
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 39-48.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021243
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wen LI1,2( ), Ting-hu WEI3, Yongcuobazhan3, Cairentaci3, Yu-hai ZHOU3, Yan-ping ZHANG1(
), Ting-hu WEI3, Yongcuobazhan3, Cairentaci3, Yu-hai ZHOU3, Yan-ping ZHANG1( ), Wen-hao LI1, Wei-xing GUO1
), Wen-hao LI1, Wei-xing GUO1
Received:2021-06-17
Revised:2021-08-31
Online:2021-11-11
Published:2021-11-11
Contact:
Yan-ping ZHANG
Wen LI, Ting-hu WEI, Yongcuobazhan, Cairentaci, Yu-hai ZHOU, Yan-ping ZHANG, Wen-hao LI, Wei-xing GUO. Effects of different mixed planting ratios on vegetation and soil characteristics of sown pasture in the Sanjiangyuan region[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 39-48.
处理 Treatment | 混播比例 Mixed ratio1 | 播量Sowing quantity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
垂穗披碱草 E. nutans | 中华羊茅 F. sinensis | 青海草地早熟禾 P. pratensis cv. Qinghai | ||
| S1 | 1∶0∶0 | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| S2 | 0∶1∶0 | 0 | 20 | 0 |
| S3 | 0∶0∶1 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| M4 | 1∶1∶1 | 10 | 6.67 | 3.33 |
| M5 | 2∶1∶1 | 15 | 5 | 2.5 |
| M6 | 1∶2∶1 | 7.5 | 10 | 2.5 |
| M7 | 1∶1∶2 | 7.5 | 5 | 5 |
| M8 | 2∶2∶1 | 12 | 8 | 2 |
| M9 | 2∶1∶2 | 12 | 4 | 4 |
| M10 | 1∶2∶2 | 6 | 8 | 4 |
Table 1 The mixed ratio of E. nutans×F. sinensis×P. pratensis cv. Qinghai (kg·hm-2)
处理 Treatment | 混播比例 Mixed ratio1 | 播量Sowing quantity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
垂穗披碱草 E. nutans | 中华羊茅 F. sinensis | 青海草地早熟禾 P. pratensis cv. Qinghai | ||
| S1 | 1∶0∶0 | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| S2 | 0∶1∶0 | 0 | 20 | 0 |
| S3 | 0∶0∶1 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| M4 | 1∶1∶1 | 10 | 6.67 | 3.33 |
| M5 | 2∶1∶1 | 15 | 5 | 2.5 |
| M6 | 1∶2∶1 | 7.5 | 10 | 2.5 |
| M7 | 1∶1∶2 | 7.5 | 5 | 5 |
| M8 | 2∶2∶1 | 12 | 8 | 2 |
| M9 | 2∶1∶2 | 12 | 4 | 4 |
| M10 | 1∶2∶2 | 6 | 8 | 4 |
| 物种Species | S1 | S2 | S3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | M8 | M9 | M10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 垂穗披碱草E. nutans | 0.894 | 0.357 | 0.427 | 0.358 | 0.349 | 0.427 | 0.415 | 0.282 | ||
| 中华羊茅 F. sinensis | 0.859 | 0.276 | 0.276 | 0.315 | 0.268 | 0.291 | 0.235 | 0.364 | ||
| 青海草地早熟禾P. pratensis cv. Qinghai | 0.853 | 0.261 | 0.206 | 0.240 | 0.295 | 0.188 | 0.262 | 0.259 | ||
| 鹅绒委陵菜P. anserina | 0.028 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.049 | 0.045 | 0.052 | 0.055 | ||
| 多裂委陵菜P. multifida | 0.036 | 0.046 | 0.051 | 0.041 | 0.053 | |||||
| 细叶亚菊A. tenuifolia | 0.042 | 0.046 | ||||||||
| 狗娃花Heteropappus hispidus | 0.044 | 0.056 | 0.042 | |||||||
| 蒲公英T. mongolicum | 0.041 | |||||||||
| 独一味L. rotata | 0.033 | 0.057 | ||||||||
| 小大黄R. pumilum | 0.036 | 0.039 | ||||||||
| 合计Total | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
Table 2 Changes in species important values of artificial grassland under different mixed-planting ratios
| 物种Species | S1 | S2 | S3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | M8 | M9 | M10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 垂穗披碱草E. nutans | 0.894 | 0.357 | 0.427 | 0.358 | 0.349 | 0.427 | 0.415 | 0.282 | ||
