

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 95-105.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021477
尉春雪( ), 何飞, 许蕾, 李霄, 张立霞, 李明娜, 陈林, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 龙瑞才(
), 何飞, 许蕾, 李霄, 张立霞, 李明娜, 陈林, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 龙瑞才( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-22
修回日期:2022-03-28
出版日期:2022-12-20
发布日期:2022-10-17
通讯作者:
龙瑞才
作者简介:E-mail: longruicai@caas.com基金资助:
Chun-xue WEI( ), Fei HE, Lei XU, Xiao LI, Li-xia ZHANG, Ming-na LI, Lin CHEN, Jun-mei KANG, Qing-chuan YANG, Rui-cai LONG(
), Fei HE, Lei XU, Xiao LI, Li-xia ZHANG, Ming-na LI, Lin CHEN, Jun-mei KANG, Qing-chuan YANG, Rui-cai LONG( )
)
Received:2021-12-22
Revised:2022-03-28
Online:2022-12-20
Published:2022-10-17
Contact:
Rui-cai LONG
摘要:
光呼吸通过清除2-磷酸乙醇酸(2-PG)使氧合光合作用成为可能,该过程对C3植物至关重要。H-蛋白是光呼吸过程中将甘氨酸转化为丝氨酸的甘氨酸脱羧酶(GDC)的关键组成蛋白之一。本研究克隆了紫花苜蓿MsGDC-H1,该基因编码166个氨基酸,具有1个硫辛酰基附着位点保守结构域和1个N6-硫辛酰赖氨酸保守位点。进化分析表明,MsGDC-H1蛋白与双子叶植物的甘氨酸脱羧酶H-蛋白(GDC-H)亲缘关系近。表达模式分析表明,MsGDC-H1在苜蓿叶中表达丰度高,且受光诱导。为了探究MsGDC-H1基因对拟南芥生长的影响,分别使用光诱导的茎叶特异性启动子ST-LS1和组成型启动子CaMV 35S驱动MsGDC-H1(ST-LS1::MsGDC-H1; CaMV 35S::MsGDC-H1)在拟南芥中异源表达。检测过表达植株生物量、淀粉、可溶性糖含量以及光合速率。数据分析显示,CaMV 35S::MsGDC-H1过表达拟南芥(G系列植株)生长受阻,淀粉含量比ST-LS1::MsGDC-H1特异性表达拟南芥(GS系列植株)增加了34%~67%,比野生型(WT)增加了7.3%~33.7%;可溶性糖含量比GS系列降低了36%~38%,比WT增加了44.3%~49.7%;与WT相比,GS系列植株生长更快,淀粉含量无显著差异(P>0.05),可溶性糖含量显著增加(P<0.05)。试验结果表明,MsGDC-H1基因在调控拟南芥光合速率、碳水化合物合成以及生长等方面发挥重要作用,未来可作为提高苜蓿产量的基因工程育种候选基因。
尉春雪, 何飞, 许蕾, 李霄, 张立霞, 李明娜, 陈林, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 龙瑞才. 紫花苜蓿甘氨酸脱羧酶H-蛋白基因MsGDC-H1功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 95-105.
Chun-xue WEI, Fei HE, Lei XU, Xiao LI, Li-xia ZHANG, Ming-na LI, Lin CHEN, Jun-mei KANG, Qing-chuan YANG, Rui-cai LONG. Functional analysis of glycine decarboxylase H-protein gene MsGDC-H1 in Medicago sativa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 95-105.
