

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 97-109.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022198
收稿日期:2022-05-05
修回日期:2022-07-28
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2022-12-01
通讯作者:
王迎春
作者简介:E-mail: ycwang@imu.edu.cn基金资助:
Jie ZHANG( ), Kai CHENG, Ying-chun WANG(
), Kai CHENG, Ying-chun WANG( )
)
Received:2022-05-05
Revised:2022-07-28
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2022-12-01
Contact:
Ying-chun WANG
摘要:
植物受到逆境刺激后,钙离子结合蛋白能够感知钙信号并将其解码,激活下游靶蛋白,从而引发胁迫应答反应,钙调蛋白激酶在其中发挥了重要作用。长叶红砂为东阿拉善-西鄂尔多斯特有的珍稀泌盐植物,对干旱、盐碱等环境胁迫具有极强的适应性。本研究基于转录组数据,克隆了长叶红砂钙调蛋白激酶RtCDPK16的开放阅读框(open reading frame, ORF),氨基酸序列比对和进化分析显示,其与拟南芥的同源性为78.46%,与葡萄VvCDPK16同源性最高(80.97%)。基因表达特性分析显示,RtCDPK16在根茎叶中均表达,且在根中表达量最高,同时其表达水平可被氯化钠(NaCl)/聚乙二醇(polyethylene glycol, PEG)/冷胁迫(cold stress, cold)/脱落酸(abscisic acid, ABA)等多种环境胁迫和氯化钙(calcium chloride, CaCl2)显著诱导。构建植物表达载体并转化拟南芥,对野生型拟南芥(WT)和过表达拟南芥(OE)株系进行干旱、盐和脱落酸胁迫,发现胁迫处理下OE株系的根长、鲜重和叶绿素含量等表型指标均显著高于WT,表明RtCDPK16的超表达使转基因株系获得了更强的胁迫耐受性;生理生化指标检测显示,胁迫处理下各株系中超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase, SOD)、过氧化物酶(peroxidase, POD)和过氧化氢酶(catalase, CAT)等抗氧化酶活性及脯氨酸(proline, Pro)、可溶性糖(soluble sugar, SS)等渗透调节物质的含量均被显著诱导,且超表达株系显著高于WT,而过氧化氢(hydrogen peroxide, H2O2)/超氧阴离子(superoxide anion, O2-)的积累量显著低于WT;实时荧光定量(quantitativereal-time, qRT-PCR)检测发现,胁迫条件下OE株系的相关抗氧化酶基因、ABA合成和信号途径关键元件基因及脯氨酸合成基因均被显著诱导。以上结果表明,RtCDPK16在拟南芥中的超表达通过调控转基因植物中抗氧化和渗透调节系统相关基因的表达和酶活性,促进转基因植物的渗透平衡和活性氧(reactive oxygen species, ROS)稳态的维持,进而提高转基因植物的胁迫耐受性,这一过程可能是通过依赖于ABA信号的途径实现的。
张洁, 程凯, 王迎春. 长叶红砂钙依赖蛋白激酶RtCDPK16的非生物胁迫应答分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 97-109.
Jie ZHANG, Kai CHENG, Ying-chun WANG. Analysis of the calcium-dependent protein kinase RtCDPK16 response to abiotic stress in Reaumuria trigyna[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 97-109.