| 中华羊茅 F. sinensis | 0.859 | 0.276 | 0.276 | 0.315 | 0.268 | 0.291 | 0.235 | 0.364 | ||
| 青海草地早熟禾P. pratensis cv. Qinghai | 0.853 | 0.261 | 0.206 | 0.240 | 0.295 | 0.188 | 0.262 | 0.259 | ||
| 鹅绒委陵菜P. anserina | 0.028 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.049 | 0.045 | 0.052 | 0.055 | ||
| 多裂委陵菜P. multifida | 0.036 | 0.046 | 0.051 | 0.041 | 0.053 | |||||
| 细叶亚菊A. tenuifolia | 0.042 | 0.046 | ||||||||
| 狗娃花Heteropappus hispidus | 0.044 | 0.056 | 0.042 | |||||||
| 蒲公英T. mongolicum | 0.041 | |||||||||
| 独一味L. rotata | 0.033 | 0.057 | ||||||||
| 小大黄R. pumilum | 0.036 | 0.039 | ||||||||
| 合计Total | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
处理 Treatment | OY (g·m-2) | OY1 | OY2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| M4 | -17.07±8.71c | -0.26±0.01c | -0.03±0.02c |
| M5 | 40.43±23.36ab | -0.17±0.03ab | 0.07±0.04ab |
| M6 | -29.88±26.61c | -0.27±0.04c | -0.05±0.05c |
| M7 | -27.62±27.43c | -0.27±0.04c | -0.05±0.05c |
| M8 | 71.12±27.10a | -0.13±0.04a | 0.13±0.05a |
| M9 | 60.89±25.96a | -0.15±0.04a | 0.11±0.05a |
| M10 | 13.11±14.38bc | -0.21±0.02bc | 0.02±0.03bc |
Table 3 Changes in over yielding and transgressive overyielding effect of artificial grassland under different mixed-planting ratios
处理 Treatment | OY (g·m-2) | OY1 | OY2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| M4 | -17.07±8.71c | -0.26±0.01c | -0.03±0.02c |
| M5 | 40.43±23.36ab | -0.17±0.03ab | 0.07±0.04ab |
| M6 | -29.88±26.61c | -0.27±0.04c | -0.05±0.05c |
| M7 | -27.62±27.43c | -0.27±0.04c | -0.05±0.05c |
| M8 | 71.12±27.10a | -0.13±0.04a | 0.13±0.05a |
| M9 | 60.89±25.96a | -0.15±0.04a | 0.11±0.05a |
| M10 | 13.11±14.38bc | -0.21±0.02bc | 0.02±0.03bc |
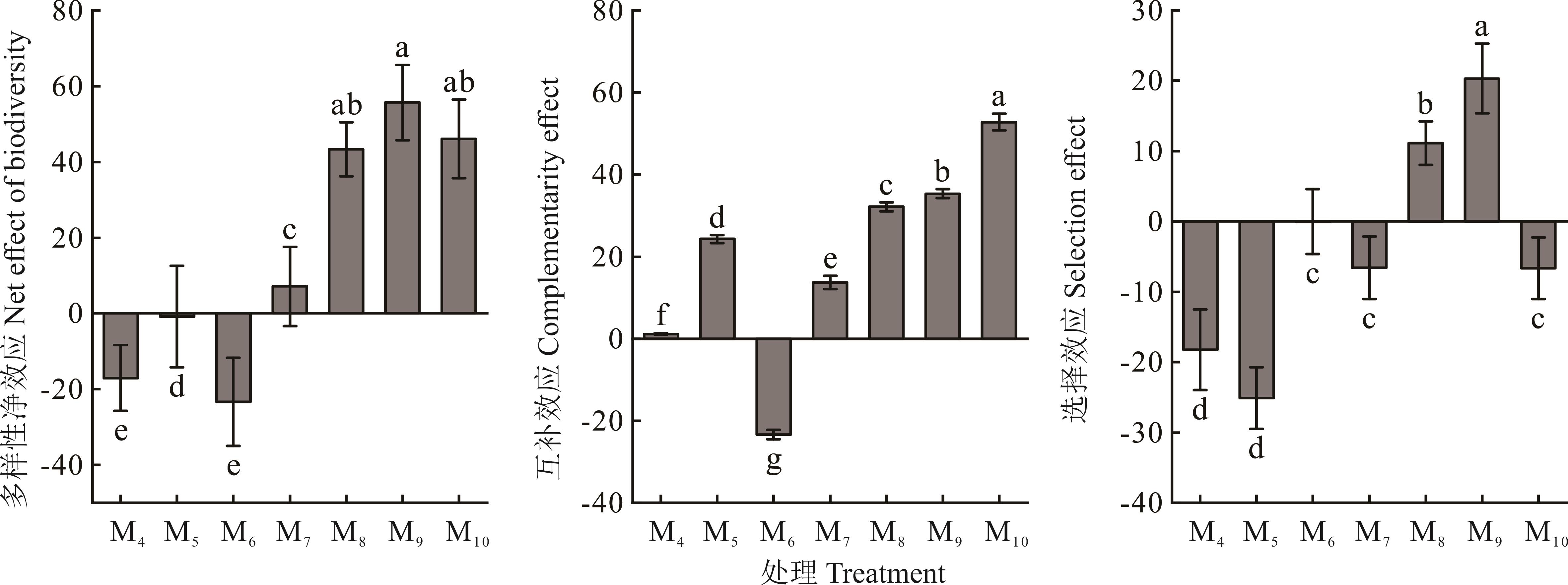
Fig.2 Changes in net effect of biodiversity, selection effect and complementarity effect of artificial grassland under different mixed-planting ratios
处理 Treatment | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou指数 Pielou index | 丰富度指数 Richness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.49±0.05d | 0.35±0.04c | 4.00±1.00b |
| S2 | 0.61±0.08c | 0.44±0.03b | 4.00±1.00b |
| S3 | 0.63±0.02c | 0.39±0.03bc | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M4 | 1.51±0.07a | 0.84±0.03a | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M5 | 1.45±0.04a | 0.81±0.06a | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M6 | 1.47±0.05a | 0.82±0.01a | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M7 | 1.49±0.04a | 0.83±0.03a | 5.00±0.00a |
| M8 | 1.32±0.05b | 0.84±0.02a | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M9 | 1.33±0.07b | 0.83±0.02a | 5.00±0.00ab |
| M10 | 1.36±0.05b | 0.84±0.03a | 5.00±0.00ab |
Table 4 Changes in species diversity of artificial grassland under different mixed-planting ratios
处理 Treatment | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou指数 Pielou index | 丰富度指数 Richness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.49±0.05d | 0.35±0.04c | 4.00±1.00b |
| S2 | 0.61±0.08c | 0.44±0.03b | 4.00±1.00b |
| S3 | 0.63±0.02c | 0.39±0.03bc | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M4 | 1.51±0.07a | 0.84±0.03a | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M5 | 1.45±0.04a | 0.81±0.06a | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M6 | 1.47±0.05a | 0.82±0.01a | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M7 | 1.49±0.04a | 0.83±0.03a | 5.00±0.00a |