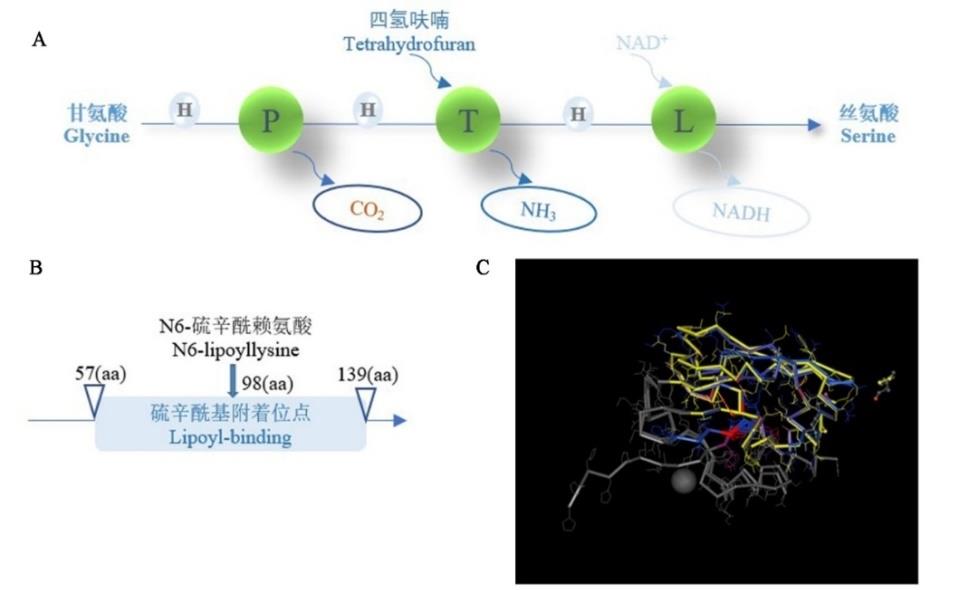
图1 MsGDC-H1蛋白功能及结构分析A: 植物光呼吸过程中甘氨酸脱羧酶功能模式Functional model of glycine decarboxylase during photorespiration in plants; H: 甘氨酸脱羧酶H-蛋白 Glycine decarboxylase H-protein; P: 甘氨酸脱羧酶P-蛋白Glycine decarboxylase P-protein; T: 甘氨酸脱羧酶T-蛋白Glycine decarboxylase T-protein; L: 甘氨酸脱羧酶L-蛋白Glycine decarboxylase L-protein; aa: 氨基酸Amino acid; 甘氨酸在H-、P-、T-、L-蛋白作用下转变为丝氨酸Glycine is converted to serine by H-, P-, T-, and L-proteins;B: MsGDC-H1保守结构域分析Analysis of MsGDC-H1 conserved domain;C: MsGDC-H1蛋白三维结构预测,黄色区域为硫辛酰基附着位点保守结构域Prediction of three-dimensional structure of MsGDC-H1 protein, the yellow area is the conserved domain of lipoyl-binding.
Fig.1 Functional and structural analysis of MsGDC-H1 protein
| 引物Primer | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| MsH-F | ATGGCACTGAGGATGTGGGCTTC |
| MsH-R | TCAATGTGCAGCATCTTCTTCCTCA |
| ST-LS1-F | GCAAGCTTTTGTTTCTATCCACTGATGTCTG |
| ST-LS1-R | GCGGATCCTTGCTCTCACTACTTAGTATGA |
| qRT-MsH-F | CACTGAGGATGTGGGCTTCTT |
| qRT-MsH-R | AGCCTTCATGCTTCACCCAT |
| qRT-Atactin-F | CAAAAGATGGCAGATGCTGAGGAT |
| qRT-Atactin-R | CATGCACCAGTATGACGAGGTCG |
| qRT-Msactin-F | GAAATCACAGCACTTGCACC |
| qRT-Msactin-R | AAGCCTTTGATCTTGAGAGC |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequence
| 引物Primer | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| MsH-F | ATGGCACTGAGGATGTGGGCTTC |
| MsH-R | TCAATGTGCAGCATCTTCTTCCTCA |
| ST-LS1-F | GCAAGCTTTTGTTTCTATCCACTGATGTCTG |
| ST-LS1-R | GCGGATCCTTGCTCTCACTACTTAGTATGA |
