

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 133-144.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023354
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-09-20
修回日期:2023-10-23
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-05-13
通讯作者:
张前兵
作者简介:E-mail: qbz102@163.com基金资助:
Ying-ying ZHANG( ), Dan-dan HU, Chun-hui MA, Qian-bing ZHANG(
), Dan-dan HU, Chun-hui MA, Qian-bing ZHANG( )
)
Received:2023-09-20
Revised:2023-10-23
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-05-13
Contact:
Qian-bing ZHANG
摘要:
探究菌磷互作对紫花苜蓿叶片解剖结构及光合特性的影响机制,明确紫花苜蓿叶片结构与光合参数之间的关系。采用双因素完全随机区组设计,接菌处理分别为单接种胶质芽孢杆菌(J1)、巨大芽孢杆菌(J2)、两种菌混合接种(J3)和不接种(J0),施磷处理为施磷(P2O5)100 mg·kg-1(P1)和不施磷(P0)。通过对紫花苜蓿叶片光合参数和解剖结构指标进行测定,并使用回归分析明确叶片光合特性与解剖结构之间的关系。结果表明,在相同接菌条件下,紫花苜蓿叶片厚度、上表皮厚度、下表皮厚度、栅栏组织厚度、海绵组织厚度、导管直径、筛管直径、净光合速率日均值(Pn)、蒸腾速率日均值(Tr)、气孔导度日均值(Gs)均为P1处理大于P0处理;叶绿素相对含量(SPAD值)均为P1处理显著大于P0处理(P<0.05);而胞间CO2浓度(Ci)日均值为P1处理小于P0处理。在相同施磷条件下,紫花苜蓿叶片厚度、上表皮厚度、下表皮厚度、栅栏组织厚度、海绵组织厚度、导管直径、筛管直径、Pn日均值、Tr日均值、Gs日均值、SPAD值均为施菌处理大于未施菌处理,且在J3处理达到最大值;而Ci日均值为施菌处理小于未施菌处理。菌、磷对苜蓿叶片厚度、上表皮厚度、下表皮厚度、栅栏组织厚度、海绵组织厚度、导管直径有极显著的影响(P<0.01),菌磷互作对苜蓿叶片厚度及栅栏组织厚度有显著影响(P<0.05)。回归分析表明,Pn日均值与叶片厚度、导管直径、筛管直径、栅栏组织厚度、海绵组织厚度呈显著正相关(P<0.05),与栅海比呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。对紫花苜蓿叶片结构及光合特性进行综合性评价,由高到低为J3P1>J1P1>J2P1>J3P0>J0P1>J1P0>J2P0>J0P0,即共同接种胶质芽孢杆菌和巨大芽孢杆菌,并施磷(P2O5)100 mg·kg-1时有利于促进紫花苜蓿叶片各组织的生长发育,进而促进紫花苜蓿叶片的光合进程。
张盈盈, 胡丹丹, 马春晖, 张前兵. 苜蓿叶片结构和光合特性对菌磷添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 133-144.
Ying-ying ZHANG, Dan-dan HU, Chun-hui MA, Qian-bing ZHANG. Leaf structure and photosynthetic properties of alfalfa in response to bacteria and phosphorus addition[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(8): 133-144.
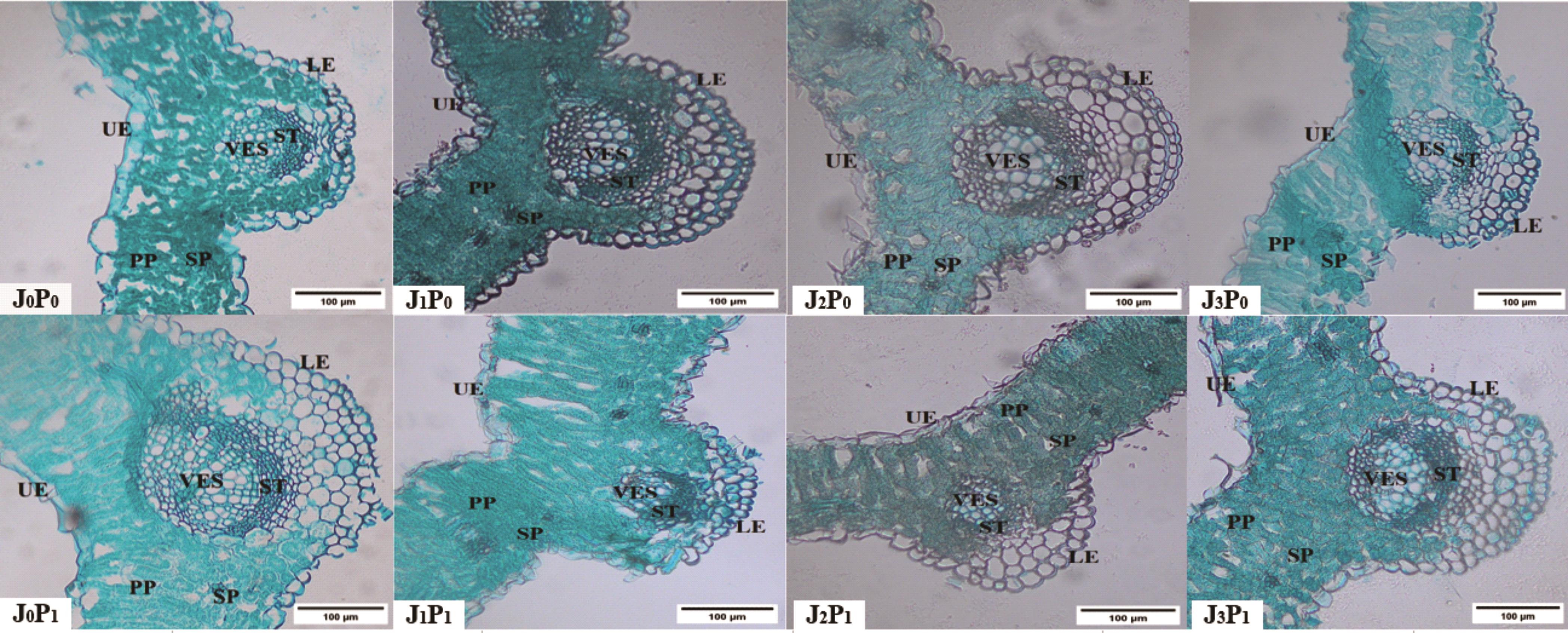
图1 不同菌磷处理下紫花苜蓿叶片解剖结构(标尺=100 μm)UE:上表皮Upper epidermis;LE:下表皮Lower epidermis;VES:导管Vessel;ST: 筛管Sieve tube;PP:栅栏组织Palisade parenchyma;SP:海绵组织Spongy parenchyma.
Fig.1 Anatomic structure of alfalfa leaf under different bacterial and phosphorus treatment (scale bars=100 μm)
处理 Treatment | 叶片厚度Leaf thickness | 上表皮厚度 Upper epidermal thickness | 下表皮厚度Lower epidermal thickness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | |
| J0P0 | 183.54±6.56Cb | 183.52±5.62Bb | 11.45±1.85Ba | 9.65±1.02Bb | 8.25±1.73Cb | 7.07±1.15Bb |
| J0P1 | 208.67±4.92Da | 218.18±8.16Ba | 12.41±1.29Ca | 12.25±1.10Ba | 12.57±1.10Ca | 10.26±1.18Ba |
| J1P0 | 200.37±5.52Bb | 188.26±6.47ABb | 17.08±2.94Ab | 11.06±1.19ABb | 16.98±3.03Ab | 9.90±2.29ABb |
| J1P1 | 223.84±7.30Ca | 223.21±8.05Ba | 21.28±1.06ABa | 14.10±1.02ABa | 20.86±2.03Aa | 12.75±2.00ABa |
| J2P0 | 206.51±5.50Bb | 188.03±6.58ABb | 11.54±2.23Bb | 10.92±1.10ABb | 11.90±1.19Bb | 9.42±1.59ABa |
