America |
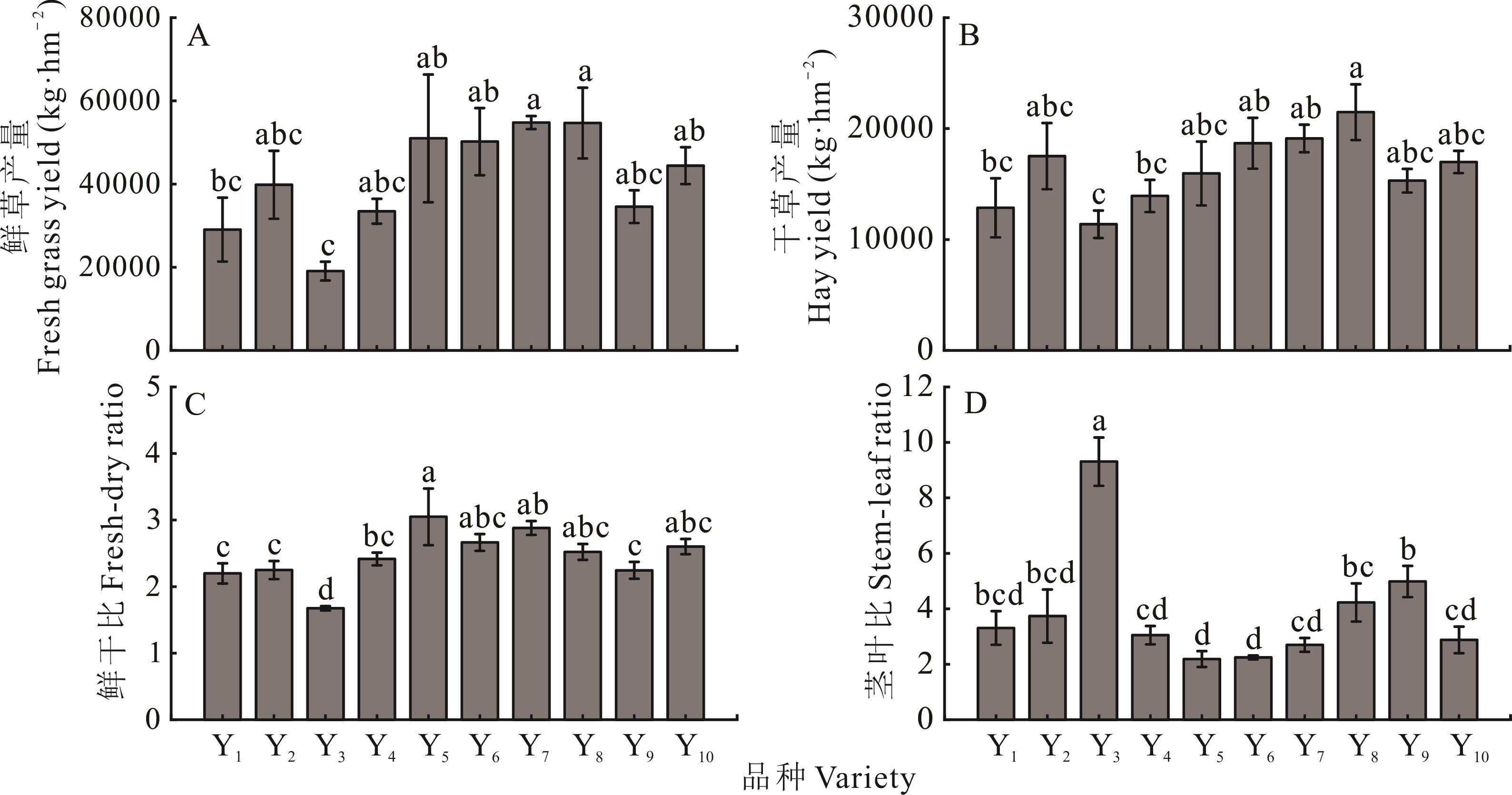
图1 不同燕麦品种产量Y1~Y10分别代表楷模、贝勒、艾斯克、贝勒2、爱沃、黑玫克、福瑞至、美达、速锐、福星。不同小写字母代表不同燕麦品种间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Y1-Y10 represent Model, Baler, Esker, Baler 2, Everleaf, Haymaker, Forage, Monida, Souris, Fuxing, respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different varieties (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Yield of different oat varieties
品种 Variety | 总可消化养分 Total digestible nutrients (%) | 可消化干物质 Digestible dry matter (%DM) | 干物质采食量 Dry matter intake (%BW) | 相对饲喂价值 Relative feed value | 相对饲草品质 Relative forage quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 65.75±0.44bc | 71.66±0.46bc | 3.09±0.05ab | 171.68±3.35b | 165.20±3.27b |
| Y2 | 66.09±0.92b | 72.02±0.96b | 3.03±0.12ab | 169.09±8.88b | 162.76±8.65b |
| Y3 | 64.30±0.57bc | 70.16±0.59bc | 2.71±0.19bcd | 147.42±11.16bc | 141.71±10.78bc |