| qRT-MsH-F | CACTGAGGATGTGGGCTTCTT |
| qRT-MsH-R | AGCCTTCATGCTTCACCCAT |
| qRT-Atactin-F | CAAAAGATGGCAGATGCTGAGGAT |
| qRT-Atactin-R | CATGCACCAGTATGACGAGGTCG |
| qRT-Msactin-F | GAAATCACAGCACTTGCACC |
| qRT-Msactin-R | AAGCCTTTGATCTTGAGAGC |
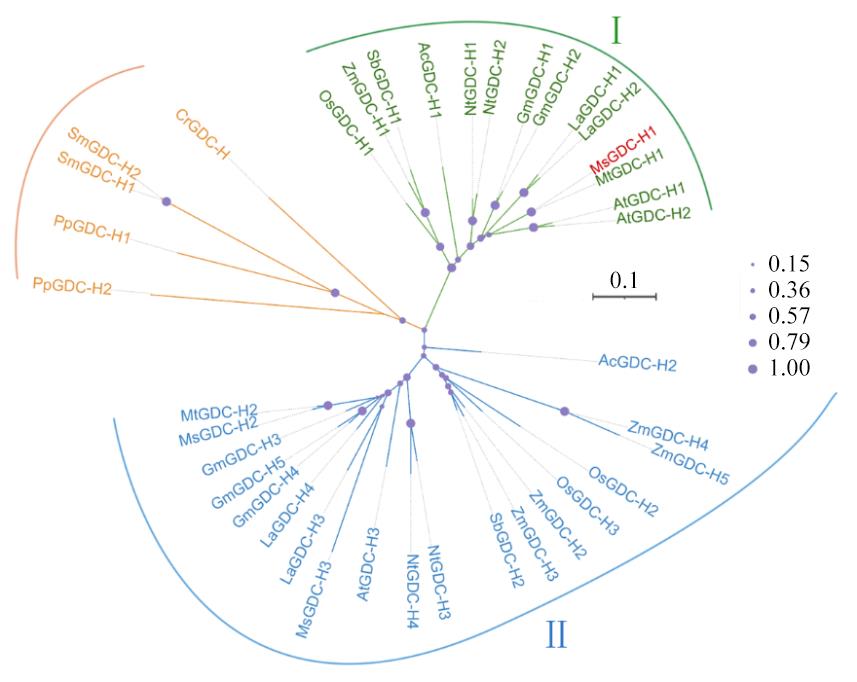
图2 多物种中H-蛋白进化树分析Ⅰ、Ⅱ:H-蛋白在高等植物中的两个亚家族Two subfamilies of H-proteins in higher plants; Ms:紫花苜蓿M. sativa;MsGDC-H1:MsG0580024678.01.T01;MsGDC-H2:MsG0480022167.01.T01;MsGDC-H3:MsG0780040690.01.T01[20];Mt:蒺藜苜蓿M. truncatula;MtGDC-H1:XP_003611464.1;MtGDC-H2:XP_003607890.1; At:拟南芥A. thaliana;AtGDC-H1:NP_181080.1;AtGDC-H2:NP_174525.1;Nt:烟草N. tabacum;NtGDC-H1:XP_016501895.1;NtGDC-H2:XP_016454762.1;NtGDC-H3:XP_016447704.1;NtGDC-H4:XP_016484703.1;Gm:大豆G. max;GmGDC-H1:NP_001238231.1;GmGDC-H2:XP_003539169.1;GmGDC-H3:XP_003556280.1;GmGDC-H4:NP_001237081.2;GmGDC-H5:NP_001242407.1;Os:水稻O. sativa;OsGDC-H1: XP_015627588.1;OsGDC-H2:XP_015643398.1;OsGDC-H3:XP_015627588.1;Pp:小立碗藓P. patens;PpGDC-H1:XP_001780120.1;PpGDC-H2:XP_001769387.1;Cr:莱茵衣藻C. reinhardtii;CrGDC-H:XP_001696637.1;Sm:江南卷柏S. moellendorffii;SmGDC-H1:XP_002980848.1;SmGDC-H2:XP_002989355.1;La:狭叶羽扇豆L. angustifolius;LaGDC-H1:XP_019445983.1;LaGDC-H2:XP_019424562.1;LaGDC-H3:XP_019420317.1;LaGDC-H4:XP_019445859.1;Sb:高粱S. bicolor;SbGDC-H1:XP_002451618.1;SbGDC-H2:XP_002451618.1;Zm:玉米Z. mays;ZmGDC-H1:NP_001141253.1;ZmGDC-H2:Zm00001eb207290;ZmGDC-H3:NP_001141253.1;ZmGDC-H4: Zm00001eb391290;ZmGDC-H5:Zm00001eb025960;Ac:凤梨A. comosus;AcGDC-H1:XP_020109774.1;AcGDC-H2:Aco008361.1. path 1.