| J2P1 | 246.65±4.00Ba | 221.24±8.81Ba | 18.29±1.27Ba | 13.62±1.18Ba | 16.16±3.49Ba | 11.38±1.36ABa |
| J3P0 | 218.58±5.89Ab | 197.62±2.71Ab | 19.72±1.11Ab | 13.06±1.52Ab | 17.72±1.05Ab | 10.55±1.41Ab |
| J3P1 | 263.39±6.87Aa | 258.39±3.33Aa | 23.07±1.59Aa | 16.27±2.28Aa | 21.63±1.14Aa | 13.91±1.69Aa |
| J | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| J×P | * | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns |
表1 不同菌磷处理下紫花苜蓿叶片厚度、上表皮厚度及下表皮厚度
Table 1 Leaf thickness, upper epidermal thickness and lower epidermal thickness of alfalfa under different bacterial and phosphorus treatment (μm)
处理 Treatment | 叶片厚度Leaf thickness | 上表皮厚度 Upper epidermal thickness | 下表皮厚度Lower epidermal thickness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | |
| J0P0 | 183.54±6.56Cb | 183.52±5.62Bb | 11.45±1.85Ba | 9.65±1.02Bb | 8.25±1.73Cb | 7.07±1.15Bb |
| J0P1 | 208.67±4.92Da | 218.18±8.16Ba | 12.41±1.29Ca | 12.25±1.10Ba | 12.57±1.10Ca | 10.26±1.18Ba |
| J1P0 | 200.37±5.52Bb | 188.26±6.47ABb | 17.08±2.94Ab | 11.06±1.19ABb | 16.98±3.03Ab | 9.90±2.29ABb |
| J1P1 | 223.84±7.30Ca | 223.21±8.05Ba | 21.28±1.06ABa | 14.10±1.02ABa | 20.86±2.03Aa | 12.75±2.00ABa |
| J2P0 | 206.51±5.50Bb | 188.03±6.58ABb | 11.54±2.23Bb | 10.92±1.10ABb | 11.90±1.19Bb | 9.42±1.59ABa |
| J2P1 | 246.65±4.00Ba | 221.24±8.81Ba | 18.29±1.27Ba | 13.62±1.18Ba | 16.16±3.49Ba | 11.38±1.36ABa |
| J3P0 | 218.58±5.89Ab | 197.62±2.71Ab | 19.72±1.11Ab | 13.06±1.52Ab | 17.72±1.05Ab | 10.55±1.41Ab |
| J3P1 | 263.39±6.87Aa | 258.39±3.33Aa | 23.07±1.59Aa | 16.27±2.28Aa | 21.63±1.14Aa | 13.91±1.69Aa |
| J | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| J×P | * | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns |
处理 Treatment | 导管直径Vessel diameter | 筛管直径Sieve tube diameter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | |
| J0P0 | 11.04±0.97Cb | 9.26±0.49Cb | 3.40±0.25Cb | 2.13±0.14Ba |
| J0P1 | 13.69±0.94Ba | 10.77±0.54Ca | 4.16±0.29Ca | 2.25±0.47Ca |
| J1P0 | 13.87±0.66ABb | 9.78±0.28Cb | 4.45±0.31Bb | 2.59±0.70Ba |
| J1P1 | 15.70±0.42Aa | 12.07±0.67Ba | 5.29±0.15Ba | 3.23±0.36Ba |
| J2P0 | 12.79±0.71Bb | 10.75±0.45Bb | 4.85±0.23Bb | 2.24±0.28Ba |
| J2P1 | 15.11±0.18Aa | 12.80±0.49Ba | 5.54±0.34Ba | 2.67±0.45BCa |
| J3P0 | 14.12±0.48Ab | 13.10±0.23Ab | 5.34±0.11Ab | 3.59±0.26Aa |
| J3P1 | 16.28±0.97Aa | 14.67±0.87Aa | 6.05±0.16Aa | 4.00±0.61Aa |
| J | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | * |
| J×P | ns | ns | ns | ns |
表2 不同菌磷处理下紫花苜蓿叶片导管及筛管直径
Table 2 Vessel diameter and sieve tube diameter of alfalfa leaves under different bacterial and phosphorus treatment (μm)
处理 Treatment | 导管直径Vessel diameter | 筛管直径Sieve tube diameter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | |
