

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4): 53-63.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024210
王斌1,2( ), 史佳梅3, 王腾飞1,2, 张译尹1,2, 马江萍1,2, 李佳旺1,2, 王小兵1,2, 邓建强1,2(
), 史佳梅3, 王腾飞1,2, 张译尹1,2, 马江萍1,2, 李佳旺1,2, 王小兵1,2, 邓建强1,2( ), 兰剑1,2(
), 兰剑1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-04
修回日期:2024-07-29
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-02-19
通讯作者:
邓建强,兰剑
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: ndlanjian@163.com基金资助:
Bin WANG1,2( ), Jia-mei SHI3, Teng-fei WANG1,2, Yi-yin ZHANG1,2, Jiang-ping MA1,2, Jia-wang LI1,2, Xiao-bing WANG1,2, Jian-qiang DENG1,2(
), Jia-mei SHI3, Teng-fei WANG1,2, Yi-yin ZHANG1,2, Jiang-ping MA1,2, Jia-wang LI1,2, Xiao-bing WANG1,2, Jian-qiang DENG1,2( ), Jian LAN1,2(
), Jian LAN1,2( )
)
Received:2024-06-04
Revised:2024-07-29
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-02-19
Contact:
Jian-qiang DENG,Jian LAN
摘要:
为了探究施氮量对饲用高粱单作及混播模式下饲草产量形成及氮素利用的影响,本研究以饲用高粱品种“绿巨人”和拉巴豆品种“高值”为试验材料,于2021-2022年在宁夏大学草业科学教学科研基地进行大田裂区试验,设置两个种植模式(饲用高粱单播,SS;饲用高粱/拉巴豆混播,SL)为主区,4个施氮量(N0,0 kg·hm-2;N90,90 kg·hm-2;N180,180 kg·hm-2;N270,270 kg·hm-2)为副区,测定生产性能、营养品质及氮肥利用效率等相关指标。结果表明,饲用高粱/拉巴豆混播结合施氮可促进饲草生长,提高草地生产性能,其中饲用高粱/拉巴豆混播结合施氮量180 kg·hm-2模式下的干草产量和粗蛋白产量均达到最高,分别为28352.5 kg·hm-2和2481.1 kg·hm-2,较单播饲用高粱分别提高了14.8%和25.9%。混播结合施氮可改善饲草营养品质,混播模式下施氮量为180 kg·hm-2时,茎秆糖锤度和相对饲喂价值较单播饲用高粱分别提高10.3%和18.9%。适宜的施氮量也可显著提高氮肥贡献率,单播模式的氮肥贡献率在施氮量为270 kg·hm-2时达到最高,混播模式在180 kg·hm-2时最高。此外,混播模式的氮肥农艺利用效率和氮肥偏生产力较单播均有不同程度的增加,在施氮量为90 kg·hm-2时达到最大值。综上所述,饲用高粱/拉巴豆混播结合施氮量180 kg·hm-2模式是宁夏干旱区增加饲草产量、改善饲草营养品质和提高氮肥利用效率的适宜种植模式和施氮水平。
王斌, 史佳梅, 王腾飞, 张译尹, 马江萍, 李佳旺, 王小兵, 邓建强, 兰剑. 施氮对饲用高粱/拉巴豆混播草地生产性能和氮肥贡献率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 53-63.
Bin WANG, Jia-mei SHI, Teng-fei WANG, Yi-yin ZHANG, Jiang-ping MA, Jia-wang LI, Xiao-bing WANG, Jian-qiang DENG, Jian LAN. Effect of nitrogen application on production performance and nitrogen fertilizer contribution of forage sorghum/lablab mixed cropping[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(4): 53-63.