Fig.2 Phylogenetic tree analysis of H-protein in multiple species
分类 Category | 物种 Species | 光合类型 Photosynthetic types | 数目Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDC-H | GDC-H外显子Exons | |||
双子叶植物 Dicot | 3 | 1,3,4 | ||
| 2 | 3,4 | |||
| 3 | 3,4 | |||
| 5 | 3,4 | |||
| 4 | 3,4 | |||
| 4 | 2,3,4 | |||
单子叶植物 | 4 | 4,9 | ||
| 6 | 3,4,5,7 | |||
| 2 | 3,4 | |||
| 2 | 4 | |||
低等植物 | 2 | 1,4 | ||
| 2 | 4 | |||
| 1 | 5 | |||
表2 GDC-H在不同物种中的信息
Table 2 Information of GDC-H in different species
分类 Category | 物种 Species | 光合类型 Photosynthetic types | 数目Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDC-H | GDC-H外显子Exons | |||
双子叶植物 Dicot | 3 | 1,3,4 | ||
| 2 | 3,4 | |||
| 3 | 3,4 | |||
| 5 | 3,4 | |||
| 4 | 3,4 | |||
| 4 | 2,3,4 | |||
单子叶植物 | 4 | 4,9 | ||
| 6 | 3,4,5,7 | |||
| 2 | 3,4 | |||
| 2 | 4 | |||
低等植物 | 2 | 1,4 | ||
| 2 | 4 | |||
| 1 | 5 | |||

图3 MsGDC-H1基因表达量分析A:紫花苜蓿中MsGDC-H1对光的响应分析Response analysis of MsGDC-H1 in M. sativa to light;B: MsGDC-H1在紫花苜蓿茎、叶、花中的表达量Expression levels of MsGDC-H1 in alfalfa stems, leaves and flowers;C:MsGDC-H1在过表达拟南芥根中的循环阈值Cycle threshold of MsGDC-H1 in overexpressed A. thaliana roots;循环阈值Cycle threshold:实时荧光定量PCR 循环过程中,荧光信号开始由本底进入指数增长阶段的拐点所对应的循环次数In the real-time quantitative PCR cycle, the number of cycles corresponding to the inflection point when the fluorescence signal begins to enter the exponential growth stage from the background;D:G系列植株在黑暗6 h和光照8 h后的表达量Expression levels of G series plants after 6 h darkness and 8 h light;E:GS系列植株在黑暗6 h和光照8 h后的表达量Expression levels of GS series plants after 6 h darkness and 8 h light;G42、G45、G66表示CaMV 35S::MsGDC-H1过表达拟南芥株系,GS39、GS34、GS3表示ST-LS1::MsGDC-H1特异性表达拟南芥株系G42, G45, G66 indicate CaMV 35S::MsGDC-H1 overexpression A. thaliana, GS39, GS34, GS3 indicate ST-LS1::MsGDC-H1 specific expression A.thaliana;不同小写字母表示不同时间、不同组织、不同株系存在显著差异(P<0.05),下同Different lowercase letters indicate that there are significant differences in different time, different tissues and different lines, the same below.
Fig.3 Analysis of MsGDC-H1 expression
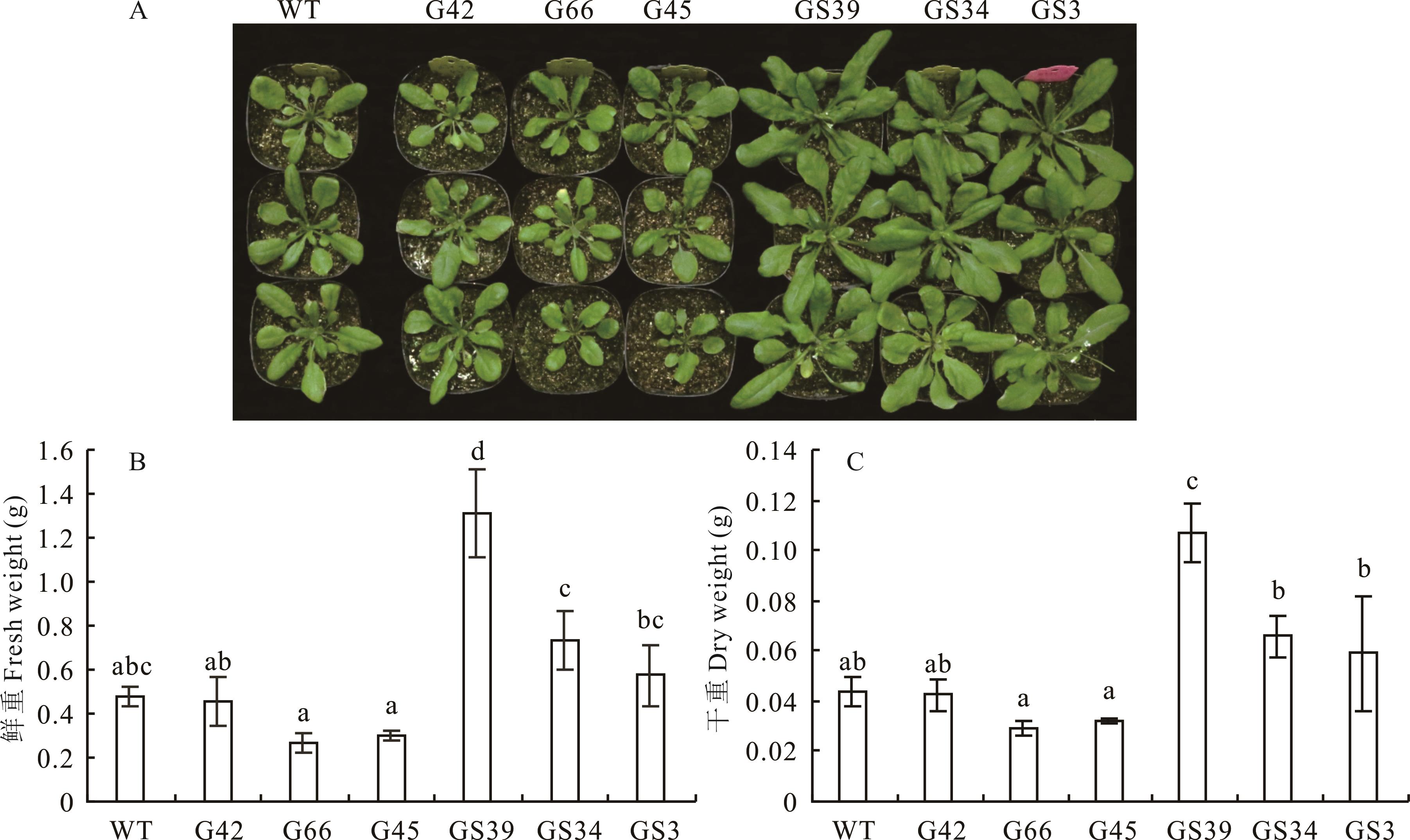
图4 T3代转基因拟南芥表型分析A:5周龄过表达拟南芥表型Overexpression of A. thaliana phenotype at 5 weeks;B:5周龄过表达拟南芥地上部分鲜重Overexpression of A. thaliana shoots fresh weight at 5 weeks;C:5周龄过表达拟南芥地上部分干重Overexpression of A. thaliana shoots dry weight at 5 weeks;WT:野生型Col-0 Wild type Col-0.
Fig.4 Phenotypic analysis of T3 transgenic A. thaliana

图5 转基因及野生型株系叶片中糖类含量分析相对含量Relative content:过表达株系淀粉及可溶性糖含量占WT的百分比The percentage of starch and soluble sugar content of overexpressed lines in WT.