| J0P0 | 11.04±0.97Cb | 9.26±0.49Cb | 3.40±0.25Cb | 2.13±0.14Ba |
| J0P1 | 13.69±0.94Ba | 10.77±0.54Ca | 4.16±0.29Ca | 2.25±0.47Ca |
| J1P0 | 13.87±0.66ABb | 9.78±0.28Cb | 4.45±0.31Bb | 2.59±0.70Ba |
| J1P1 | 15.70±0.42Aa | 12.07±0.67Ba | 5.29±0.15Ba | 3.23±0.36Ba |
| J2P0 | 12.79±0.71Bb | 10.75±0.45Bb | 4.85±0.23Bb | 2.24±0.28Ba |
| J2P1 | 15.11±0.18Aa | 12.80±0.49Ba | 5.54±0.34Ba | 2.67±0.45BCa |
| J3P0 | 14.12±0.48Ab | 13.10±0.23Ab | 5.34±0.11Ab | 3.59±0.26Aa |
| J3P1 | 16.28±0.97Aa | 14.67±0.87Aa | 6.05±0.16Aa | 4.00±0.61Aa |
| J | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | * |
| J×P | ns | ns | ns | ns |
处理 Treatment | 栅栏组织厚度 Palisade parenchyma thickness (μm) | 海绵组织厚度 Spongy parenchyma thickness (μm) | 栅海比 PPT/SPT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | |
| J0P0 | 85.77±4.33Cb | 84.52±4.98Bb | 47.60±3.48Cb | 45.73±4.23Cb | 1.80±0.07Aa | 1.86±0.16Aa |
| J0P1 | 104.15±5.69Da | 94.42±4.45Ca | 73.60±5.47Ba | 59.92±3.89Da | 1.42±0.03Ab | 1.58±0.08Ab |
| J1P0 | 95.53±6.56Bb | 92.57±2.45ABb | 53.40±7.33BCb | 67.04±4.18Bb | 1.81±0.26Aa | 1.38±0.07Bb |
| J1P1 | 115.69±6.54Ca | 116.88±7.47Ba | 83.18±2.37Aa | 73.93±2.46Ca | 1.39±0.12Ab | 1.58±0.05Aa |
| J2P0 | 88.84±1.04BCb | 87.86±1.55ABb | 56.80±3.26Ba | 62.81±2.21Bb | 1.57±0.08Ba | 1.40±0.04Ba |
| J2P1 | 127.13±3.85Ba | 100.31±6.36Ca | 85.87±4.81Aa | 79.76±2.55Ba | 1.49±0.13Aa | 1.26±0.09Ba |
| J3P0 | 110.37±7.77Ab | 94.76±6.44Ab | 66.00±6.67Ab | 76.18±3.28Ab | 1.68±0.06ABa | 1.25±0.13Bb |
| J3P1 | 136.56±2.21Aa | 138.51±2.91Aa | 91.42±3.35Aa | 88.33±1.35Aa | 1.50±0.06Aa | 1.57±0.05Aa |
| J | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ns |
| J×P | ** | ** | ns | ns | ns | ** |
表3 不同菌磷处理下紫花苜蓿叶片栅栏组织及海绵组织厚度
Table 3 Palisade parenchyma (PPT) and spongy parenchyma thickness (SPT) of alfalfa leaves under different bacterial and phosphorus treatment
处理 Treatment | 栅栏组织厚度 Palisade parenchyma thickness (μm) | 海绵组织厚度 Spongy parenchyma thickness (μm) | 栅海比 PPT/SPT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | 第1茬First cut | 第2茬Second cut | |
| J0P0 | 85.77±4.33Cb | 84.52±4.98Bb | 47.60±3.48Cb | 45.73±4.23Cb | 1.80±0.07Aa | 1.86±0.16Aa |
| J0P1 | 104.15±5.69Da | 94.42±4.45Ca | 73.60±5.47Ba | 59.92±3.89Da | 1.42±0.03Ab | 1.58±0.08Ab |
| J1P0 | 95.53±6.56Bb | 92.57±2.45ABb | 53.40±7.33BCb | 67.04±4.18Bb | 1.81±0.26Aa | 1.38±0.07Bb |
| J1P1 | 115.69±6.54Ca | 116.88±7.47Ba | 83.18±2.37Aa | 73.93±2.46Ca | 1.39±0.12Ab | 1.58±0.05Aa |
| J2P0 | 88.84±1.04BCb | 87.86±1.55ABb | 56.80±3.26Ba | 62.81±2.21Bb | 1.57±0.08Ba | 1.40±0.04Ba |
| J2P1 | 127.13±3.85Ba | 100.31±6.36Ca | 85.87±4.81Aa | 79.76±2.55Ba | 1.49±0.13Aa | 1.26±0.09Ba |