材料 Material | 品种 Variety | 纯净度 Purity (%) | 发芽率 Germination rate (%) | 千粒重 Thousand seeds weight (g) | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 饲用高粱S. bicolor | 绿巨人Green hulk | 99 | 98 | 29.74 | 北京百斯特草业有限公司 Beijing Best Grass Industry Co., Ltd |
| 拉巴豆D. lablab | 高值High value | 99 | 91 | 268.52 |
表1 供试材料信息
Table 1 Information of test materials
材料 Material | 品种 Variety | 纯净度 Purity (%) | 发芽率 Germination rate (%) | 千粒重 Thousand seeds weight (g) | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 饲用高粱S. bicolor | 绿巨人Green hulk | 99 | 98 | 29.74 | 北京百斯特草业有限公司 Beijing Best Grass Industry Co., Ltd |
| 拉巴豆D. lablab | 高值High value | 99 | 91 | 268.52 |
| 因素Factor | DM | CPY | TCD | CP | NDF | ADF | RFV | NEL | TDN | CN | NAE | NPFP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份Year | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 种植模式Planting pattern | *** | *** | NS | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** |
| 氮水平Nitrogen level | *** | *** | ** | ** | * | NS | * | NS | NS | * | ** | *** |
| 年份×种植模式Year×planting pattern | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ** | NS | ** | ** | NS | NS | NS |