Fig.5 Analysis of carbohydrate content in leaves of transgenic and wild-type strains
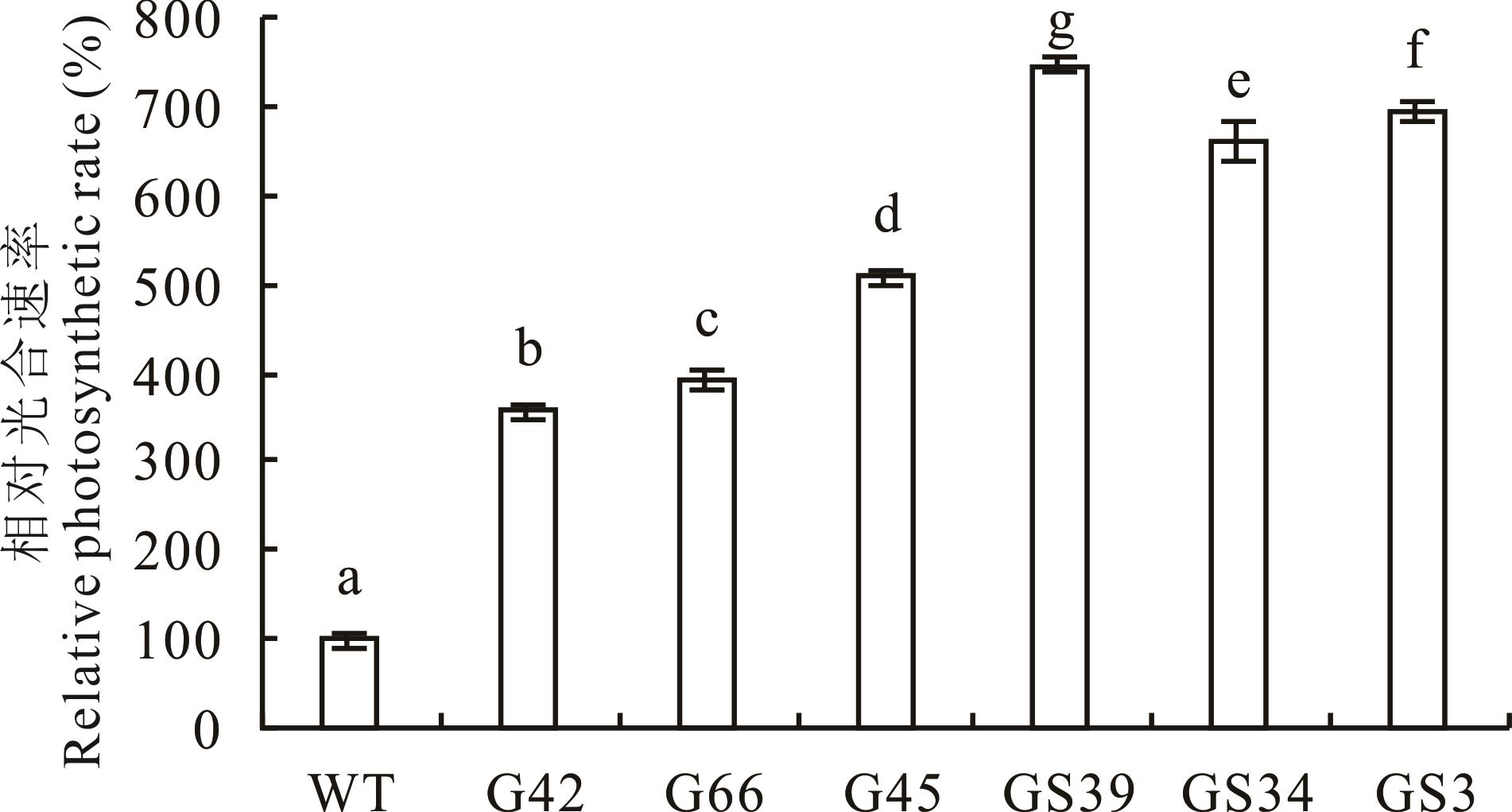
图6 转基因及野生型株系光合速率检测分析相对光合速率Relative photosynthetic rate:过表达株系光合速率占WT的百分比The percentage of photosynthetic rate of overexpressed lines in WT.
Fig.6 Detection and analysis of photosynthetic rate of transgenic and wild-type strains
| 1 | Pan X, Gao Y, Liu B, et al. Current situation and prospect of alfalfa industry. Green Science and Technology, 2017(13): 104-107. |
| 潘霞, 高永, 刘博, 等. 苜蓿产业发展现状及前景展望. 绿色科技, 2017(13): 104-107. | |
| 2 | Timm S, Mielewczik M, Florian A, et al. High-to-low CO2 acclimation reveals plasticity of the photorespiratory pathway and indicates regulatory links to cellular metabolism of Arabidopsis. PLoS One, 2012, 7(8): e42809. |
| 3 | Haimovich-Dayan M, Lieman-Hurwitz J, Orf I, et al. Does 2-phosphoglycolate serve as an internal signal molecule of inorganic carbon deprivation in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803? Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 17(5): 1794-1804. |
| 4 | Walker B J, VanLoocke A, Bernacchi C J, et al. The costs of photorespiration to food production now and in the future. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2016, 67: 107-129. |
| 5 | Zhu X G, Long S P, Ort D R. What is the maximum efficiency with which photosynthesis can convert solar energy into biomass? Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2008, 19(2): 153-159. |
| 6 | Suzuki Y, Ohkubo M, Hatakeyama H, et al. Increased rubisco content in transgenic rice transformed with the “Sense” rbcS gene. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2007, 48(4): 626-637. |
| 7 | Heineke D, Bykova N, Gardeström P, et al. Metabolic response of potato plants to an antisense reduction of the P-protein of glycine decarboxylase. Planta, 2001, 212(516): 880-887. |
| 8 | Schjoerring J K, Mäck G, Nielsen K H, et al. Antisense reduction of serine hydroxymethyltransferase results in diurnal displacement of NH4 + assimilation in leaves of Solanum tuberosum. The Plant Journal, 2006, 45(1): 71-82. |
| 9 | Xu H W, Zhang J J, Zeng J W, et al. Inducible antisense suppression of glycolate oxidase reveals its strong regulation over photosynthesis in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2009, 60(6): 1799-1809. |