| 引物Primer | 上游引物序列Forward primer sequences (F) | 下游引物序列Reverse primer sequences (R) |
|---|---|---|
| RtCDPK16 | CGCTCTAGAATGGGTTCTTGTTTCTC | CGCGAGCTCTCACAGCTTACGTGAA |
| RtCDPK16-Q | GTGGATGCTCAAGCGAGAAGTC | TCCAGCAATTCACCGCCTTCAC |
| RtActin-Q | CTGGATTCTCCTGATGGTGTGTCT | GAACCACCGATCCAGACTCGATAC |
| RtCDPK16-1300 | CGCGAGCTCATGGGTTCTTGTTT | CGCTCTAGACAGCTTACGTGAAG |
| AtActin | CTGGATTCTGGTGATGGTGTGTCT | GAACCACCGATCCAGACACTGTAC |
| AtPOD1 | AAAGCGAACATTTTACTCTGGG | CAACAAGTCAATCCTCTAGG |
| AtSOD1 | AGGAAACATCACTGTTGGAGAT | GAGTTTGTGATCGCAGAGAGGAA |
| AtCAT1 | TCCTGTTATCGTTCGTTTCTCA | CAAAGTTCCCCTCTCTGGTGTA |
| AtAPX1 | AAATACGTCCCTGATGAAGATG | CGAGCTACGATCGCACACAG |
| AtP5CS1 | GCGCATAGTTTCTGATGCAA | TGCAACTTCGTGATCCTCTG |
| AtRD29A | TTCTGTAAGGACGACGTTTACA | CGTACTCGTTACATCCTCTGTT |
| AtDREB2A | AACCTGTCAGAACAACAGCAGG | TTAAGCCTGCAAACACATCGTCGC |
| AtRD22 | GATTTGTCTATGCACTGCTCTG | TGGAAGCTTTCTGTTACAAACG |
| AtABF4 | AACAACTTAGGAGGTGGTGGTC | CTTCAGGAGTTCATCCATGTTC |
| AtSnRK2.2 | ATATGCCATCGGGATCTGAA | TTGGTTGGGAATGAAGAACAG |
| AtSnRK2.3 | GTTGGATGGAAGTCCTGCTC | TGCCATCATATTCCTGACGA |
| AtNCED3 | GATGAATTTGTTACTGAGAGCG | AACACTAGGATCAGCCGTTTTA |
表1 RT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 RT-PCR primer sequences (5′-3′)
| 引物Primer | 上游引物序列Forward primer sequences (F) | 下游引物序列Reverse primer sequences (R) |
|---|---|---|
| RtCDPK16 | CGCTCTAGAATGGGTTCTTGTTTCTC | CGCGAGCTCTCACAGCTTACGTGAA |
| RtCDPK16-Q | GTGGATGCTCAAGCGAGAAGTC | TCCAGCAATTCACCGCCTTCAC |
| RtActin-Q | CTGGATTCTCCTGATGGTGTGTCT | GAACCACCGATCCAGACTCGATAC |
| RtCDPK16-1300 | CGCGAGCTCATGGGTTCTTGTTT | CGCTCTAGACAGCTTACGTGAAG |
| AtActin | CTGGATTCTGGTGATGGTGTGTCT | GAACCACCGATCCAGACACTGTAC |
| AtPOD1 | AAAGCGAACATTTTACTCTGGG | CAACAAGTCAATCCTCTAGG |
| AtSOD1 | AGGAAACATCACTGTTGGAGAT | GAGTTTGTGATCGCAGAGAGGAA |
| AtCAT1 | TCCTGTTATCGTTCGTTTCTCA | CAAAGTTCCCCTCTCTGGTGTA |
| AtAPX1 | AAATACGTCCCTGATGAAGATG | CGAGCTACGATCGCACACAG |
| AtP5CS1 | GCGCATAGTTTCTGATGCAA | TGCAACTTCGTGATCCTCTG |
| AtRD29A | TTCTGTAAGGACGACGTTTACA | CGTACTCGTTACATCCTCTGTT |
| AtDREB2A | AACCTGTCAGAACAACAGCAGG | TTAAGCCTGCAAACACATCGTCGC |
| AtRD22 | GATTTGTCTATGCACTGCTCTG | TGGAAGCTTTCTGTTACAAACG |
| AtABF4 | AACAACTTAGGAGGTGGTGGTC | CTTCAGGAGTTCATCCATGTTC |
| AtSnRK2.2 | ATATGCCATCGGGATCTGAA | TTGGTTGGGAATGAAGAACAG |
| AtSnRK2.3 | GTTGGATGGAAGTCCTGCTC | TGCCATCATATTCCTGACGA |
| AtNCED3 | GATGAATTTGTTACTGAGAGCG | AACACTAGGATCAGCCGTTTTA |

图1 RtCDPK16基因氨基酸序列比对和进化分析*: 代表长叶红砂中的RtCDPK16这个基因 Represents the gene RtCDPK16 in R. trigyna
Fig.1 Amino acid sequence alignment and evolution analysis of RtCDPK16
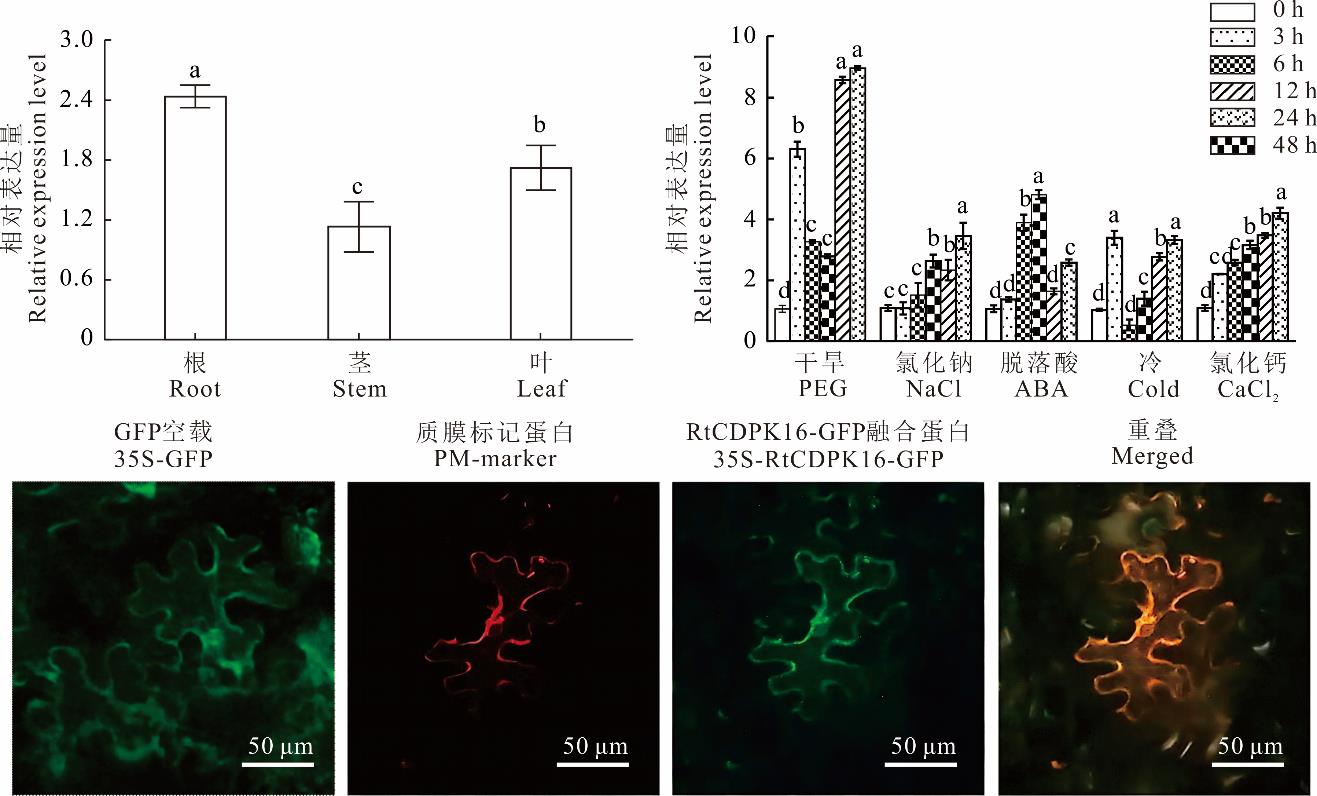
图2 RtCDPK16的表达特性与亚细胞定位分析不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between the different treatments at the 0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.2 RtCDPK16 specific expression and subcellular localization analysis