| Y4 | 68.65±0.41a | 74.67±0.43a | 3.43±0.07a | 198.73±5.22a | 191.63±5.09a |
| Y5 | 65.15±0.99bc | 71.03±1.02bc | 2.75±0.29bc | 151.78±18.14bc | 146.01±17.55bc |
| Y6 | 65.04±0.49bc | 70.92±0.50bc | 2.91±0.02bc | 159.88±1.62b | 153.76±1.60b |
| Y7 | 61.01±0.27d | 66.74±0.28d | 2.31±0.06d | 119.73±3.11d | 114.77±2.98d |
| Y8 | 65.88±0.19b | 71.79±0.19b | 3.02±0.01ab | 168.30±0.87b | 161.97±0.85b |
| Y9 | 62.08±0.49d | 67.85±0.51d | 2.49±0.11cd | 131.01±6.51cd | 125.71±6.29cd |
| Y10 | 63.89±0.70c | 69.73±0.73c | 2.79±0.09bc | 150.91±5.90bc | 145.01±5.74bc |
表2 不同燕麦品种饲用价值
Table 2 Forage value of different oat varieties
品种 Variety | 总可消化养分 Total digestible nutrients (%) | 可消化干物质 Digestible dry matter (%DM) | 干物质采食量 Dry matter intake (%BW) | 相对饲喂价值 Relative feed value | 相对饲草品质 Relative forage quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 65.75±0.44bc | 71.66±0.46bc | 3.09±0.05ab | 171.68±3.35b | 165.20±3.27b |