| 10 | Carvalho Jde F, Madgwick P J, Powers S J, et al. An engineered pathway for glyoxylate metabolism in tobacco plants aimed to avoid the release of ammonia in photorespiration. BMC Biotechnology, 2011, 11: 111. |
| 11 | Kebeish R, Niessen M, Thiruveedhi K, et al. Chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass increases photosynthesis and biomass production in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25(5): 593-599. |
| 12 | Maier A, Fahnenstich H, von Caemmerer S, et al. Transgenic introduction of a glycolate oxidative cycle into A. thaliana chloroplasts leads to growth improvement. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2012, 3: 38. |
| 13 | Peterhansel C, Krause K, Braun H P, et al. Engineering photorespiration: Current state and future possibilities. Plant Biology, 2013, 15(4): 754-758. |
| 14 | Timm S, Florian A, Fernie A R, et al. The regulatory interplay between photorespiration and photosynthesis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(10): 2923-2929. |
| 15 | Bauwe H, Kolukisaoglu U. Genetic manipulation of glycine decarboxylation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2003, 54(387): 1523-1535. |
| 16 | Hasse D, Mikkat S, Hagemann M, et al. Alternative splicing produces an H-protein with better substrate properties for the P-protein of glycine decarboxylase. Febs Journal, 2009, 276(23): 6985-6991. |
| 17 | Douce R, Bourguignon J, Neuburger M, et al. The glycine decarboxylase system: A fascinating complex. Trends in Plant Science, 2001, 6(4): 167-176. |
| 18 | Timm S, Florian A, Arrivault S, et al. Glycine decarboxylase controls photosynthesis and plant growth. Febs Letters, 2012, 586(20): 3692-3697. |
| 19 | López-Calcagno P E, Fisk S, Brown K L, et al. Overexpressing the H-protein of the glycine cleavage system increases biomass yield in glasshouse and field-grown transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(1): 141-151. |
| 20 | Simkin A J, Lopez-Calcagno P E, Davey P A, et al. Simultaneous stimulation of sedoheptulose 1, 7-bisphosphatase, fructose 1, 6-bisphophate aldolase and the photorespiratory glycine decarboxylase-H protein increases CO2 assimilation, vegetative biomass and seed yield in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(7): 805-816. |
| 21 | Shen C, Du H L, Chen Z, et al. The chromosome-level genome sequence of the autotetraploid alfalfa and resequencing of core germplasms provide genomic resources for alfalfa research. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(9): 1250-1261. |