| 年份×氮水平Year×nitrogen level | NS | NS | NS | NS | * | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 种植模式×氮水平Planting pattern×nitrogen level | * | ** | NS | NS | ** | NS | ** | NS | NS | NS | * | *** |
| 年份×种植模式×氮水平Year×planting pattern×nitrogen level | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
表2 饲草产量、营养品质以及氮肥利用效率的方差分析
Table 2 Analysis of variance for forage yield, nutritional quality, and nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency
| 因素Factor | DM | CPY | TCD | CP | NDF | ADF | RFV | NEL | TDN | CN | NAE | NPFP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份Year | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 种植模式Planting pattern | *** | *** | NS | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** |
| 氮水平Nitrogen level | *** | *** | ** | ** | * | NS | * | NS | NS | * | ** | *** |
| 年份×种植模式Year×planting pattern | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ** | NS | ** | ** | NS | NS | NS |
| 年份×氮水平Year×nitrogen level | NS | NS | NS | NS | * | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| 种植模式×氮水平Planting pattern×nitrogen level | * | ** | NS | NS | ** | NS | ** | NS | NS | NS | * | *** |
| 年份×种植模式×氮水平Year×planting pattern×nitrogen level | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |

图3 不同种植模式及施氮水平下干草产量和粗蛋白产量的差异SS:饲用高粱单播Forage sorghum monoculture; SL:饲用高粱拉巴豆混播Forage sorghum and lablab bean mixed. N0:氮肥 Nitrogen 0 kg·ha-1; N90:氮肥 Nitrogen 90 kg·ha-1; N180:氮肥 Nitrogen 180 kg·ha-1; N270:氮肥Nitrogen 270 kg·ha-1.不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05) Different letters meant significant difference at 0.05 level. 下同The same below.
Fig. 3 Differences in dry matter yield and crude protein yield under different cropping patterns and nitrogen application levels
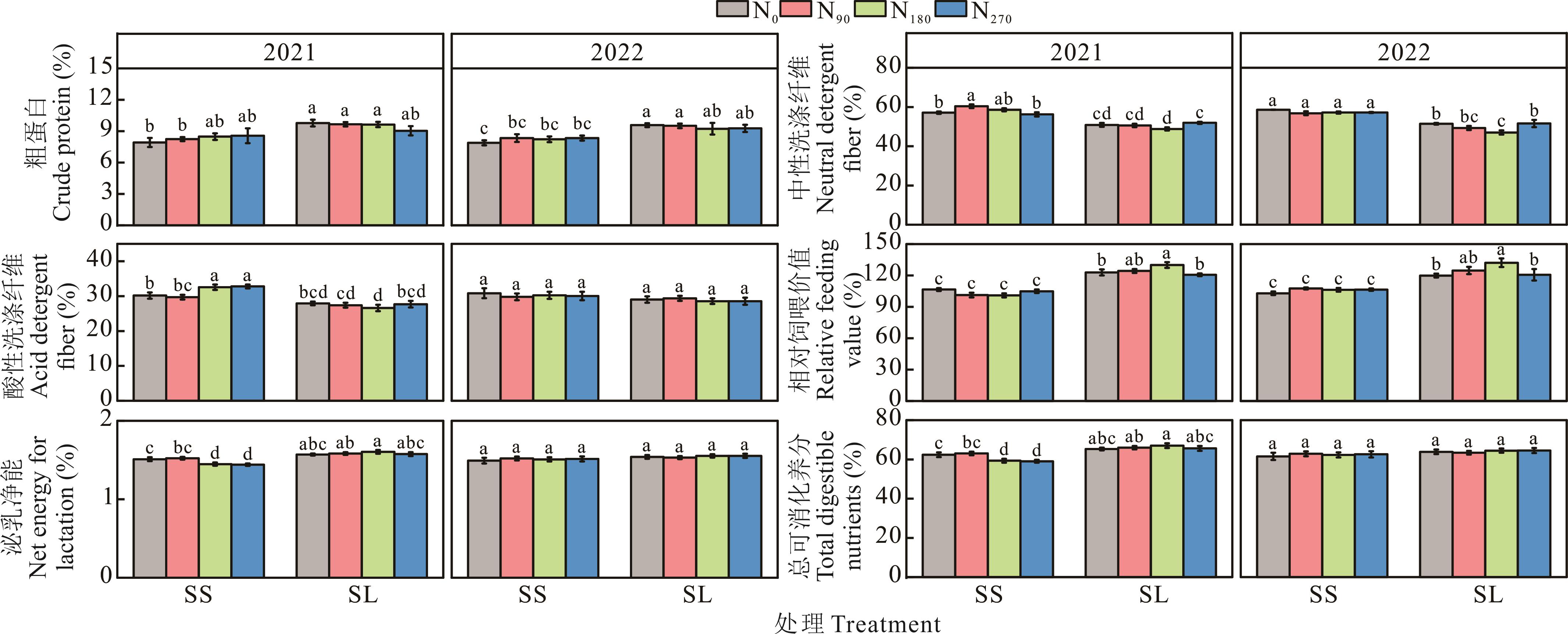
图5 不同种植模式及施氮水平下牧草营养品质的差异
Fig.5 Differences in nutritional quality of pasture grasses under different cropping patterns and nitrogen application levels
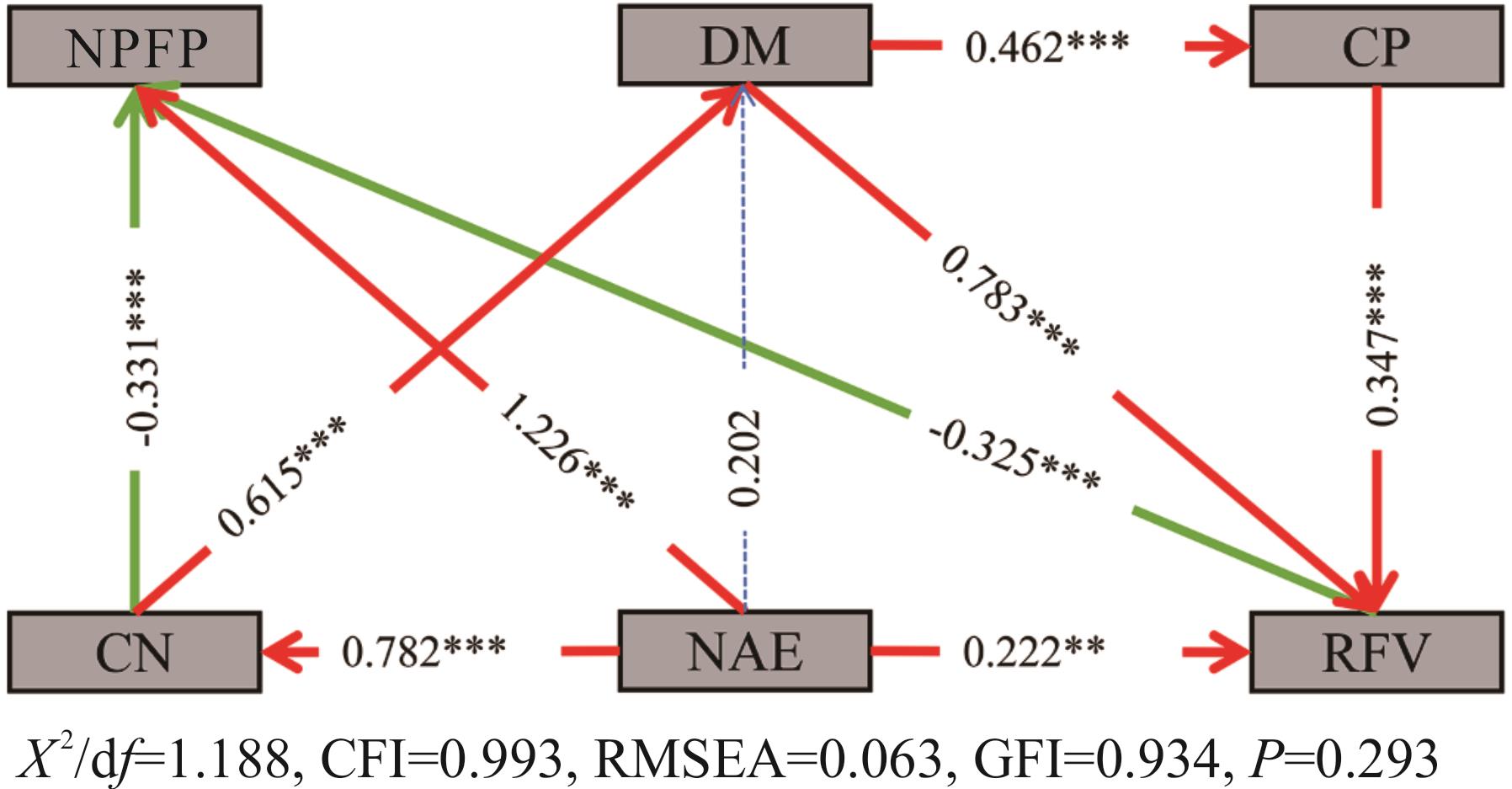
图8 结构方程模型红色线条表示正相关关系,绿色线条表示负相关关系,蓝色线条表示无显著相关关系。箭头宽度表示显著的标准化路径系数强度(P<0.05)。***:P<0.001;**:P<0.01。Red lines indicate positive correlations, green lines indicate negative correlations, and blue lines indicate no significant correlations. Arrow widths indicate significant standardized path coefficient strengths (P<0.05). ***: P<0.001; **: P<0.01. NPFP: 氮肥偏生产力Nitrogen fertilizer partial factor productivity; DM: 干草产量 Dry matter yield; CP: 粗蛋白Crude protein; RFV: 相对饲喂价值Relative feeding value; NAE: 氮肥农艺利用效率Nitrogen fertilizer agronomic use efficiency; CN: 氮肥贡献率Nitrogen fertilizer contribution.