| Y2 | 66.09±0.92b | 72.02±0.96b | 3.03±0.12ab | 169.09±8.88b | 162.76±8.65b |
| Y3 | 64.30±0.57bc | 70.16±0.59bc | 2.71±0.19bcd | 147.42±11.16bc | 141.71±10.78bc |
| Y4 | 68.65±0.41a | 74.67±0.43a | 3.43±0.07a | 198.73±5.22a | 191.63±5.09a |
| Y5 | 65.15±0.99bc | 71.03±1.02bc | 2.75±0.29bc | 151.78±18.14bc | 146.01±17.55bc |
| Y6 | 65.04±0.49bc | 70.92±0.50bc | 2.91±0.02bc | 159.88±1.62b | 153.76±1.60b |
| Y7 | 61.01±0.27d | 66.74±0.28d | 2.31±0.06d | 119.73±3.11d | 114.77±2.98d |
| Y8 | 65.88±0.19b | 71.79±0.19b | 3.02±0.01ab | 168.30±0.87b | 161.97±0.85b |
| Y9 | 62.08±0.49d | 67.85±0.51d | 2.49±0.11cd | 131.01±6.51cd | 125.71±6.29cd |
| Y10 | 63.89±0.70c | 69.73±0.73c | 2.79±0.09bc | 150.91±5.90bc | 145.01±5.74bc |
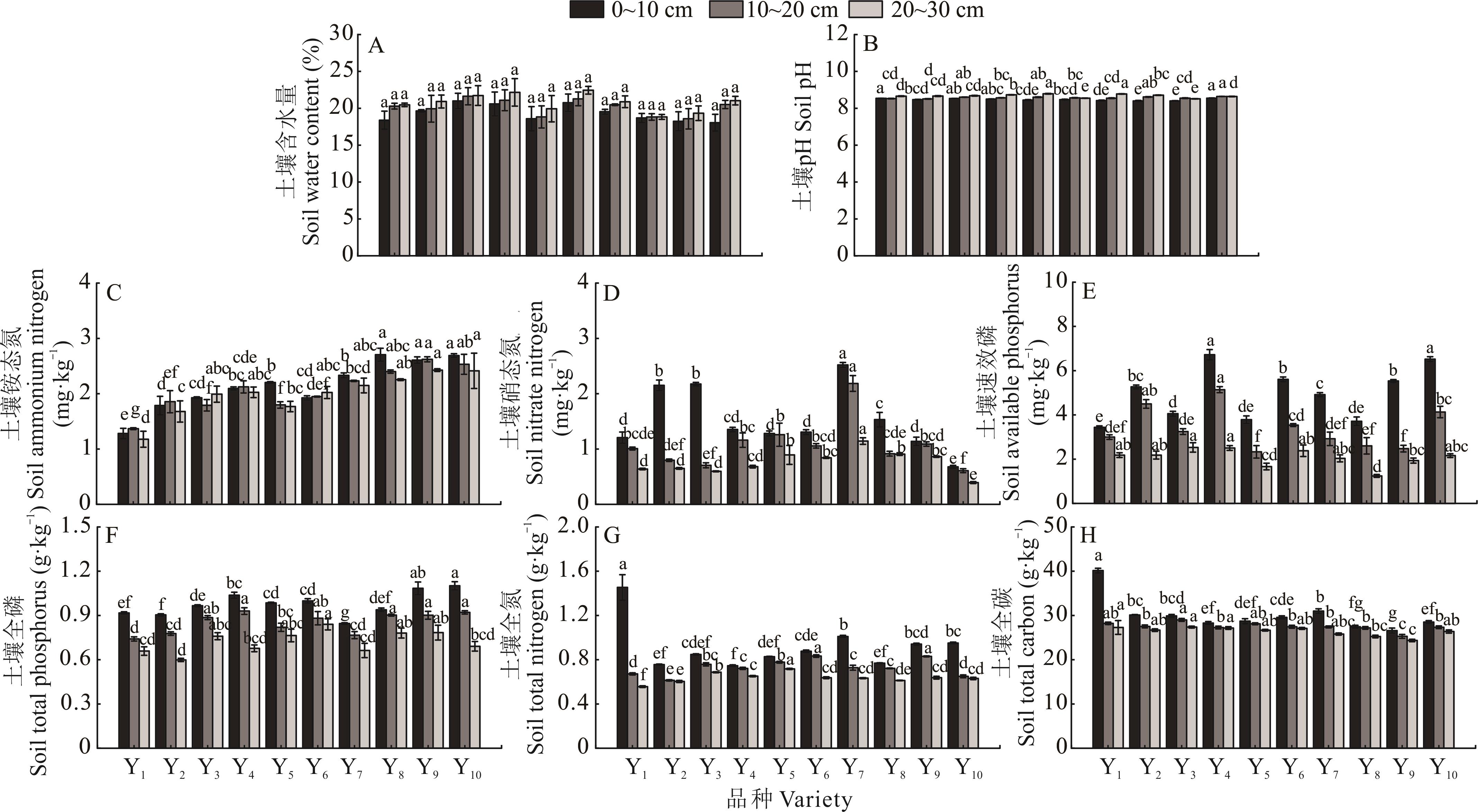
图3 不同燕麦品种的土壤理化性质不同小写字母代表同一土层下不同燕麦品种的土壤理化性质指标间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in soil physicochemical properties among oat varieties within the same soil layer (P<0.05).