| M8 | 1.32±0.05b | 0.84±0.02a | 5.00±1.00ab |
| M9 | 1.33±0.07b | 0.83±0.02a | 5.00±0.00ab |
| M10 | 1.36±0.05b | 0.84±0.03a | 5.00±0.00ab |
| 1 | Deng J J, Bai X J, Zhou Y B, et al. Variations of soil microbial communities accompanied by different vegetation restoration in an open-cut iron mining area. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 704: 1-11. |
| 2 | Mu C C, Abbott B W, Norris A J, et al. The status and stability of permafrost carbon on the Tibetan Plateau. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 211: 3382-3393. |
| 3 | Miehe G, Schleuss M, Seeber E, et al. The Kobresia pygmaea ecosystem of the Tibetan highlands-origin, functioning and degradation of the world’s largest pastoral alpine ecosystem: Kobresia pastures of Tibetan. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 648: 754-771. |
| 4 | Shang Z H, Dong Q M, Shi J J, et al. Research progress in recent ten years of ecological restoration for “black soil land” degraded grassland on Tibetan Plateau-Concurrently discuss of ecological restoration in Sanjiangyuan Region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(1): 1-21. |
| 尚占环, 董全民, 施建军, 等. 青藏高原“黑土滩”退化草地及其生态恢复近10年研究进展兼论三江源生态恢复问题. 草地学报, 2018, 26(1): 1-21. | |
| 5 | Dong S K, Shang Z H, Gao J X, et al. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2020, 287: 1-16. |
| 6 | Bai Y F, Ma L N, Degen A A, et al. Long-term active restoration of extremely degraded alpine grassland accelerated turnover and increased stability of soil carbon. Global Change Biology, 2020, 26(12): 7217-7228. |
| 7 | Wu S N, Zhang X, Gao X X, et al. Succession dynamics of a plant community of degraded alpine meadow during the human-induced restoration process in the Three Rivers Source region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(7): 2444-2453. |
| 武胜男, 张曦, 高晓霞, 等. 三江源区“黑土滩”型退化草地人工恢复植物群落的演替动态. 生态学报, 2019, 39(7): 2444-2453. | |
| 8 | Dong Q M, Ma Y S, Xu C J, et al. Study of classification and gradation, restoration of black-soil beach degraded grassland in the Headwaters of Three Rivers. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(3): 441-447. |
| 董全民, 马玉寿, 许长军, 等. 三江源区黑土滩退化草地分类分级体系及分类恢复研究. 草地学报, 2015, 23(3): 441-447. | |
| 9 | Qin Y, Chen J J, Yi S H. Plateau pikas burrowing activity accelerates ecosystem carbon emission from alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 84: 287-291. |
| 10 | Shang Z H, Dong Q M, Degen A A, et al. Ecological restoration on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Problems, strategies and prospects. New York: Nova Science Publishers, 2016. |
| 11 | Li X L, Perry G L W, Brierley G, et al. Quantitative assessment of degradation classifications for degraded alpine meadows (Heitutan), Sanjiangyuan, Western China. Land Degradation & Development, 2015, 25(5): 417-427. |
| 12 | Zhang Y, Zhang C B, Wang Z Q, et al. Quantitative assessment of relative roles of climate change and human activities on grassland net primary productivity in the Three-River Source Region, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(5): 1-14. |
| 张颖, 章超斌, 王钊齐, 等. 气候变化与人为活动度对三江源草地生产力影响的定量研究. 草业学报, 2017, 26(5): 1-14. | |
