

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 76-86.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021113
刘荣荣1( ), 王平1, 代心灵1, 陈科宇1, 李国梁2, 宛新荣2, 纪宝明1(
), 王平1, 代心灵1, 陈科宇1, 李国梁2, 宛新荣2, 纪宝明1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-24
修回日期:2021-04-19
出版日期:2021-10-19
发布日期:2021-10-19
通讯作者:
纪宝明
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: baomingji@bjfu.edu.cn基金资助:
Rong-rong LIU1( ), Ping WANG1, Xin-ling DAI1, Ke-yu CHEN1, Guo-liang LI2, Xin-rong WAN2, Bao-ming JI1(
), Ping WANG1, Xin-ling DAI1, Ke-yu CHEN1, Guo-liang LI2, Xin-rong WAN2, Bao-ming JI1( )
)
Received:2021-03-24
Revised:2021-04-19
Online:2021-10-19
Published:2021-10-19
Contact:
Bao-ming JI
摘要:
布氏田鼠是内蒙古典型草原的主要啮齿类动物,其活动既可以改变植物群落组成和多样性,又可以改变土壤理化性质,进而潜在影响与绝大多数草原植物共生的重要土壤微生物-丛枝菌根真菌(AMF),但目前关于啮齿动物活动对AMF群落组成和多样性影响的研究鲜有报道。基于此,依托内蒙古自治区锡林浩特市毛登牧场的大型野外布氏田鼠围栏实验平台,选择其中3个田鼠密度处理(低、中、高密度,对应的初始投放布氏田鼠数量分别为12、24和48只·样地-1),利用Illumina Miseq测序技术分析不同密度布氏田鼠处理对AMF群落的影响,采用标准网格交叉法测定根系侵染率和土壤菌丝密度,探究布氏田鼠活动对典型草原AMF群落的影响机制和作用途径。主要结果表明:1)在土壤样品中共鉴定到6科9属的AMF,其中优势属为球囊霉属(Glomus);2)高密度布氏田鼠处理显著降低了植物生物量、植被盖度、群落丰富度和多样性,显著降低土壤水分、pH,显著增加土壤硝态氮含量;显著降低AMF侵染率、菌丝密度、丰富度和多样性;3)相关性分析表明,菌丝密度与植物丰富度、多样性指数、土壤pH和含水量显著正相关,与硝态氮含量显著负相关;侵染率与植物多样性指数、土壤pH和含水量显著正相关;AMF多样性指数与土壤pH和含水量显著正相关,不同操作分类单元(OTU)丰富度与植物多样性指数和pH显著正相关;4)NMDS 和 PerMANOVA 分析显示AMF群落结构在低密度和高密度处理间差异显著,其中土壤NO3-和pH是影响AMF群落组成的主要因子。因此,布氏田鼠密度过高会导致植物群落生物量、多样性以及土壤养分含量下降,同时两者的改变导致了AMF群落多样性显著降低,可能会加速典型草原的退化。
刘荣荣, 王平, 代心灵, 陈科宇, 李国梁, 宛新荣, 纪宝明. 不同密度布氏田鼠对内蒙古典型草原菌根真菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 76-86.
Rong-rong LIU, Ping WANG, Xin-ling DAI, Ke-yu CHEN, Guo-liang LI, Xin-rong WAN, Bao-ming JI. Effects of different densities of Brandt’s voles on communities of mycorrhizal fungal in the typical steppe of Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 76-86.