Fig.3 Soil physicochemical properties of different oat varieties
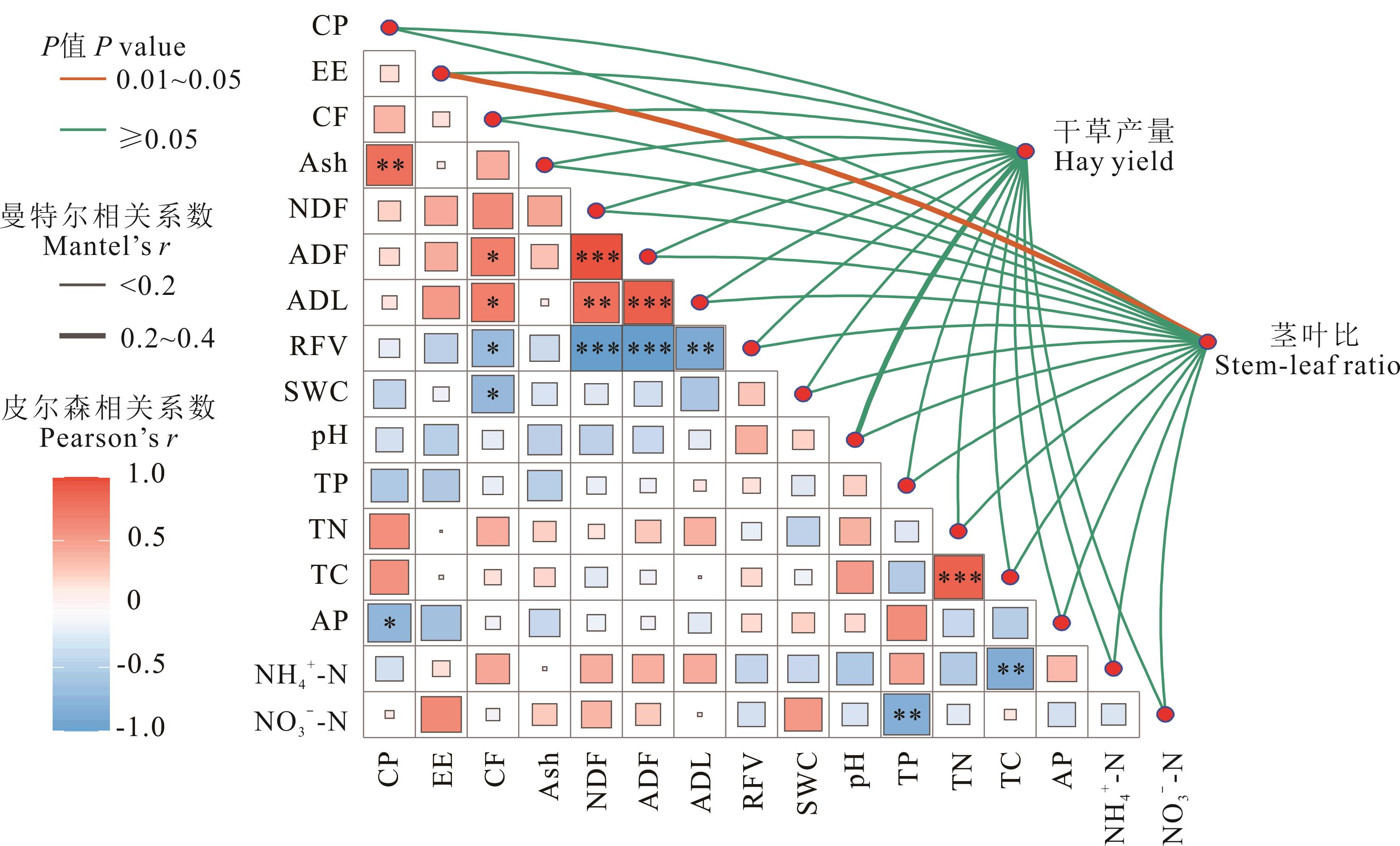
图4 不同燕麦品种的产量与营养价值、土壤理化性质的相关性CP: 粗蛋白Crude protein; EE: 粗脂肪Ether extract; CF: 粗纤维Crude fiber; Ash: 粗灰分Crude ash; NDF: 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber; ADF: 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber; ADL: 酸性洗涤木质素Acid detergent lignin; RFV: 相对饲喂价值Relative feed value; SWC: 土壤含水量Soil water content; TP: 全磷Total phosphorus; TN: 全氮Total nitrogen; TC: 全碳Total carbon; AP: 速效磷Available phosphorus; NH4+-N: 铵态氮Ammonium nitrogen; NO3--N: 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen.