| J3P0 | 110.37±7.77Ab | 94.76±6.44Ab | 66.00±6.67Ab | 76.18±3.28Ab | 1.68±0.06ABa | 1.25±0.13Bb |
| J3P1 | 136.56±2.21Aa | 138.51±2.91Aa | 91.42±3.35Aa | 88.33±1.35Aa | 1.50±0.06Aa | 1.57±0.05Aa |
| J | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ns |
| J×P | ** | ** | ns | ns | ns | ** |
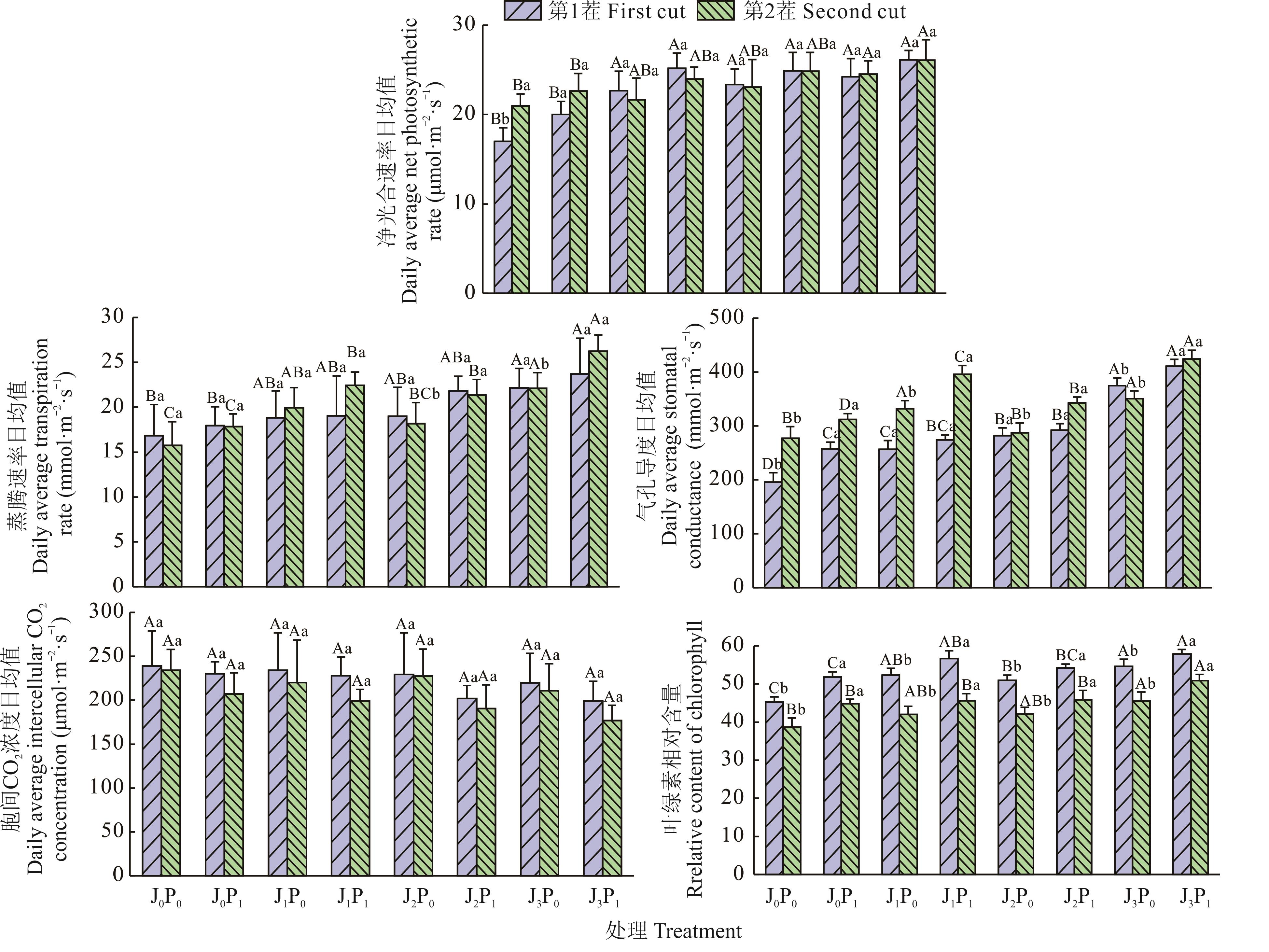
图2 不同菌磷处理下紫花苜蓿叶片光合参数日均值及叶绿素相对含量不同小写字母表示同一茬次间同一菌添加下,不同磷水平间差异显著(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示同一茬次间同一磷添加下,不同菌水平间差异显著(P<0.05)。The different lowercase letters indicate that the difference between different phosphorus levels is significant under the same bacteria addition in the same crop (P<0.05); different capital letters indicate that the difference among different bacterial levels is significant under the same phosphorus addition in the same crop (P<0.05).
Fig.2 Daily mean values of the photosynthetic parameters and relative chlorophyll content of alfalfa under different bacterial and phosphorus treatment
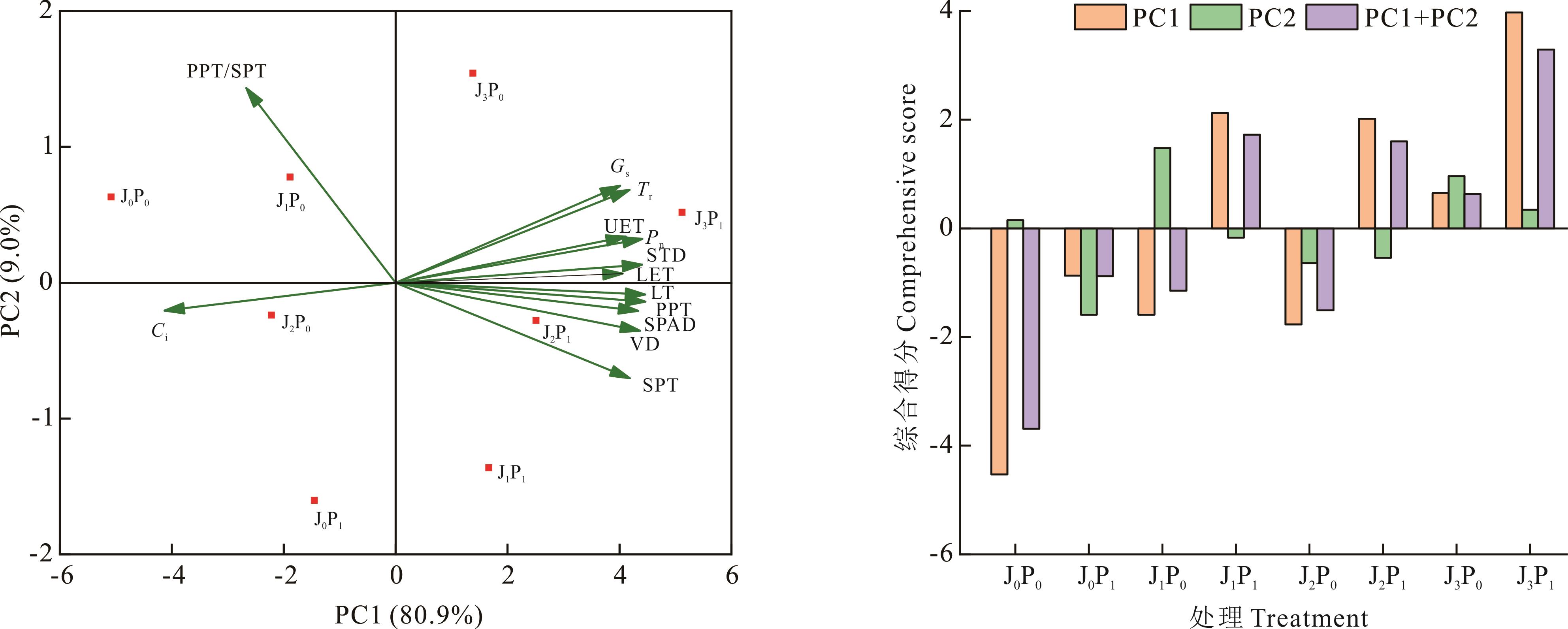
图4 不同菌磷处理下紫花苜蓿叶片指标主成分分析及评价Ci:胞间CO2浓度Intercellular CO2 concentration;Gs:气孔导度Stomatal conductance;Tr:蒸腾速率Transpiration rate;Pn:净光合速率Net photosynthetic rate;UET:上表皮厚度Upper epidermal thickness;STD:筛管直径 Sieve tube diameter;LET:下表皮厚度Lower epidermal thickness;LT:叶片厚度 Leaf thickness;PPT:栅栏组织厚度 Palisade parenchyma thickness;SPAD:叶绿素相对含量 Relative chlorophyll content;VD:导管直径 Vessel diameter;SPT:海绵组织厚度Spongy parenchyma thickness.
Fig.4 Principal component analysis and evaluation of alfalfa leaves index under different bacterial and phosphorus treatment
| 1 | Liu J Y, Hui J F, Sun M Y, et al. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculation arbuscular mycorrhizae fungi (AMF) and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on dry matter yield and phosphorus use efficiency of alfalfa. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(19): 142-149. |
| 刘俊英, 回金峰, 孙梦瑶, 等. 施磷水平和接种AMF与解磷细菌对苜蓿产量及磷素利用效率的影响. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(19): 142-149. | |
| 2 | Hou E Q, Luo Y Q, Kuang Y W, et al. Global meta-analysis shows pervasive phosphorus limitation of aboveground plant production in natural terrestrial ecosystems. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1-9. |
| 3 | Shu Y, Huang G J, Zhang Q Q, et al. Reduction of photosynthesis under P deficiency is mainly caused by the decreased CO2 diffusional capacities in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2023, 198: 10768. |
| 4 | Cao L Q, Zhong Q P, Zou Y L, et al. Leaf structural and photosynthetic characteristics of different Vcmicia montana germplasms. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2022, 42(6): 592-599. |