图1 不同密度布氏田鼠对植物群落生物量和盖度的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of different densities of Brandt’s voles on the biomass and coverage of plant communities
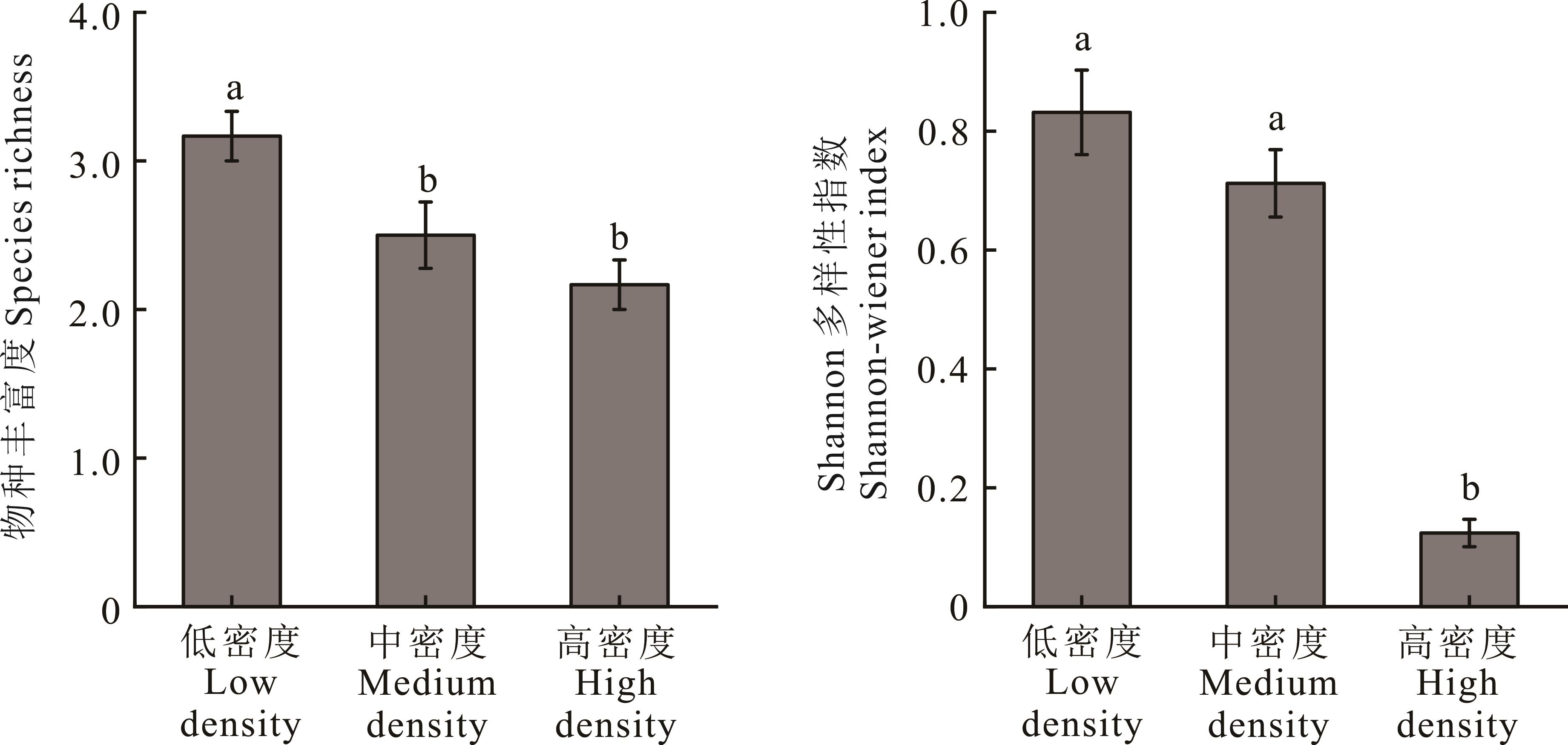
图2 不同密度布氏田鼠对植物群落物种丰富度和香农-威纳指数的影响
Fig.2 Effects of different densities of Brandt’s voles on the plant communities OTU richness and Shannon-wiener index
密度处理 Density treatment | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture (%) | pH | 全氮 TN (g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP (g·kg-1) | 有效磷 AP (mg·kg-1) | 土壤有机质 SOM (g·kg-1) | 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低密度Low density | 8.48±0.39a | 7.48±0.07a | 1.48±0.07a | 0.34±0.01a | 11.46±0.36a | 23.10±0.96a | 6.68±0.17a | 1.31±0.03b |
| 中密度Medium density | 8.74±0.41a | 7.39±0.05a | 1.33±0.05a | 0.33±0.01a | 10.96±0.50a | 19.58±0.60b | 5.27±0.16ab | 1.52±0.18b |
| 高密度High density | 5.87±0.49b | 7.14±0.23b | 1.14±0.02b | 0.27±0.01b | 11.70±0.29a | 17.31±0.27c | 4.17±0.37b | 2.22±0.25a |
表1 不同密度布氏田鼠处理下土壤理化性质
Table 1 Soil characteristics in different densities of Brandt’s voles
密度处理 Density treatment | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture (%) | pH | 全氮 TN (g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP (g·kg-1) | 有效磷 AP (mg·kg-1) | 土壤有机质 SOM (g·kg-1) | 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低密度Low density | 8.48±0.39a | 7.48±0.07a | 1.48±0.07a | 0.34±0.01a | 11.46±0.36a | 23.10±0.96a | 6.68±0.17a | 1.31±0.03b |
| 中密度Medium density | 8.74±0.41a | 7.39±0.05a | 1.33±0.05a | 0.33±0.01a | 10.96±0.50a | 19.58±0.60b | 5.27±0.16ab | 1.52±0.18b |
| 高密度High density | 5.87±0.49b | 7.14±0.23b | 1.14±0.02b | 0.27±0.01b | 11.70±0.29a | 17.31±0.27c | 4.17±0.37b | 2.22±0.25a |
环境因子 Environmental variables | 菌丝密度 Hyphal length density | 菌丝侵染率 Mycorrhizal colonization | OTU丰富度 OTU richness | 香农-威纳指数 Shannon-Wiener index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮Total nitrogen | 0.68** | 0.14 | 0.32 | 0.18 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus | 0.71** | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.39 |
| 酸碱度pH | 0.89** | 0.63** | 0.50* | 0.56* |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture | 0.76** | 0.62** | 0.45 | 0.58* |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 0.64** | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.14 |
| 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen | -0.60** | -0.31 | -0.45 | -0.36 |
| 物种丰富度Species richness | 0.55* | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.03 |
| 物种香农威纳指数Shannon-Wiener index | 0.77** | 0.59* | 0.51* | 0.44 |
表2 菌丝密度、菌丝侵染率、AMF群落多样性与环境因子的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of hyphal length density, mycorrhizal rate, AMF community diversity and environmental variables
环境因子 Environmental variables | 菌丝密度 Hyphal length density | 菌丝侵染率 Mycorrhizal colonization | OTU丰富度 OTU richness | 香农-威纳指数 Shannon-Wiener index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮Total nitrogen | 0.68** | 0.14 | 0.32 | 0.18 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus | 0.71** | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.39 |