Fig.4 Correlation between yield, nutritional value, and soil physicochemical properties of different oat varieties

图5 品种对燕麦产量、营养价值和土壤理化性质的影响路径实线和虚线箭头分别表示显著和不显著的路径关系;红线和蓝线分别表示正和负的路径关系。线上的数值为标准化路径系数。Solid and dashed arrows represent significant (P<0.05) and insignificant paths, respectively. Red and blue line represent positive and negative coefficients, respectively. The values on the lines are standardized path coefficients. *: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ***: P<0.001.
Fig.5 Pathways of cultivar effects on oat yield, nutritional quality, and soil physiochemical properties
品种 Variety | 最优距离 Optimal distance | 最劣距离 Worst distance | 相对贴合度 Relative fit | 排序 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 0.137 | 0.189 | 0.580 | 1 |
| Y2 | 0.181 | 0.108 | 0.374 | 10 |
| Y3 | 0.174 | 0.142 | 0.450 | 3 |
| Y4 | 0.201 | 0.123 | 0.380 | 8 |
| Y5 | 0.183 | 0.110 | 0.376 | 9 |
| Y6 | 0.173 | 0.117 | 0.404 | 6 |
| Y7 | 0.140 | 0.157 | 0.530 | 2 |
| Y8 | 0.193 | 0.120 | 0.383 | 7 |
| Y9 | 0.182 | 0.125 | 0.406 | 5 |
| Y10 | 0.188 | 0.136 | 0.420 | 4 |
表3 不同燕麦品种产量、营养价值及土壤理化性质综合评价
Table 3 Comprehensive evaluation of yield, nutritional quality, and soil physicochemical properties across oat varieties
品种 Variety | 最优距离 Optimal distance | 最劣距离 Worst distance | 相对贴合度 Relative fit | 排序 Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 0.137 | 0.189 | 0.580 | 1 |
| Y2 | 0.181 | 0.108 | 0.374 | 10 |
| Y3 | 0.174 | 0.142 | 0.450 | 3 |
| Y4 | 0.201 | 0.123 | 0.380 | 8 |
| Y5 | 0.183 | 0.110 | 0.376 | 9 |
| Y6 | 0.173 | 0.117 | 0.404 | 6 |
| Y7 | 0.140 | 0.157 | 0.530 | 2 |
| Y8 | 0.193 | 0.120 | 0.383 | 7 |
| Y9 | 0.182 | 0.125 | 0.406 | 5 |
| Y10 | 0.188 | 0.136 | 0.420 | 4 |
| [1] | Yang Y H, Sun J N. Current status and development prospects of livestock and feed industries in the Qinghai Lake region. Feed Industry, 2006, 27(23): 61-63. |
| 杨予海, 孙佳妮. 环青海湖地区畜牧业和饲料业现状及发展的思考. 饲料工业, 2006, 27(23): 61-63. | |
| [2] | Li F X, Fu Y, Yang Q, et al. Climate change and its environmental effects in the surrounding area of Qinghai Lake. Resources Science, 2008, 30(3): 348-353. |
| 李凤霞, 伏洋, 杨琼, 等. 环青海湖地区气候变化及其环境效应. 资源科学, 2008, 30(3): 348-353. | |
| [3] | Ding S X. Study on the sustainable development of animal husbandry in minority areas around Qinghai Lake. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(22): 11832-11834, 11837. |
| 丁生喜. 环青海湖少数民族地区畜牧业可持续发展研究. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(22): 11832-11834, 11837. | |
| [4] | Li H M, Zhou B R. Dividing of phenological season around Qinghai Lake and application in animal husbandry. Pratacultural Science, 2006, 23(9): 103-105. |
| 李红梅, 周秉荣. 环青海湖地区物候季节划分及在畜牧业生产中的应用. 草业科学, 2006, 23(9): 103-105. | |
| [5] | Ren Y X, Liu H C, Tian X H, et al. Selection of succeeding crops for a double-cropping system in alpine pastoral areas of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Grass and Forage Science, 2024, 79(1): 47-55. |
| [6] | Hou L Y, Zhu Z Y, Yang J, et al. Current status, problems and potentials of forage oat in China. Journal of Southwest Minzu University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 45(3): 248-253. |
| 侯龙鱼, 朱泽义, 杨杰, 等. 我国饲草用燕麦现状、问题和潜力. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 45(3): 248-253. | |
| [7] | Ye X L, Gan Z, Wan Y, et al. Advances and perspectives in forage oat breeding. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. |
| 叶雪玲, 甘圳, 万燕, 等. 饲用燕麦育种研究进展与展望. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 160-177. | |