Fig.8 Structural equation mode
| 1 | Zhang Z, Whish J P M, Bell L W, et al. Forage production, quality and water-use-efficiency of four warm-season annual crops at three sowing times in the Loess Plateau region of China. European Journal of Agronomy, 2017, 84: 84-94. |
| 2 | Gao W, Shou N, Jiang C, et al. Optimizing N application for forage sorghum to maximize yield, quality, and N use efficiency while reducing environmental costs. Agronomy, 2022, 12(12): 2969. |
| 3 | Marsalis M A, Angadi S V, Contreras-Govea F E. Dry matter yield and nutritive value of corn, forage sorghum, and BMR forage sorghum at different plant populations and nitrogen rates. Field Crops Research, 2010, 116(1/2): 52-57. |
| 4 | Wang X, Feng Y, Yu L, et al. Sugarcane/soybean intercropping with reduced nitrogen input improves crop productivity and reduces carbon footprint in China. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 719: 137517. |
| 5 | Zhang X, Davidson E A, Mauzerall D L, et al. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature, 2015, 528(7580): 51-59. |
| 6 | Wang X R, Zhang R Z, Li S M, et al. Simulation of dry matter accumulation and nitrogen absorption in a maize/soybean intercropping system supplied with different nitrogen levels. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(9): 1354-1363. |
| 王雪蓉, 张润芝, 李淑敏, 等. 不同供氮水平下玉米/大豆间作体系干物质积累和氮素吸收动态模拟. 中国生态农业学报, 2019, 27(9): 1354-1363. | |
| 7 | Li C, Hoffland E, Kuyper T W, et al. Syndromes of production in intercropping impact yield gains. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(6): 653-660. |
| 8 | Wang B, Deng J Q, Wang T F, et al. Effect of seeding options on interspecific competition in oat (Avena sativa L.)-common vetch (Vicia sativa L.) forage crops. Agronomy, 2022, 12(12): 3119. |
| 9 | Liu Z Y, Zhu Y A, Dong Y, et al. Interspecies interaction for nitrogen use efficiency via up-regulated glutamine and glutamate synthase under wheat-faba bean intercropping. Field Crops Research, 2021, 274: 108324. |
| 10 | Li Q, Sun J, Wei X, et al. Overyielding and interspecific interactions mediated by nitrogen fertilization in strip intercropping of maize with faba bean, wheat and barley. Plant and Soil, 2011, 339(1/2): 147-161. |
| 11 | Yu C B, Li Y Y, Li C J, et al. An improved nitrogen difference method for estimating biological nitrogen fixation in legume-based intercropping systems. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2010, 46(3): 227-235. |
| 12 | Hu F, Zhao C, Feng F, et al. Improving N management through intercropping alleviates the inhibitory effect of mineral N on nodulation in pea. Plant and Soil, 2017, 412(1/2): 235-251. |
| 13 | Umesh M R, Angadi S, Begna S, et al. Intercropping and species interactions on physiological and light use characteristics of forage cereals-legumes combinations in semi-arid regions. Field Crops Research, 2023, 290: 108755. |
| 14 | Wang B, Dong X, Li M Y, et al. Effects of mixed planting of Dolichos lablab with different sowing rates and silage corn on grassland productivity and forage quality. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(4): 828-834. |
| 王斌, 董秀, 李满有, 等. 不同播量拉巴豆与青贮玉米混播对草地生产性能及牧草品质的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(4): 828-834. | |
| 15 | Wang T F, Wang B, Deng J Q, et al. Effect of sowing rate on yield and forage quality of a Dolichos lablab-Sorghum bicolor mixture under drip irrigation in arid areas of Ningxia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 30-40. |
| 王腾飞, 王斌, 邓建强, 等. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下拉巴豆不同播种量与甜高粱混播饲草生产性能研究. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 30-40. | |
| 16 | Wei Z Y, Zhang H X, Shi W, et al. Effects of planting methods and nitrogen application on forage crop yield, quality and water use in arid area of northwest China. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2638-2653. |