| 酸碱度pH | 0.89** | 0.63** | 0.50* | 0.56* |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture | 0.76** | 0.62** | 0.45 | 0.58* |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 0.64** | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.14 |
| 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen | -0.60** | -0.31 | -0.45 | -0.36 |
| 物种丰富度Species richness | 0.55* | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.03 |
| 物种香农威纳指数Shannon-Wiener index | 0.77** | 0.59* | 0.51* | 0.44 |
| 1 | Lou P Q, Fu B L, Liu H X, et al. Dynamic evaluation of grassland ecosystem services in Xilingol League. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(11): 3837-3849. |
| 娄佩卿, 付波霖, 刘海新, 等. 锡林郭勒盟草地生态系统服务功能价值动态估算. 生态学报, 2019, 39(11): 3837-3849. | |
| 2 | Jiang Y E, Wang D, Yi J, et al. Study on the habitat characteristics of Brandt’s vole. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2012, 20(1): 179-182. |
| 蒋永恩, 王登, 易津, 等. 布氏田鼠栖息地特征的研究. 草地学报, 2012, 20(1): 179-182. | |
| 3 | Zhong W Q. Role of rodent in grassland ecosystem and scientific management. Bulletin of Biology, 2008(1): 1-3. |
| 钟文勤. 啮齿动物在草原生态系统中的作用与科学管理. 生物学通报, 2008(1): 1-3. | |
| 4 | Sun F, Chen W Y, Liu L, et al. Effects of plateau pika activities on seasonal plant biomass and soil properties in the alpine meadow ecosystems of the Tibetan Plateau. Grassland Science, 2015, 61(4): 195-203. |
| 5 | Pang X P, Guo Z G. Effects of plateau pika disturbance levels on the plant diversity and biomass of an alpine meadow. Grassland Science, 2018, 64(3): 159-166. |
| 6 | Qin Y, Chen J J, Yi S H. Plateau pikas burrowing activity accelerates ecosystem carbon emission from alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 84: 287-291. |
| 7 | Chen J J, Yi S H, Qin Y. The contribution of plateau pika disturbance and erosion on patchy alpine grassland soil on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Implications for grassland restoration. Geoderma, 2017, 297: 1-9. |
| 8 | Liu Y S, Fan J W, Harris W, et al. Effects of plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae) on net ecosystem carbon exchange of grassland in the Three Rivers Headwaters region, Qinghai-Tibet, China. Plant and Soil, 2013, 366(1): 491-504. |
| 9 | Yu H L, Fan J W, Li Y Z, et al. Effects of Myospalax baileyi disturbance on plant community at alpine meadow in Three Rivers Headwater region, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(6): 1902-1910. |
| 于海玲, 樊江文, 李愈哲, 等. 高原鼢鼠干扰对三江源区高寒草甸群落特征的影响. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(6): 1902-1910. | |
| 10 | Liu Y D, Fan J W, Shi Z J, et al. Relationships between plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae) densities and biomass and biodiversity indices of alpine meadow steppe on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecological Engineering, 2017, 102: 509-518. |
| 11 | Lindtner P, Ujházy K, Svitok M, et al. The European ground squirrel increases diversity and structural complexity of grasslands in the Western Carpathians. Mammal Research, 2018, 63(2): 223-229. |