| 13 | Wu X H, Shan X K, Dong S K, et al. Prediction of alpine artificial grassland restoration based on an improved Lotka-Volterra interspecific competition model. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(9): 3187-3198. |
| 吴晓慧, 单熙凯, 董世魁, 等. 基于改进的Lotka-Volterra种间竞争模型预测退化高寒草地人工恢复演替结果. 生态学报, 2019, 39(9): 3187-3198. | |
| 14 | Guo N, Degen A A, Deng B, et al. Changes in vegetation parameters and soil nutrients along degradation and recovery successions on alpine grasslands of the Tibetan plateau. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2019, 284: 1-12. |
| 15 | Xu S H, Shang Z H. The three-stage species niche and reproductive characteristics of poisonous weeds in the three-stages of the secondary vegetation’s formation of ‘bare land’ degraded grassland in the Three Rivers Source region, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(4): 949-955. |
| 徐松鹤, 尚占环. 三江源区“黑土滩”次生植被形成的三阶段物种生态位与毒杂草繁殖特征. 草地学报, 2019, 27(4): 949-955. | |
| 16 | Ma Y S, Shang Z H, Shi J J, et al. Studies on allocate skills of artificial community of “black soil type” degraded grassland in the Yellow River source region. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2007, 16(5): 1-6. |
| 马玉寿, 尚占环, 施建军, 等. 黄河源区“黑土型”退化草地人工群落组分配置技术研究. 西北农业学报, 2007, 16(5): 1-6. | |
| 17 | Ma Y S, Shi J J, Dong Q M, et al. Study on screening of forage species fittingly cultivated in black-soil beach. Chinese Qinghai Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2011, 41(4): 1-4. |
| 马玉寿, 施建军, 董全民, 等. 适宜黑土滩栽培的牧草品种筛选研究. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2011, 41(4): 1-4. | |
| 18 | Ma Y S, Lang B N, Li Q Y, et al. Study on rehabilitating and rebuilding technologies for degenerated alpine meadow in the Changjiang and Yellow river source region. Pratacultural Science, 2002, 19(9): 1-5. |
| 马玉寿, 郎百宁, 李青云, 等. 江河源区高寒草甸退化草地恢复与重建技术研究. 草业科学, 2002, 19(9): 1-5. | |
| 19 | Bao S D. Soil agro-chemistrical analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2001. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2001. | |
| 20 | Ma K P, Huang J H, Yu S L, et al. Plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China: Ⅱ. Species richness, evenness and species diversities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1995, 15(3): 268-277. |
| 马克平, 黄建辉, 于顺利, 等. 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究Ⅱ丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性指数. 生态学报, 1995, 15(3): 268-277. | |
| 21 | Loreau M, Hector A. Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature, 2001, 412: 72-76. |
| 22 | Li J, Pan P, Wang C T, et al. Root dynamics of artificial grassland for swards of differing ages in the ‘Three-River Source’ region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 28-40. |
| 李洁, 潘攀, 王长庭, 等. 三江源区不同建植年限人工草地根系动态特征. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 28-40. | |
| 23 | Guan H L, Fan J W, Li Y Z. The impact of different introduced artificial grassland species combinations on community biomass and species diversity in temperate steppe of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(9): 192-201. |
| 官惠玲, 樊江文, 李愈哲. 不同人工草地对青藏高原温性草原群落生物量组成及物种多样性的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 192-201. | |