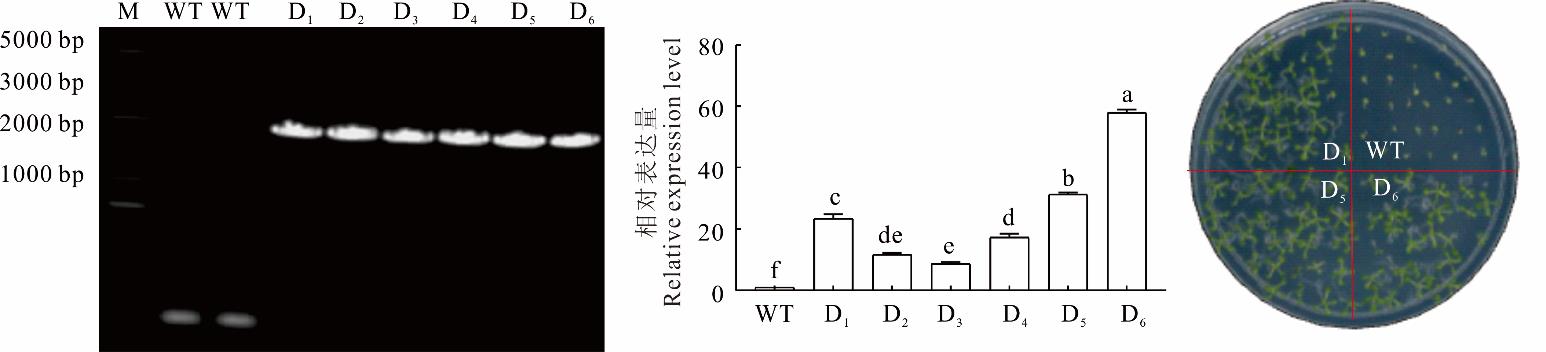
图3 RtCDPK16转基因拟南芥的鉴定M: 标记;WT: 野生型;D1~D6: RtCDPK16的6个过表达株系。下同。M: Marker;WT: Wild-type; D1-D6: Six overexpressing lines of RtCDPK16. The same below.
Fig.3 Identification of RtCDPK16 transgenic A. thaliana
| 1 | Tang Y C. Physiological response of exogenous Ca2+ to Nitraria tangutorum under drought stress, cloning and functional analysis of NtCDPK1 and NtCIPK5. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia University, 2019. |
| 汤宇晨. 干旱胁迫下唐古特白刺对外源Ca2+的生理响应及NtCDPK1,NtCIPK5的克隆与功能分析. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2019. | |
| 2 | Perochon A, Aldon D, Galaud J P, et al. Calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant calcium signaling. Biochimie, 2011, 93(12): 2048-2053. |
| 3 | Liese A, Romeis T. Biochemical regulation of in vivo function of plant calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPK). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 2013, 1833(7): 1582-1589. |
| 4 | Jiang S S, Zhang D, Kong X P, et al. Research progress of structural characteristics and functions of calcium-dependent protein kinases in plants. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2013, 23(6): 18-25. |
| 姜珊珊, 张丹, 孔祥培, 等. 植物中的钙依赖蛋白激酶(CDPK)的结构特征和功能研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2013, 23(6):18-25. | |
| 5 | Batistič O, Kudla J. Analysis of calcium signaling pathways in plants. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2012, 1820(8): 1283-1293. |
| 6 | Wang W H, Yi X Q, Han A D, et al. Calcium-sensing receptor regulates stomatal closure through hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide in response to extracellular calcium in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(2): 177-190. |
| 7 | Zhu J K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Plant Cell, 2016, 167(2): 313-324. |
| 8 | Das R, Pandey G K. Expressional analysis and role of calcium regulated kinases in abiotic stress signaling. Current Genomics, 2010(11): 2-13. |
| 9 | Jaworski K, Pawełek A, Kopcewicz J,et al. The calcium-dependent protein kinase (PnCDPK1) is involved in Pharbitis nil flowering. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2012, 169(16): 1578-1585. |
| 10 | Matschi S, Werner S, Schulze W X, et al. Function of calcium dependent protein kinase CPK28 of Arabidopsis thaliana in plant stem elongation and vascular development. The Plant Journal, 2013, 73(6): 883-896. |
| 11 | Zhang J. Cloning and functional analysis of RtCML42 and RtCDPK16 in rare salt-secreting plant Reaumuria trigyna. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2020. |
| 张洁. 珍稀泌盐植物长叶红砂RtCML42 和RtCDPK16的克隆与功能分析. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2020. | |
| 12 | Zhang K, Han Y T, Zhao F L, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CDPK gene family in grape, Vitis spp. BMC Plant Biology, 2015, 15(1): 164. |