| 12 | Pang X P, Wang Q, Guo Z G. The impact of the plateau pika on the relationship between plant aboveground biomass and plant species richness. Land Degradation & Development, 2021, 32(3): 1205-1212. |
| 13 | Ding J X, Chen K L, Cui H, et al. Disturbance of Ochotona curzoniae on soil respiration in alpine marsh meadow plateau. Ecological Science, 2019, 38(6): 1-7. |
| 丁俊霞, 陈克龙, 崔航, 等. 高原鼠兔对高寒沼泽草甸土壤呼吸的干扰. 生态科学, 2019, 38(6): 1-7. | |
| 14 | Hagenah N, Bennett N C. Mole rats act as ecosystem engineers within a biodiversity hotspot, the Cape Fynbos. Journal of Zoology, 2013, 289(1): 19-26. |
| 15 | Galiano D, Kubiak B B, Overbeck G E, et al. Effects of rodents on plant cover, soil hardness, and soil nutrient content: A case study on tuco-tucos (Ctenomys minutus). Acta Theriologica, 2014, 59(4): 583-587. |
| 16 | Yu C, Zhang J, Pang X P, et al. Soil disturbance and disturbance intensity: Response of soil nutrient concentrations of alpine meadow to plateau pika bioturbation in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Geoderma, 2017, 307: 98-106. |
| 17 | Kivlin S N, Hawkes C V. Differentiating between effects of invasion and diversity: Impacts of aboveground plant communities on belowground fungal communities. New Phytologist, 2011, 189(2): 526-535. |
| 18 | Ma J G, Hou F J, Saman. Effects of toxic plants on soil physicochemical properties and soil microbial abundance in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(12): 3033-3040. |
| 马建国, 侯扶江, Saman. 青藏高原高寒草甸有毒植物对土壤理化性质和土壤微生物丰度的影响. 草业科学, 2019, 36(12): 3033-3040. | |
| 19 | Khalvati M A, Hu Y, Mozafar A, et al. Quantification of water uptake by arbuscular mycorrhizal hyphae and its significance for leaf growth, water relations, and gas exchange of barley subjected to drought stress. Plant Biology, 2005, 7(6): 706-712. |
| 20 | Bowles T M, Jackson L E, Cavagnaro T R. Mycorrhizal fungi enhance plant nutrient acquisition and modulate nitrogen loss with variable water regimes. Global Change Biology, 2018, 24(1): 171-182. |
| 21 | Shi W Q, Ding X D, Zhang S R. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on Leymus chinensis growth and soil carbon. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2011, 31(2): 357-362. |
| 石伟琦, 丁效东, 张士荣. 丛枝菌根真菌对羊草生物量和氮磷吸收及土壤碳的影响. 西北植物学报, 2011, 31(2): 357-362. | |
| 22 | Mardhiah U, Caruso T, Gurnell A, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal hyphae reduce soil erosion by surface water flow in a greenhouse experiment. Applied Soil Ecology, 2016, 99: 137-140. |
| 23 | Li Y M, Jiang L L, Lv W W, et al. Fungal pathogens pose a potential threat to animal and plant health in desertified and pika-burrowed alpine meadows on the Tibetan Plateau. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2019, 65(5): 365-376. |
| 24 | Chen Y L, Zhang X, Ye J S, et al. Six-year fertilization modifies the biodiversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a temperate steppe in Inner Mongolia. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 69: 371-381. |