| 魏正业, 张海星, 石薇, 等. 种植方式与施氮对西北旱区饲草作物产量、品质和水分利用的影响. 作物学报, 2022, 48(10): 2638-2653. | |
| 17 | Gao W, Shou N, Jiang C Z, et al. Effect of nitrogen application rate on dry matter accumulation,allocation and water use efficiency of forage sorghum. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 26-35. |
| 高玮, 受娜, 蒋丛泽, 等. 施氮量对饲用高粱干物质积累、分配及水分利用效率的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 26-35. | |
| 18 | Tan Y, Hu F, Chai Q, et al. Expanding row ratio with lowered nitrogen fertilization improves system productivity of maize/pea strip intercropping. European Journal of Agronomy, 2020, 113: 125986. |
| 19 | Deng J, Zhang Z, Liang Z, et al. Replacing summer fallow with annual forage improves crude protein productivity and water use efficiency of the summer fallow-winter wheat cropping system. Agricultural Water Management, 2020, 230: 105980. |
| 20 | Li J B. Quality inspection and quality management of feed and feed additives. China Animal Industry, 2023(15): 64-65. |
| 厉建兵. 饲料及饲料添加剂质量检测与品质管理. 中国畜牧业, 2023(15): 64-65. | |
| 21 | Lithourgidis A S, Vasilakoglou I B, Dhima K V, et al. Forage yield and quality of common vetch mixtures with oat and triticale in two seeding ratios. Field Crops Research, 2006, 99(2/3): 106-113. |
| 22 | Sadeghpour A, Jahanzad E, Esmaeili A, et al. Forage yield, quality and economic benefit of intercropped barley and annual medic in semi-arid conditions: Additive series. Field Crops Research, 2013, 148: 43-48. |
| 23 | Liu Z, Nan Z, Lin S, et al. Millet/peanut intercropping at a moderate N rate increases crop productivity and N use efficiency, as well as economic benefits, under rain-fed conditions. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2023, 22(3): 738-751. |
| 24 | Liu X, Meng L, Yin T, et al. Maize/soybean intercrop over time has higher yield stability relative to matched monoculture under different nitrogen-application rates. Field Crops Research, 2023, 301: 109015. |
| 25 | Li R, Zhang Z, Tang W, et al. Common vetch cultivars improve yield of oat row intercropping on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau by optimizing photosynthetic performance. European Journal of Agronomy, 2020, 117: 126088. |
| 26 | Gong X, Dang K, Liu L, et al. Intercropping combined with nitrogen input promotes proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) growth and resource use efficiency to increase grain yield on the loess plateau of China. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 243: 106434. |
| 27 | St Luce M, Grant C A, Zebarth B J, et al. Legumes can reduce economic optimum nitrogen rates and increase yields in a wheat-canola cropping sequence in western Canada. Field Crops Research, 2015, 179: 12-25. |
| 28 | Chen P, Du Q, Liu X, et al. Effects of reduced nitrogen inputs on crop yield and nitrogen use efficiency in a long-term maize-soybean relay strip intercropping system. PLoS One, 2017, 12(9): 0184503. |
| 29 | Du Q, Zhou L, Chen P, et al. Relay-intercropping soybean with maize maintains soil fertility and increases nitrogen recovery efficiency by reducing nitrogen input. Crop Journal, 2020, 8(1): 140-152. |
| 30 | Zhao D Q, Liu S H, Zhao K C. Effect of maize-soybean intercropping and reduced nitrogen application on maize growth, yield and soil nitrate content. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 1159-1166. |
| 赵笃勤, 刘淑慧, 赵凯超. 玉米-大豆间作和减量施氮对玉米生长、产量及土壤硝态氮含量的影响. 西北农业学报, 2020, 29(8): 1159-1166. | |
| 31 | Lithourgidis A S, Dordas C A. Forage yield, growth rate, and nitrogen uptake of faba bean intercrops with wheat, barley, and rye in three seeding ratios. Crop Science, 2010, 50(5): 2148-2158. |
| 32 | Wang C G, Zhao M J, Pei W D, et al. Effects of nitrogen rates on grain yield and forage quality of dual-purpose maize. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2020, 28(6): 148-153. |