| 曹林青, 钟秋平, 邹玉玲, 等. 不同千年桐种质叶片结构及光合特性. 森林与环境学报, 2022, 42(6): 592-599. | |
| 5 | Li J X, Tian Q, Li J Z, et al. The leaf anatomical structure of 9 garden plants in different air environments in Lanzhou city. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(11): 2189-2198. |
| 李娟霞, 田青, 李娇珍, 等. 兰州市不同空气环境下9种园林植物叶片解剖结构特征. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(11): 2189-2198. | |
| 6 | Fleisher D H, Wang Q G, Timlin D J, et al. Response of potato gas exchange and productivity to phosphorus deficiency and carbon dioxide enrichment. Crop Science, 2012, 52(4): 1803-1815. |
| 7 | Yue H F, Zhou M, Hou X K, et al. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on phenotype, photosynthesis and biomass accumulation at juvenile phase of Prunus armeniaca×sibirica. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2022, 54(2): 577-588. |
| 8 | Xu B. Effects of different phosphorous fertilizer and phosphorus fractions on leaf micromorphology, N/P acquisition and yield of sickle lucerne (Medicago falcata L). Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2021. |
| 徐勃. 不同磷肥和磷形态对黄花苜蓿(Medicago falcata L.)叶片微观结构、氮磷吸收及产量的影响. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2021. | |
| 9 | Wang X X, Zhang M, Zhang X Y, et al. Effects of different varieties of phosphate fertilizer application on soil phosphorus transformation and phosphorus uptake and utilization of winter wheat. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2023, 56(6): 1113-1126. |
| 王箫璇, 张敏, 张鑫尧, 等. 不同磷肥对砂姜黑土和红壤磷库转化及冬小麦磷素吸收利用的影响. 中国农业科学, 2023, 56(6): 1113-1126. | |
| 10 | Suriyagod L D B, Ryan M H, Renton M, et al. Above- and belowground interactions of grass and pasture legume species when grown together under drought and low phosphorus availability. Plant and Soil, 2011, 348(1): 281-297. |
| 11 | Pratibha R, Sudeshna D, Deepti S C, et al. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: mechanism and their role in phosphate solubilization and uptake. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2021, 21(1): 49-68. |
| 12 | Kafi M, Nabati J, Rezazadeh E B, et al. Single and poly capsule sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) productivity in response to plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and foliar application of silicon potassium and calcium. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2022, 44(10): 4-14. |
| 13 | Nacoon S, Seemakram W, Ekprasert J, et al. Promoting growth and production of sunchoke (Helianthus tuberosus) by co-inoculation with phosphate solubilizing bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under drought. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 1-18. |