| 25 | Landis F C, Gargas A, Givnish T J. Relationships among arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, vascular plants and environmental conditions in oak savannas. New Phytologist, 2004, 164(3): 493-504. |
| 26 | Zhong W, Wang G, Zhou Q, et al. Effects of winter food availability on the abundance of Daurian pikas (Ochotona dauurica) in Inner Mongolian grasslands. Journal of Arid Environments, 2008, 72(7): 1383-1387. |
| 27 | Dai X L, Wang P, Liu R R, et al. Effects of extreme drought on community composition of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the typical grasslands in Inner Mongolia during different growing seasons. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(8): 1440-1447. |
| 代心灵, 王平, 刘荣荣, 等. 极端干旱条件对不同生长季内蒙古典型草原丛枝菌根真菌群落组成的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(8): 1440-1447. | |
| 28 | Lu R K. Methods of agricultural chemical analysis of soil. Beijing: China Agriculture Science and Technique Press, 2000: 12-193. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000: 12-193. | |
| 29 | Nelson D W, Sommers L E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter//Sparks D L, Page A L, Helmke P A, et al. Methods of soil analysis. Part 3: Chemical methods. Madison, Wisconsin, USA: Soil Science Society of America, 1996: 961-1010. |
| 30 | Bremner J M, Mulvaney C S. Nitrogen-total//Page A L, Miller R H, Keeney D R, et al. Methods of soil analysis. Part 2: Chemical and microbiological properties (2nd Edition). Madison: American Society of Agronomy, 1982: 595-624. |
| 31 | Olsen S R. Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. United States Department of Agriculture, 1954, 939: 1-19. |
| 32 | Hautier Y, Isbell F, Borer E T, et al. Local loss and spatial homogenization of plant diversity reduce ecosystem multifunctionality. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2018, 2(1): 50-56. |
| 33 | Sun M F. Research on investigation and evaluation of plant community landscape in Shennong City, Zhuzhou. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2017. |
| 孙美芳. 株洲神农城植物群落景观调查与评价研究. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2017. | |
| 34 | Yang Z Y, Jiang X L. The harm of plateau pika on grassland vegetation and its control threshold value. Pratacultural Science, 2002(4): 63-65 |
| 杨振宇, 江小蕾. 高原鼠兔对草地植被的危害及防治阈值研究. 草业科学, 2002(4): 63-65 | |
| 35 | Zhang X L, Li G. Effects of rodents activities on grazing land and ecosystem in alpine meadow. Pratacultural Science, 2015, 32(5): 816-822. |
| 张兴禄, 李广. 高原鼠兔和高原鼢鼠在高寒草甸生态系统的作用. 草业科学, 2015, 32(5): 816-822. | |
| 36 | Semenov Y, Ramousse R, Berre M L, et al. Impact of the black-capped marmot (Marmota camtschatica bungei) on floristic diversity of arctic tundra in Northern Siberia. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research, 2001, 33(2): 204-210. |
| 37 | Root M, Ebensperger L A. Meta-analysis of the effects of small mammal disturbances on species diversity, richness and plant biomass. Austral Ecology, 2013, 38(3): 289-299. |
| 38 | Sun F D, Long R J, Lu C X, et al. Effects of rodent activities on primary productivity and soil physical characteristics in alpine meadow. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 16: 225-229. |