| [8] | Guan H, Xu D, Li H P, et al. A study of nutritional quality and rumen degradation characteristics of 17 oat varieties in high cold regions. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(9): 185-198. |
| 关皓, 许多, 李海萍, 等. 高寒地区17个燕麦品种营养品质及瘤胃降解特性研究. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 185-198. | |
| [9] | Ibrahim M S, Ahmad A, Sohail A, et al. Nutritional and functional characterization of different oat (Avena sativa L.) cultivars. International Journal of Food Properties, 2020, 23(1): 1373-1385. |
| [10] | Van den Broeck H C, Londono D M, Timmer R, et al. Profiling of nutritional and health-related compounds in oat varieties. Foods, 2015, 5(1): 2. |
| [11] | Mut Z, Akay H, Erbaş Köse Ö D. Grain yield, quality traits and grain yield stability of local oat cultivars. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2018, 18(1): 269-281. |
| [12] | Wang X J, Wang J L, Ju Z L, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on production performance and nutritional quality of different varieties of forage oat in the Qinghai Lake area. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2024, 57(19): 3730-3742. |
| 王小军, 王金兰, 琚泽亮, 等. 环青海湖地区不同饲用燕麦品种生产性能和营养品质综合评价. 中国农业科学, 2024, 57(19): 3730-3742. | |
| [13] | Cao Y, Malipati·Nuertai, Alehesi·Jiaerdemutila, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the production performance of 18 oat germplasm resources based on the affiliation function method. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(16): 26-28, 32. |
| 曹禹, 玛力帕提·努尔太, 阿勒合斯·加尔得木拉提, 等. 基于隶属函数法的18份燕麦种质资源生产性能的综合评价. 安徽农业科学, 2023, 51(16): 26-28, 32. | |
| [14] | Shah S A S, Akhtar L H, Minhas R, et al. Evaluation of different oat (Avena sativa L.) varieties for forage yield and related characteristics. Science Letters, 2015, 3(1): 13-16. |
| [15] | Sun H R, Zeng H, Liu J Y, et al. Preliminary study on abundance-deficiency index of soil available P and appropriate phosphorus application rate for oats in the farming-grazing transitional zone of China. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 34(10): 101-105. |
| 孙洪仁, 曾红, 刘江扬, 等. 中国农牧交错带燕麦土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量初步研究. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(10): 101-105. | |
| [16] | Van Soest P J, Robertson J B, Lewis B A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. Journal of Dairy Science, 1991, 74(10): 3583-3597. |
| [17] | Zhang L Y. Feed analysis and feed quality testing technology (4th edition). Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2016. |
| 张丽英. 饲料分析及饲料质量检测技术(第4版). 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2016. | |
| [18] | Rohweder D A, Barnes R F, Jorgensen N. Proposed hay grading standards based on laboratory analyses for evaluating quality. Journal of Animal Science, 1978, 47(3): 747-759. |
| [19] | Moore J E, Undersander D J. Relative forage quality: an alternative to relative feed value and quality index//Proceedings of 13th Annual Florida Ruminant Nutrition Symposium. Gainesville: University of Florida, 2002: 16-29. |
| [20] | Bao S D. Agrochemical analysis of soil. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2001. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2001. | |
| [21] | Wei K T, Xiang H, Liu Y F, et al. Mixed cropping of Medicago ruthenica-Bromus inermis exhibits higher yield and quality advantages in the Longxi Loess Plateau region of northwest China. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 2024, 8: 1411687. |
| [22] | Zhou Q L, Duojidunzhu, Yixiyangzong. Evaluation of gray relational grade analysis to 16 oats varieties introduced in Lasa region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(2): 389-396. |