| 14 | Liu X S, Sun Y L, An X X, et al. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria on the photosynthetic characteristics and biomass of alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. |
| 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 等. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. | |
| 15 | Sun Y L, Wang X Z, Ma C H, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on agronomic characters, photosynthetic performance and anatomical structure of alfalfa in northern Xinjiang, China. Agronomy, 2022, 12(7): 1-21. |
| 16 | Ren S F. Allometric growth and ecological adaptability of the leaf anatomical structure of Nitraria spp. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(5): 1150-1158. |
| 任尚福. 白刺叶片解剖结构性状异速生长与生态适应性研究. 草地学报, 2022, 30(5): 1150-1158. | |
| 17 | Aguraijuja K, Klõšeiko J, Ots K, et al. Effect of wood ash on leaf and shoot anatomy photosynthesis and carbohydrate concentrations in birch on a cutaway peatland. Environmental Monitoring and Assessmente, 2015, 18(7): 1-13. |
| 18 | Sun Y Q, Yan F, Cui X Y, et al. Plasticity in stomatal size and density of potato leaves under different irrigation and phosphorus regimes. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2014, 171(14): 1248-1255. |
| 19 | Cai Q, Ji C J, Yan Z B, et al. Anatomical responses of leaf and stem of Arabidopsis thaliana to nitrogen and phosphorus addition. Journal of Plant Research, 2017, 130(6): 1035-1045. |
| 20 | Gashash E A, Ashmawi A E, El-Taher A, et al. Effect of fertilizing with different levels of phosphorous and zinc on the botanical characteristics of table beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca, 2022, 50(1): 12579. |
| 21 | Delgado M N, Gomes M R D, Bao S N, et al. Fertilisation residues alter leaf scleromorphy in an evergreen savannah shrub (Maprounea brasiliensis, Euphorbiaceae). Australian Journal of Botany, 2013, 61(4): 266-273. |
| 22 | Khajeeyan R, Salehi A, Dehnavi M, et al. Growth parameters, water productivity and aloin content of Aloe vera affected by mycorrhiza and PGPR application under different irrigation regimes. South African Journal of Botany, 2021, 147(2): 1188-1198. |
| 23 | Kim J H, Kim S J, Nam I H. Effect of treating acid sulfate soils with phosphate solubilizing bacteria on germination and growth of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(17): 1-10. |
| 24 | Li Z W. Study on the influence of different bacteria on the quality and soil environment of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Chongqing:Chongqing Three GorgesUniversity, 2023. |
| 李卓蔚. 施加不同解有机磷细菌对滇重楼品质与土壤环境影响研究. 重庆: 重庆三峡学院, 2023. | |