| 13 | Hubbard K E, Siegel R S, Valerio G, et al. Abscisic acid and CO2 signalling via calcium sensitivity priming in guard cells, new CDPK mutant phenotypes and a method for improved resolution of stomatal stimulus-response analyses. Annals of Botany, 2012, 109(1): 5-17. |
| 14 | Ren X L, Qi G N, Feng H Q, et al. Calcineurin B-like protein CBL10 directly interacts with AKT1 and modulates K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 2013, 74(2): 258-266. |
| 15 | McCormack E, Braam J. Calmodulins and related potential calcium sensors of Arabidopsis. New Phytologist, 2010, 159(3): 585-598. |
| 16 | Boudsocq M, Sheen J. CDPKs in immune and stress signaling. Trends in Plant Science, 2013, 18(1): 30-40. |
| 17 | Asai S, Ichikawa T, Nomura H, et al. The variable domain of a plant calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK) confers subcellular localization and substrate recognition for NADPH oxidase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2013, 288(20): 14332-14340. |
| 18 | Knight H. Calcium signaling during abiotic stress in plants. International Review of Cytology, 2000, 195(3): 269-324. |
| 19 | Weckwerth P, Ehlert B, Romeis T. ZmCPK1, a calcium-independent kinase member of the Zea mays CDPK gene family, functions as a negative regulator in cold stress signalling. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2015, 38(3): 544-558. |
| 20 | Jiang S, Zhang D, Wang L, et al. A maize calcium-dependent protein kinase gene, ZmCPK4, positively regulated abscisic acid signaling and enhanced drought stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2013, 71(5): 112-120. |
| 21 | Asano T, Hayashi N, Kikuchi S, et al. CDPK-mediated abiotic stress signaling. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2012, 7(7): 817-821. |
| 22 | Mehlmer N, Wurzinger B, Stael S, et al. The Ca2+-dependent protein kinase CPK3 is required for MAPK-independent salt-stress acclimation in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 2010, 23(1): 484-498. |
| 23 | Xu J, Tian Y S, Peng R H, et al. AtCPK6, a functionally redundant and positive regulator involved in salt/drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Planta, 2010, 231(6): 1251-1260. |
| 24 | Zou J J, Wei F J, Wang C, et al. Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK10 functions in abscisic acid- and Ca2+- mediated stomatal regulation in response to drought stress. Plant Physiology, 2010, 154(3): 1232-1243. |
| 25 | Franz S, Ehlert B, Liese A, et al . Calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK21 functions in abiotic stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular Plant, 2011, 4(1): 83-96. |
| 26 | Li N, Wang X, Ma B, et al. Expression of a Na+/H+ antiporter RtNHX1 from a recretohalophyte Reaumuria trigyna improved salt tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2017, 218(4): 109-120. |