| 24 | Cox S, Peel M D, Creech J E, et al. Forage production of grass-legume binary mixtures on intermountain Western USA irrigated pastures. Crop Science, 2017, 57: 1742-1753. |
| 25 | Hector A, Hautier Y, Saner P, et al. General stabilizing effects of plant diversity on grassland productivity through population asynchrony and overyielding. Ecology, 2010, 91(8): 2213-2220. |
| 26 | Li L, Tilman D, Lambers H, et al. Plant diversity and overyielding: Insights from belowground facilitation of intercropping in agriculture. New Phytologist, 2014, 203: 63-69. |
| 27 | Wang Y K, Ding X F, Wang X P, et al. Genotypic diversity of a dominant species Leymus chinensis inhibited ecological function of species diversity in the Inner Mongolia Steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(5): 1507-1516. |
| 王宇坤, 丁新峰, 王小平, 等. 内蒙古典型草原建群种羊草基因型多样性抑制群落物种多样性的生态功能. 生态学报, 2019, 39(5): 1507-1516. | |
| 28 | Li S S, Wang N X, Zheng W, et al. Comparison of transgressive overyielding effect and plant diversity effects of annual and perennial legume-grass mixtures. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2021, 45(1): 23-37. |
| 黎松松, 王宁欣, 郑伟, 等. 一年生和多年生豆禾混播草地超产与多样性效应的比较. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(1): 23-37. | |
| 29 | Li C J, Li Y Y, Yu C B, et al. Crop nitrogen use and soil mineral nitrogen accumulation under different crop combinations and patterns of strip intercropping in northwest China. Plant and Soil, 2011, 342(1): 221-231. |
| 30 | Bauters M, Moonen P, Summerauer L, et al. Soil nutrient depletion and tree functional composition shift following repeated clearing in secondary forests of the Congo Basin. Ecosystems, 2021, 24(1): 1-14. |
| 31 | Xie K Y, Zhao Y, Li X L, et al. Relationships between grasses and legumes in mixed grassland: A review. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(3): 284-296. |
| 谢开云, 赵云, 李向林, 等. 豆-禾混播草地种间关系研究进展. 草业学报, 2013, 22(3): 284-296. | |
| 32 | Wu X J, Yang M, Lu Y X, et al. Effects of mixing ratio and nitrogen fertilization on root characteristics in the common vetch/oat mixture. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(9): 106-116. |
| 吴晓娟, 杨梅, 芦奕晓, 等. 混播比例和施氮肥对箭筈豌豆/燕麦草地根系特性的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 106-116. | |
| 33 | Lai X L, Shi S L, Wu F, et al. Nutrient characteristics of soil sowed with different combinations of alfalfa and three perennial grasses. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(1): 52-64. |
| 来幸樑, 师尚礼, 吴芳, 等. 紫花苜蓿与3种多年生禾草混播草地的土壤养分特征. 草业科学, 2020, 37(1): 52-64. |
| [1] | Xiao-ding LIN, Le CHANG, Dan FENG. Remote-sensing estimation of vegetation gross primary productivity and its spatiotemporal changes in Qinghai Province from 2000 to 2019 [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 16-27. |
| [2] | Jie LI, Pan PAN, Chang-ting WANG, Lei HU, Ke-yu CHEN, Wen-gao YANG. Root dynamics of artificial grassland for swards of differing ages in the ‘Three-River Source’ region [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 28-40. |
| [3] | Si-li LIU, Chang-ting WANG, Chang-bing ZHANG, Lei HU, Li-tao TANG, Pan PAN. A comparative study of root characteristics of three gramineous herbage species in the Northwest Sichuan Plateau [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 41-53. |