| 25 | Sahandi M S, Mehrafarin A, Badi H N, et al. Improving growth phytochemical and antioxidant characteristics of peppermint by phosphate-solubilizing bacteria along with reducing phosphorus fertilizer use. Industrial Crops and Products, 2019, 141: 1-10. |
| 26 | Majid M, Ali M, Shahzad K, et al. Mitigation of osmotic stress in cotton for the improvement in growth and yield through inoculation of rhizobacteria and phosphate solubilizing bacteria coated diammonium phosphate. Sustainability, 2020, 12(24): 2-14. |
| 27 | Bakhshandeh E, Rahimian H, Pirdashti H, et al. Evaluation of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on the growth and grain yield of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cropped in northern Iran. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2015, 119(5): 1371-1382. |
| 28 | Guan S H, Chai Y Q, Cui H X, et al. Effects of low temperature stress on photosynthetic parameters and physiological characteristics for seedlings of two pomegranate varieties. Journal of Fruit Science, 2023, 40(5): 946-958. |
| 关思慧, 柴亚倩, 崔洪鑫, 等. 低温胁迫对2个石榴品种幼苗光合参数和生理特性的影响. 果树学报, 2023, 40(5): 946-958. | |
| 29 | Yang Q, Han J L, Li Y M, et al. Effects of phosphorus fertilization on flag leaves photosynthesis and yield components in wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2006, 12(6): 816-821. |
| 杨晴, 韩金玲, 李雁鸣, 等. 不同施磷量对小麦旗叶光合性能和产量性状的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2006, 12(6): 816-821. | |
| 30 | Warren C R. How does P affect photosynthesis and metabolite profiles of Eucalyptus globulus? Tree Physiology, 2011, 31(7): 727-739. |
| 31 | Li N, Qiao Z W, Hong J P, et al. Phosphorus solubilizing bacteria growth and effects on soil phosphorus adsorption-desorption characteristics in reclaimed soils. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2015, 23(8): 964-972. |
| 李娜, 乔志伟, 洪坚平, 等. 磷细菌在复垦土壤上生长规律及对磷解析特性的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(8): 964-972. | |
| 32 | Zhao J, Yu D B, Meng F G, et al. Regulation of phosphorus supply level on phosphorus-iron ratio and photosynthetic efficiency at different growth stages of soybean. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(4): 665-674. |
| 赵婧, 于德彬, 孟凡钢, 等. 磷供应水平对大豆不同生育期磷铁比及光合效率的调节. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(4): 665-674. | |
| 33 | Li H J, Hu Y T, Liu M J, et al. Growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of Leymus chinensis in response to applications of phosphorus at differing intensities. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(10): 2041-2049. |
| 李会军, 胡雨彤, 刘美君, 等. 羊草生长和光合生理特性对不同施磷强度的响应. 草业科学, 2021, 38(10): 2041-2049. | |