| 39 | Zhou W P, Xiang D, Hu Y J, et al. Influences of long-term enclosure on the restoration of plant and AM fungal communities on grassland under different grazing intensities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(11): 3383-3393. |
| 周文萍, 向丹, 胡亚军, 等. 长期围封对不同放牧强度下草地植物和AM真菌群落恢复的影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(11): 3383-3393. | |
| 40 | Li C C, Zhou Y X, Gu Q, et al. The species diversity and community assembly of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in typical alpine grassland in Sanjiangyuan Region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 46-58. |
| 李聪聪, 周亚星, 谷强, 等. 三江源区典型高寒草地丛枝菌根真菌多样性及构建机制. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 46-58. | |
| 41 | Hiiesalu I, Paertel M, Davison J, et al. Species richness of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Associations with grassland plant richness and biomass. New Phytologist, 2014, 203(1): 233-244. |
| 42 | Wang Z J, Ma K, Cui H Z, et al. Correlations between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and distribution of main grassland types in Ningxia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 150-160. |
| 王占军, 马琨, 崔慧珍, 等. 土壤丛枝菌根真菌与宁夏主要草原类型植被群落分布间的相互关系研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 150-160. | |
| 43 | Lange M, Eisenhauer N M, Eisenhauer N, et al. Plant diversity increases soil microbial activity and soil carbon storage. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 1-8. |
| 44 | Ba L, Ning J X, Wang D L, et al. The relationship between the diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and grazing in a meadow steppe. Plant and Soil, 2012, 352(1): 143-156. |
| 45 | Cavagnaro R A, Pero E, Dudinszky N, et al. Under pressure from above: Overgrazing decreases mycorrhizal colonization of both preferred and unpreferred grasses in the Patagonian steppe. Fungal Ecology, 2019(40): 92-97. |
| 46 | Zi H B, A D L J, Ma L, et al. Changes of ratio of root to soil and soil nutrient content at different grassland types alpine meadow. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 29(12): 2916-2921. |
| 字洪标, 阿的鲁骥, 马力, 等. 高寒草甸不同类型草地群落根土比、土壤养分变化. 西南农业学报, 2016, 29(12): 2916-2921. | |
| 47 | Tian F, Cheng Y X, Zhou G L, et al. Relations of density of pika burrows with plant community structure and soil in alpine meadows on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(4): 1094-1104. |
| 田富, 程云湘, 周国利, 等. 高原鼠兔洞穴密度与高寒草甸植物群落结构以及土壤因子的关系. 草业科学, 2019, 36(4): 1094-1104. | |
| 48 | Lara N, Sassi P, Borghi C E. Effect of herbivory and disturbances by tuco-tucos (Ctenomys mendocinus) on a plant community in the southern Puna Desert. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research, 2007, 39(1): 110-116. |
| 49 | Malizia A I, Kittlein M J, Busch C. Influence of the subterranean herbivorous rodent Ctenomys mendocinus on vegetation and soil. Zeitschrift fur Saugetierkunde, 2000, 65(3): 172-182. |