| 王晨光, 赵美娟, 裴文东, 等. 施氮量对粮饲兼用玉米子粒产量和饲用品质的影响. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(6): 148-153. | |
| 33 | Jiang Z W, Liu G Y, An H Y, et al. Effects of planting density and nitrogen application on forage yield, quality and nitrogen use efficiency in a maize/forage soybean intercropping system. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 157-171. |
| 蒋紫薇, 刘桂宇, 安昊云, 等. 种植密度与施氮对玉米/秣食豆间作系统饲草产量、品质和氮肥利用的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 157-171. | |
| 34 | Shen X T, Deng X, Li M Y, et al. Comparative study of production performance and nutritional value of Sorghum dochna varieties in rainfed areas in Ningxia, China. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(6): 1235-1244. |
| 沈笑天, 邓雪, 李满有, 等. 宁夏雨养区饲用甜高粱品种的生产性能和营养价值. 草业科学, 2022, 39(6): 1235-1244. | |
| 35 | Zaituniguli·K E B, Tuerxun·T E H, Tu Z D, et al. Effects of fertilization on growth and yield of continuously cropped sweet sorghum. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 81-92. |
| 再吐尼古丽·库尔班, 吐尔逊·吐尔洪, 涂振东, 等. 长期不同施肥处理对连作高粱生长规律及产量的影响研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 81-92. | |
| 36 | Wang B. Effects of mixed cropping ratio and NPK fertilization production performance and soil physical and chemical properties of Sorghum bicolor/Dolichos lablab grassland.Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2022. |
| 王斌. 混播比例与氮磷钾肥配施对甜高粱/拉巴豆草地生产性能和土壤理化性质的影响. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2022. | |
| 37 | Li Q, Chen J, Wu L, et al. Belowground interactions impact the soil bacterial community, soil fertility, and crop yield in maize/peanut intercropping systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(2): 622. |
| 38 | Stomph T, Dordas C, Baranger A, et al. Designing intercrops for high yield, yield stability and efficient use of resources: Are there principles. Advances in Agronomy, 2020, 160(1): 1-50. |
| [1] | 王腾飞, 马霞, 刘金龙, 王斌, 张译尹, 李佳旺, 马江萍, 王小兵, 兰剑. 引黄灌区复种饲用燕麦种植模式产量、品质及经济效益分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 27-37. |
| [2] | 张晓娟, 魏娇娇, 陈彩锦, 李雪雪, 马宏秀, 李凯, 陈永伟, 孙权. 氮肥周年优化对灌区饲用小黑麦-青贮玉米复种系统生产力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 38-52. |
| [3] | 马江萍, 张译尹, 王腾飞, 王斌, 兰剑. 饲用高粱与拉巴豆混播对种间关系及草地生产力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 111-122. |
| [4] | 赵雅姣, 刘晓静, 蔺芳. 适宜于黄土高原半干旱区豆禾饲草间套作组合的筛选[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 97-110. |
| [5] | 王文虎, 梁国玲, 刘文辉, 王凤宇, 李文. 青藏高原区8份老芒麦资源农艺性状与生产性能综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 123-132. |
| [6] | 李中利, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 高玮, 受娜, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 陇东旱塬区5个饲用甜高粱品种生产适宜性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 50-62. |
| [7] | 桑瑞娟, 崔超杰, 何云, 张晓霞, 姚晋, 董春阳, 孙浩, 史莹华, 朱晓艳, 李德锋. 豫北地区18个秋播饲用燕麦品种抗倒伏特性及生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 74-85. |
| [8] | 赵洁, 陈恒光, 裴晓蒙, 于昊, 徐银莹, 茆达干. 围产期日粮添加白藜芦醇对山羊生产性能、血液指标及炎症因子基因表达的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 210-220. |
| [9] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| [10] | 冯琴, 何小莉, 王斌, 王腾飞, 倪旺, 马霞, 明雪花, 邓建强, 兰剑. 宁夏引黄灌区燕麦与箭筈豌豆的混播效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 107-119. |
| [11] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [12] | 张永亮, 滕泽, 郝凤, 于铁峰, 张玉霞. 苜蓿混播方式及比例对混播草地生产力和稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 185-197. |
| [13] | 高兴发, 聂莹莹, 徐丽君, 杨敏, 徐树花, 朱孟. 干旱条件下乌蒙山区冬闲田燕麦引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 215-227. |
| [14] | 张仲鹃, 郝曦煜, 王雪, 李峰, 李文龙. 齐齐哈尔地区适宜青贮玉米品种的筛选及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 228-240. |
| [15] | 王金兰, 王小军, 刘启林, 梁国玲, 琚泽亮, 石红梅, 汪小兵, 文培, 青梅然丁null, 李文. 不同燕麦品种在三江源区的生产性能和营养品质综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 83-95. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||