| 27 | Li N, Wang X, Ma B, et al. A leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase gene (RtLDOX2) from the feral forage plant Reaumuria trigyna promotes the accumulation of flavonoids and improves tolerance to abiotic stresses. Journal of Plant Research, 2021, 134(5): 1121-1138. |
| 28 | Ma B, Liu X, Guo S, et al. RtNAC100 involved in the regulation of ROS, Na+ accumulation and induced salt-related PCD through MeJA signal pathways in recretohalophyte Reaumuria trigyna. Plant Science, 2021, 310(4): 110976-110985. |
| 29 | Choi W G, Toyota M, Kim S H, et al. Salt stress-induced Ca2+ waves are associated with rapid, long-distance root-to-shoot signaling in plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014, 111(17): 6497-6502. |
| 30 | Zuo R, Hu R, Chai G, et al. Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression analysis of CDPK and its closely related gene families in poplar (Populus trichocarpa). Molecular Biology Reports, 2013, 40(3): 2645-2662. |
| 31 | Dubrovina A S, Kiselev K V, Khristenko V S, et al. VaCPK20, a calcium-dependent protein kinase gene of wild grapevine Vitis amurensis Rupr., mediates cold and drought stress tolerance. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2015, 185(18): 1-12. |
| 32 | Apel K, Hirt H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2004, 55(3): 373-399. |
| 33 | Foyer C H, Noctor G. Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: A metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. The Plant Cell, 2005, 17(3): 1866-1875. |
| 34 | Torres M A, Dangl J L. Functions of the respiratory burst oxidase in biotic interactions, abiotic stress and development. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2005, 8(4): 397-403. |
| 35 | Fantino E, Segretin M E, Santin F, et al. Analysis of the potato calcium-dependent protein kinase family and characterization of StCDPK7, a member induced upon infection with Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell Reports, 2017, 36(7): 1137-1157. |
| 36 | Asano T, Hayashi N, Kobayashi M, et al. A rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCPK12 oppositely modulates salt-stress tolerance and blast disease resistance. The Plant Journal, 2012, 69(1): 26-36. |
| 37 | Dubiella U, Seybold H, Durian G, et al. Calcium-dependent protein kinase/NADPH oxidase activation circuit is required for rapid defense signal propagation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(21): 8744-8749. |
| 38 | Wan B, Lin Y, Mou T. Expression of rice Ca2+-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) genes under different environmental stresses. FEBS Letters, 2007, 581(6): 1179-1189. |