| 22 | Qu Y, Zhang N, Chang J, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of light-inducible, and stem and leaf-specific expression promoter ST-LS1 in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2013, 21(7): 828-837. |
| 瞿韵, 张宁, 常璟, 等. 马铃薯光诱导型茎叶特异表达启动子ST-LS1的克隆与功能分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2013, 21(7): 828-837. | |
| 23 | Clough S J, Bent A F. Floral dip: A simplified method for agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal, 1998, 16(6): 735-743. |
| 24 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 25 | Köhler I H, Ruiz-Vera U M, VanLoocke A, et al. Expression of cyanobacterial FBP/SBPase in soybean prevents yield depression under future climate conditions. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68(3): 715-726. |
| 26 | Timm S, Wittmiß M, Gamlien S, et al. Mitochondrial dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase activity shapes photosynthesis and photorespiration of Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(7): 1968-1984. |
| 27 | Timm S, Giese J, Engel N, et al. T-protein is present in large excess over the other proteins of the glycine cleavage system in leaves of Arabidopsis. Planta, 2018, 247(1): 41-51. |
| 28 | Stitt M, Zeeman S C. Starch turnover: Pathways, regulation and role in growth. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2012, 15(3): 282-292. |
| 29 | Sulpice R, Pyl E T, Ishihara H, et al. Starch as a major integrator in the regulation of plant growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(25): 10348-10353. |
| 30 | Caspar T, Lin T P, Kakefuda G, et al. Mutants of Arabidopsis with altered regulation of starch degradation. Plant Physiology, 1991, 95(4): 1181-1188. |
| 31 | Niittylä T, Messerli G, Trevisan M, et al. A previously unknown maltose transporter essential for starch degradation in leaves. Science, 2004, 303(5654): 87-89. |
| 32 | Streb S, Zeeman S C. Starch metabolism in Arabidopsis. The Arabidopsis Book, 2012, 10: e0160. |
| 33 | Yu T S, Kofler H, Häusler R E, et al. The Arabidopsis sex1 mutant is defective in the R1 protein, a general regulator of starch degradation in plants, and not in the chloroplast hexose transporter. Plant Cell, 2001, 13(8): 1907-1918. |
| 34 | Dinkins R, Pflipsen C, Thompson A, et al. Ectopic expression of an Arabidopsis single zinc finger gene in tobacco results in dwarf plants. Plant Cell Physiology, 2002, 43(7): 743-750. |