| 周启龙, 多吉顿珠, 益西央宗. 拉萨地区16个燕麦引进品种的灰色关联度评价. 草地学报, 2020, 28(2): 389-396. | |
| [23] | Li J, Nan M, Liu Y M, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the yield, quality and feeding performance on different oat varieties. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(4): 1089-1098. |
| 李晶, 南铭, 刘彦明, 等. 不同燕麦品种产量和品质及饲喂性能综合评价. 草地学报, 2023, 31(4): 1089-1098. | |
| [24] | Gao X F, Nie Y Y, Xu L J, et al. Adaptability evaluation of oat introduction in winter fallow field of Wumeng Mountain area under drought condition. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 215-227. |
| 高兴发, 聂莹莹, 徐丽君, 等. 干旱条件下乌蒙山区冬闲田燕麦引种适应性评价. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 215-227. | |
| [25] | Sun J P, Dong K H, Kuai X Y, et al. Comparison of productivity and feeding value of introduced oat varieties in the agro-pasture ecotone of northern Shanxi. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(11): 222-230. |
| 孙建平, 董宽虎, 蒯晓妍, 等. 晋北农牧交错区引进燕麦品种生产性能及饲用价值比较. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 222-230. | |
| [26] | Dong Z X, Gou W L, Liu Y J, et al. Evaluation of production performance and nutritional value of 15 feed barley varieties in the Liangshan region. Pratacultural Science, 2024, 41(11): 2651-2663. |
| 董志晓, 苟文龙, 刘英杰, 等. 15份饲用燕麦品种在凉山地区的生产性能和营养价值评价. 草业科学, 2024, 41(11): 2651-2663. | |
| [27] | Lei X, You M H, Bai S Q, et al. Genetic diversity analysis and multivariate evaluation of agronomic traits of 50 oat germplasm lines in northwest Sichuan. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(7): 131-142. |
| 雷雄, 游明鸿, 白史且, 等. 川西北高原50份燕麦种质农艺性状遗传多样性分析及综合评价. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 131-142. | |
| [28] | Rearte D H. New insights into the nutritional value of grass//Utilisation of grazed grass in temperate animal systems. Wageningen: Wageningen Academic Publishers, 2005: 49-59. |
| [29] | Razafindrazaka A, Stuerz S, Cotter M, et al. Genotypic yield responses of lowland rice in high-altitude cropping systems. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2020, 206(4): 444-455. |
| [30] | Wang F, Ma X D, Li G, et al. Adaptability evaluation of forage oat varieties in Ar Horqin Sandland. Pratacultural Science, 2024, 41(4): 931-941. |
| 王飞, 马晓东, 李刚, 等. 阿鲁科尔沁沙地饲用燕麦品种适应性评价. 草业科学, 2024, 41(4): 931-941. | |
| [31] | Basinskiene L, Cizeikiene D. Cereal-based nonalcoholic beverages//Galanakis C M. Trends in non-alcoholic beverages. London: Academic Press, 2020: 63-99. |
| [32] | Liu G, Zhao G Q, Wei L M. Primary application of the entropy weight-based gray systematic theory to integrated evaluation of oat. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2007, 29(3): 84-89. |
| 刘刚, 赵桂琴, 魏黎明. 基于熵权赋权法的灰色系统理论在燕麦品种综合评价中的应用. 中国草地学报, 2007, 29(3): 84-89. | |
| [33] | Yang F, Zheng M N, Kang J H, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of production performance and feeding value of 9 oat varieties in Northern Shanxi. Crops, 2019(2): 94-98. |
| 杨富, 郑敏娜, 康佳惠, 等. 9个燕麦品种在晋北地区的生产性能及饲用价值综合评价. 作物杂志, 2019(2): 94-98. | |
| [34] | Yan Y F. Study on productivity performance and nutritional quality of different forage in Hetao irrigation district. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2016. |
| 闫亚飞. 河套灌区不同饲草生产性能与品质研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2016. | |
| [35] | Wang X, Li D, Pan X L, et al. Adaptability evaluation of 10 forage oat varieties in Chifeng semiarid area. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(2): 521-529. |