| 50 | Canals R M, Herman D J, Firestone M K. How disturbance by fossorial mammals alters N cycling in a California annual grassland. Ecology, 2003, 84(4): 875-881. |
| 51 | Zhang Y, Dong S K, Gao Q Z, et al. Responses of alpine vegetation and soils to the disturbance of plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae) at burrow level on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 88: 232-236. |
| 52 | Luo H Z, Liu W, Yang N, et al. Disturbing effects of plateau zokor (Myospalax baileyi) on soil properties and plant biomass in zoige plateau marshes. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(3): 626-630. |
| 罗华智, 刘伟, 杨楠, 等. 高原鼢鼠对若尔盖高原湿地草原土壤性质和植物生物量的扰动效应. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(3): 626-630. | |
| 53 | Liu B Y, Wang Y, Liu M, et al. Response of vegetation community and soil properties of grassland to different density gradients of Ochotona curzoniae in the Sanjiangyuan Region. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(4): 1105-1116. |
| 刘碧颖, 王毅, 刘苗, 等. 三江源草地植被群落与土壤性质对不同鼠兔密度的响应. 草业科学, 2019, 36(4): 1105-1116. | |
| 54 | Zhu J X, He N P, Wang Q F, et al. The composition, spatial patterns, and influencing factors of atmospheric wet nitrogen deposition in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 511: 777-785. |
| 55 | Yang Y H, Ji C J, Ma W H, et al. Significant soil acidification across Northern China’s grasslands during 1980s-2000s. Global Change Biology, 2012, 18(7): 2292-2300. |
| 56 | Li Q Q, Li A W, Yu X L, et al. Soil acidification of the soil profile across Chengdu Plain of China from the 1980s to 2010s. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 698: 134320. |
| 57 | Lu M, Yang Y H, Luo Y Q, et al. Responses of ecosystem nitrogen cycle to nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. New Phytologist, 2011, 189(4): 1040-1050. |
| 58 | Ngwene B, George E, Claussen W, et al. Phosphorus uptake by cowpea plants from sparingly available or soluble sources as affected by nitrogen form and arbuscular-mycorrhiza-fungal inoculation. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2010, 173(3): 353-359. |
| 59 | Li X J, Xu T L, Chen B D, et al. Diversity and community structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in desert and steppe ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(10): 2734-2743. |
| 李雪静, 徐天乐, 陈保冬, 等. 荒漠和草原生态系统丛枝菌根真菌多样性和群落结构. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(10): 2734-2743. | |
| 60 | Xiang D, Xu T L, Li H, et al. Ecological distribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and the influencing factors. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 1-10. |
| 向丹, 徐天乐, 李欢, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌的生态分布及其影响因子研究进展. 生态学报, 2017, 37(11): 1-10. | |
| 61 | Xiang D, Verbruggen E, Hu Y, et al. Land use influences arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in the farming-pastoral ecotone of Northern China. New Phytologist, 2014, 204(4): 968-978. |
| 62 | Uhlmann E, Görke C, Petersen A, et al. Comparison of species diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in winter-rainfall areas of South Africa and summer-rainfall areas of Namibia. Mycological Progress, 2004, 3(4): 267-274. |