| 34 | Wang Y, Liu C H, Hu K H, et al. Effects of different phosphorus levels on leaf nutrition, photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of walnut seedlings. China Fruits, 2021, 62(6): 13-18. |
| 王阳, 刘春花, 胡凯红, 等. 不同供磷水平对核桃实生幼苗叶片营养、光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 中国果树, 2021, 62(6): 13-18. | |
| 35 | Mihalache G, Zamfirache M M, Hamburda S, et al. Synergistic effect of Pseudomonas lini and Bacillus pumilus on runner bean growth enhancement. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 2016, 15(8): 1823-1831. |
| 36 | Rawat P, Shankhdhar D, Shankhdhar S C, et al. Synergistic impact of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and phosphorus rates on growth, antioxidative defense system and yield characteristics of upland rice (Oryza sativa L.). Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2022, 41(6): 2449-2461. |
| 37 | Nosheen A, Yasmin H, Naz R, et al. Pseudomonas putida improved soil enzyme activity and growth of kasumbha under low input of mineral fertilizers. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2018, 64(4): 520-525. |
| [1] | 谭湘蛟, 董逵才, 张华, 唐川川, 杨燕. 积雪增加对青藏高原高寒草甸土壤磷有效性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 205-214. |
| [2] | 张成兰, 刘春增, 吕玉虎, 李本银, 张琳, 丁丽, 杜光辉, 张香凝, 郑春风, 张济世, 李敏, 曹卫东. 不同年限紫云英配施减量化肥对土壤磷吸附解吸特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 41-52. |
| [3] | 高金柱, 赵东豪, 高乐, 苏喜浩, 何学青. 硝酸铈与脱落酸处理对紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [4] | 伍国强, 于祖隆, 魏明. PGPR调控植物响应逆境胁迫的作用机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 203-218. |
| [5] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [6] | 王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 包爱科. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. |
| [7] | 张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 马嵩科, 张冬霞, 张静, 乔唱唱, 李爽, 黄明, 王贺正. 秸秆还田配施磷肥对豫西旱地小麦碳同化物积累的影响及其生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 89-104. |
| [8] | 孔海明, 宋家兴, 杨静, 李倩, 杨培志, 曹玉曼. 紫花苜蓿CAMTA基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [9] | 何升然, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 汪雪, 王静. 紫花苜蓿/甜高粱间作对根际土壤特性及微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 92-105. |
| [10] | 常单娜, 陈子英, 韩梅, 李正鹏, 严清彪, 吕帅磊, 周国朋, 孙小凤, 曹卫东. 毛叶苕子磷获取特征及根际特性的基因型差异[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 122-134. |
| [11] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [12] | 李显炀, 刘昊, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿WRKY转录因子家族鉴定与表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. |
| [13] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [14] | 李秀芳, 魏文静, 蒲勇, 李廷轩, 叶代桦. 水蓼种植下猪粪处理土壤剖面磷组分与磷酸酶活性变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 61-72. |
| [15] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||