| 35 | McGurl B, Orozco-Cardenas M, Pearce G, et al. Overexpression of the prosystem in gene in transgenic tomato plants generates a systemic signal that constitutively induces proteinase inhibitor synthesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91(21): 9799-9802. |
| [1] | 银敏华, 马彦麟, 康燕霞, 贾琼, 齐广平, 汪精海. 氮素添加对中国苜蓿产量与品质效应的Meta分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 36-49. |
| [2] | 孙延亮, 赵俊威, 刘选帅, 李生仪, 马春晖, 王旭哲, 张前兵. 施氮对苜蓿初花期光合日变化、叶片形态及干物质产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. |
| [3] | 王星, 黄薇, 余淑艳, 李小云, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲. 宁夏地区地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 76-85. |
| [4] | 张铎, 李岚涛, 林迪, 郑龙辉, 耿赛男, 石纹碹, 盛开, 苗玉红, 王宜伦. 施磷水平对菊芋块茎产量、品质、植株生理特性与磷利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 139-149. |
| [5] | 张晴, 邢静, 姚佳明, 殷庭超, 黄心如, 何悦, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草细胞分裂素信号通路B类ARR转录因子LpARR10的耐镉功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| [6] | 李满有, 李东宁, 王斌, 李小云, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 倪旺, 王腾飞, 兰剑. 不同苜蓿品种混播和播种量对牧草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 61-75. |
| [7] | 刘春增, 郑春风, 聂良鹏, 张琳, 张济世, 吕玉虎, 李本银, 曹卫东. 现蕾期叶面喷素对紫云英籽粒数和籽粒重的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 76-83. |
| [8] | 高丽敏, 陈春, 沈益新. 氮磷肥对季节性栽培紫花苜蓿生长及再生的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 43-52. |
| [9] | 李满有, 杨彦军, 王斌, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 李小云, 倪旺, 兰剑. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下燕麦与光叶紫花苕不同混播模式的生产性能、品质及综合评价研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 62-71. |
| [10] | 刘启宇, 云岚, 陈逸凡, 郭宏宇, 李珍, 高志琦, 王俊, 石凤翎. 苜蓿—禾草混播草地牧草产量及种间竞争关系的动态研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 181-191. |
| [11] | 王斌, 杨雨琦, 李满有, 倪旺, 海艺蕊, 张顺香, 董秀, 兰剑. 不同播种量下行距配置对紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 147-158. |
| [12] | 张辉辉, 师尚礼, 武蓓, 李自立, 李小龙. 苜蓿与3种多年生禾草混播效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 159-170. |
| [13] | 王海娣, 张勇, 高玉红, 吴兵, 剡斌, 崔政军, 王一帆, 张雪. 胡麻籽粒产量及相关农艺性状对多元化轮作模式的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 52-65. |
| [14] | 韩重阳, 王栓, 左粟田, 闫三博, 汪阳, 蔡家邦, 马骢毓, 张新全, 聂刚. 10个白三叶品种在成都平原的生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 105-117. |
| [15] | 姜渊博, 康燕霞, 齐广平, 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 康瑶, 张宏斌, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞. 基于产量与品质的无芒雀麦灌溉制度研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 158-171. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||