| 63 | Martínez-García L B, De Dios J, Pugnaire F I. Impacts of changing rainfall patterns on mycorrhizal status of a shrub from arid environments. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2012, 50: 64-67. |
| 64 | Deveautour C, Donn S, Power S A, et al. Experimentally altered rainfall regimes and host root traits affect grassland arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities. Molecular Ecology, 2018, 27(8): 2152-2163. |
| 65 | Xiang D, Veresoglou S D, Rillig M C, et al. Relative importance of individual climatic drivers shaping arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities. Soil Microbiology, 2016, 72(2): 418-427. |
| 66 | Seck-Mbengue M F, Muller A, Ngwene B, et al. Transport of nitrogen and zinc to rhodes grass by arbuscular mycorrhiza and roots as affected by different nitrogen sources (NH4+-N and NO3--N). Symbiosis, 2017, 73(3): 191-200. |
| 67 | Bai E, Li S, Xu W, et al. A meta-analysis of experimental warming effects on terrestrial nitrogen pools and dynamics. New Phytologist, 2013, 199(2): 441-451. |
| [1] | 张静静, 刘尊驰, 鄢创, 王云霞, 刘凯, 时新荣, 袁志友. 土壤pH值变化对3种草原类型土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 69-81. |
| [2] | 李聪聪, 周亚星, 谷强, 杨明新, 朱传鲁, 彭子原, 薛凯, 赵新全, 王艳芬, 纪宝明, 张静. 三江源区典型高寒草地丛枝菌根真菌多样性及构建机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 46-58. |
| [3] | 邢易梅, 蕫理, 战力峰, 才华, 杨圣秋, 孙娜. 混合接种摩西球囊霉和根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿耐碱能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 136-145. |
| [4] | 贾红梅, 方千, 张秫华, 严铸云, 柳敏. AM真菌对丹参生长及根际土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 83-92. |
| [5] | 赵昕, 吴子龙, 张浩, 杨旭钊, 韩超, 高杰. 峰峰矿区煤矸石山周边植物丛枝菌根真菌的侵染及Cd含量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 78-87. |
| [6] | 王英逵, 杨玉荣, 王德利. 盐碱胁迫下AMF对羊草的离子吸收和分配作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 95-104. |
| [7] | 高亚敏, 罗慧琴, 姚拓, 张建贵, 李海云, 杨琰珊, 兰晓君. 高寒退化草地委陵菜根围丛枝菌根菌(AMF)分离鉴定及促生效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 145-154. |
| [8] | 李文彬, 宁楚涵, 李伟, 李峰, 郭绍霞. 菲和芘胁迫下AMF和PGPR对高羊茅生理生态的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 84-94. |
| [9] | 宿婷婷, 马红彬, 周瑶, 贾希洋, 张蕊, 张双乔, 胡艳莉. 黄土丘陵典型草原土壤理化性质对生态恢复措施的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 34-46. |
| [10] | 聂明鹤, 沈艳, 饶丽仙. 宁夏典型草原区退耕草地群落演替序列与环境解释[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 11-20. |
| [11] | 李继伟, 悦飞雪, 王艳芳, 张亚梅, 倪瑞景, 王发园, 付国占, 刘领. 施用生物炭和AM真菌对镉胁迫下玉米生长和生理生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 120-129. |
| [12] | 贾希洋, 马红彬, 周瑶, 张蕊, 宿婷婷, 张双乔, 张俊. 不同生态恢复措施下宁夏黄土丘陵区典型草原植物群落数量分类和演替[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 15-25. |
| [13] | 亓琳, 杨莹博, 张博, 赵威, 王晓凌, 刘玉华. 丛枝菌根真菌强化高粱幼苗修复锶污染土壤的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 103-112. |
| [14] | 李文彬, 宁楚涵, 徐孟, 刘润进, 郭绍霞. 丛枝菌根真菌和高羊茅对压实土壤的改良效应[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 131-141. |
| [15] | 张蕊, 马红彬, 贾希洋, 周瑶, 宿婷婷, 蔡育蓉, 周静静. 不同生态恢复措施下宁夏黄土丘陵区典型草原土壤种子库特征[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 32-41. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||