| [4] | Hua-fang SUN, Xi-lai LI, Li-qun JIN, Cheng-yi LI, Jing ZHANG. Change over time in soil microbial diversity of artificial grassland in the Yellow River source zone [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(2): 46-58. |
| [5] | Wen-rong LUO, Guo-zheng HU, Ganjurjav H, Qing-zhu GAO, Yan LI, Yi-qing Ge, Yu LI, Shi-cheng HE, Luo-bu DANJIU. Effects of simulated drought on plant phenology and productivity in an alpine meadow in Northern Tibet [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(2): 82-92. |
| [6] | Hui-long LIN, Di FAN, Qi-sheng FENG, Tian-gang LIANG. New focus for the study of the Comprehensive Sequential Classification System for grassland: A review from 2008 to 2020 and prospects for future research [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 201-213. |
| [7] | Wan-di LIU, Xiao-wei LI, Wen-guang HUANG, Hui-cheng MA, Hong-ying MA, Wen-xiao WANG. Community diversity, patterns of productivity, and factors influencing them in Stipa in Ningxia grassland [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 12-23. |
| [8] | Fu-gui HAN, Duo-qing MAN, Qing-zhong ZHENG, Yan-li ZHAO, Yu-nian ZHANG, Bin XIAO, Gui-quan FU, Juan DU. Species diversity and soil nutrient changes of a Nitraria tangutorum shrub community in Qingtu Lake wetland [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 36-45. |
| [9] | CUI Bo-chao, ZHENG Jiang-hua, TUERXUN·Hasimu, DUAN Su-su, DU Meng-jie. Spatio-temporal characteristics of grassland net primary productivity (NPP) in the Tarim River basin [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(6): 1-13. |
| [10] | HUANG Yu-fan, SHU Ying-ge, XIAO Sheng-yang, CHEN Meng-jun. Quantification of soil nutrient levels and enzyme activities in different grassland categories in karst mountains [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(6): 93-104. |
| [11] | QIU Yue, WU Peng-fei, WEI Xue. Differences among three artificial grasslands in dynamics and community diversity of soil microarthropods [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(5): 21-32. |
| [12] | HE Guo-xing, SONG Jian-chao, WEN Ya-jie, LIU Cai-ting, QI Juan. Effects of different rhizobium fertilizers on alfalfa productivity and soil fertility [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(5): 109-120. |
| [13] | WEI Peng, AN Sha-zhou, DONG Yi-qiang, SUN Zong-jiu, Bieerdawulieti·Xihayi, LI Chao. A high-throughput sequencing evaluation of bacterial diversity and community structure of the desert soil in the Junggar Basin [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(5): 182-190. |
| [14] | Chelmeg, LIU Xin-ping, HE Yu-hui, SUN Shan-shan, WANG Ming-ming. Response of herbaceous plant community characteristics to short-term precipitation change in semi-arid sandy land [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 19-28. |
| [15] | XIE Kai-yun, CAO Kai, WAN Jiang-chun, WANG Yu-xiang, ZHAO Yun, ZHU Jin-zhong. Change in productivity of swards of different forage legume and grass species monocultures and combinations in the semi-arid region of Xinjiang Province [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 29-40. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||