| 39 | Pandey G K, Kanwar P, Singh A, et al. Calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase CIPK21 regulates osmotic and salt stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 2015, 83(5): 25-28. |
| 40 | Cutler S R, Rodriguez P L, Finkelstein R R, et al. Abscisic acid: Emergence of a core signaling network. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61(5): 651-679. |
| 41 | Zhu S Y, Yu X C. Two calcium-dependent protein kinases, CPK4 and CPK11, regulate abscisic acid signal transduction in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 2007, 19(30): 3019-3036. |
| 42 | Choi H I, Park H J, Park J H, et al. Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase AtCPK32 interacts with ABF4, a transcriptional regulator of abscisic acid-responsive gene expression, and modulates its activity. Plant Physiology, 2005, 13(9): 50-61. |
| [1] | 陈卫东, 张玉霞, 张庆昕, 刘庭玉, 王显国, 王东儒. 末次刈割时间对苜蓿根颈抗氧化系统及抗寒性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 129-138. |
| [2] | 田骄阳, 王秋霞, 郑淑文, 刘文献. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿CPP基因家族的鉴定及表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 111-121. |
| [3] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 孙晓梵. 两类新疆狗牙根抗旱基因型抗氧化酶保护系统及其基因表达差异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 122-132. |
| [4] | 孙晓梵, 张一龙, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同施氮量对干旱下狗牙根抗氧化酶活性及渗透调节物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 69-78. |
| [5] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 黄书超, 杨琰珊, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 张银翠. 微生物肥料与化肥减量配施对多年生黑麦草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 136-143. |
| [6] | 张国香, 郭卫冷, 毕铭钰, 张力爽, 王丹, 郭长虹. 紫花苜蓿CAX基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 106-117. |
| [7] | 周力, 王志有, 杨葆春, 侯生珍, 张峰硕, 桂林生. 饲粮中性洗涤纤维水平对黑藏羊肌纤维类型组成比例与肉质特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 75-85. |
| [8] | 张家驹, 于洁, 李明娜, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 龙瑞才. 蒺藜苜蓿lncRNA167及其剪切产物miR167c的鉴定和功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 164-180. |
| [9] | 柳福智, 张迎芳, 陈垣. 外源海藻糖对NaHCO3胁迫下甘草幼苗生长调节及总黄酮含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 148-156. |
| [10] | 田甜, 王海江, 王金刚, 朱永琪, 史晓艳, 李维弟, 李文瑞玉. 盐胁迫下施加氮素对饲用油菜有机渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 125-136. |
| [11] | 李振松, 万里强, 李硕, 李向林. 苜蓿根系构型及生理特性对干旱复水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [12] | 张利霞, 常青山, 薛娴, 刘伟, 张巧明, 陈苏丹, 郑轶琦, 李景林, 陈婉东, 李大钊. 酸胁迫对夏枯草叶绿素荧光特性和根系抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 134-142. |
| [13] | 侯洁茹, 段晓玥, 李州, 彭燕. 白三叶TrSAMDC1克隆及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 170-178. |
| [14] | 郭欢, 潘雅清, 包爱科. NaCl在四翅滨藜适应渗透胁迫中的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 112-121. |
| [15] | 李柯, 周庄煜, 李四菊, 姚浩铮, 周莹, 缪雨静, 唐晓清, 王康才. 荆芥的生长、渗透调节和抗氧化能力对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 150-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||