| 王筱, 李夺, 潘翔磊, 等. 赤峰半干旱区10个饲用燕麦品种适应性评价. 草业科学, 2023, 40(2): 521-529. | |
| [36] | Delgado A, Gómez J A. The soil physical, chemical and biological properties//Villalobos F J, Fereres E. Principles of agronomy for sustainable agriculture. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 15-26. |
| [37] | Chen R X. The rhizosphere micro-ecology of different oat varieties and their mechanism of cadmium absorption and transport. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2024. |
| 陈若潇. 不同燕麦品种根际微生态及镉吸收转运机制. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2024. | |
| [38] | Bao X R. Response of soil microbial communities in the rhizosphere of oats to saline-alkali stress. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2024. |
| 鲍鑫茹. 燕麦根际土壤微生物群落对盐碱胁迫的响应. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2024. | |
| [39] | Hoad S P, Russell G, Lucas M E, et al. The management of wheat, barley, and oat root systems. Advances in Agronomy, 2001, 74: 193-246. |
| [40] | Wang W. The phenotype of Avena sativa traits, nutrients and microbe community structure of soil under mixed sowing of Avena sativa and Vicia sativa. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 王玮. 燕麦与箭筈豌豆混播下燕麦性状表型和土壤养分及微生物群落结构的研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2023. | |
| [41] | Wang J L, Wang X J, Liu Q L, et al. A multi-trait evaluation of production performance and nutritional quality of different oat varieties in the Sanjiangyuan area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 83-95. |
| 王金兰, 王小军, 刘启林, 等. 不同燕麦品种在三江源区的生产性能和营养品质综合评价. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 83-95. |
| [1] | 张志鹏, 蒋庆雪, 周昕越, 苗童, 唐俊, 仪登霞, 王学敏, 马琳. 转录组和蛋白组联合筛选饲用燕麦株高性状候选基因[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 147-161. |
| [2] | 张琨, 乔建霞, 李金升, 王育鹏, 刘克思. 不同修复材料对退化高寒草地土壤理化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 132-148. |
| [3] | 张邦彦, 谢小伟, 张朝辉, 武晋民, 王彬, 许兴. 有机-无机改良物料对盐碱地土壤质量及湖南稷子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 15-29. |
| [4] | 毛海龙, 邰继承, 杨恒山, 张玉芹, 张瑞富, 王真真. 带型配置对青贮玉米-大豆复合种植体冠层特性、产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 30-42. |
| [5] | 张译尹, 王斌, 王腾飞, 兰剑, 胡海英. 苜蓿种子田间作小黑麦对饲草产量、水分利用及苜蓿种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 43-53. |
| [6] | 樊文娟, 宋建超, 张小娟, 盛宇航, 史金涛, 张龙骥, 鱼小军. 氮磷配施对甘肃省武威灌区扁蓿豆种子产量和质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 54-65. |
| [7] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [8] | 姜沛沛, 郭锦花, 肖慧淑, 彭彦珉, 张军, 田文仲, 吕军杰, 吴金芝, 王贺正, 付国占, 黄明, 李友军. 轮耕模式对旱地玉-麦两熟体系作物产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 181-192. |
| [9] | 刘启林, 王小军, 王金兰, 刘文辉, 马巧玲, 李建辉, 张生原, 曹文侠, 李文. 氮磷配施对高寒区老芒麦饲草产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 193-202. |
| [10] | 秦文利, 张静, 肖广敏, 崔素倩, 叶建勋, 智健飞, 张立锋, 谢楠, 冯伟, 刘振宇, 潘璇, 代云霞, 刘忠宽. 绿肥部分替代化肥氮对土壤物理性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 27-45. |
| [11] | 刘耀博, 裴渌, 刘琛琢, 李晓霞, 邹博坤. 基于Meta分析中国老芒麦种子产量和产量组分对施肥的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 85-98. |
| [12] | 韩航琪, 王梓凡, 丁赫, 陈玉荣, 王琦, 张晓庆. 燕麦干草与燕麦草块对绵羊瘤胃发酵及微生物组成影响的比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 212-222. |
| [13] | 冯雅琪, 陈嘉慧, 张静妮, 隋超, 陈基伟, 刘志鹏, 周强, 刘文献. 基于重测序紫花苜蓿高蛋白、高产关联InDel分子标记开发[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 137-149. |
| [14] | 王腾飞, 马霞, 刘金龙, 王斌, 张译尹, 李佳旺, 马江萍, 王小兵, 兰剑. 引黄灌区复种饲用燕麦种植模式产量、品质及经济效益分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 27-37. |
| [15] | 蒋鹏, 李磊, 解昊郡, 徐得甲, 王锐, 虎强, 孙权. 净化沼液滴灌对砂壤土质量、青贮玉米生产力的影响及安全消纳容量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 64-81. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||