

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 223-240.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025063
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
窦苗苗( ), 姜晓东, 孙慧琼, 徐宏申, 王锡亮, 杨博慧, 柴文婷, 赵珊珊, 张春来(
), 姜晓东, 孙慧琼, 徐宏申, 王锡亮, 杨博慧, 柴文婷, 赵珊珊, 张春来( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-04
修回日期:2025-05-06
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2025-11-13
通讯作者:
张春来
作者简介:E-mail: chunlaiz@hotmail.com基金资助:
Miao-miao DOU( ), Xiao-dong JIANG, Hui-qiong SUN, Hong-shen XU, Xi-liang WANG, Bo-hui YANG, Wen-ting CHAI, Shan-shan ZHAO, Chun-lai ZHANG(
), Xiao-dong JIANG, Hui-qiong SUN, Hong-shen XU, Xi-liang WANG, Bo-hui YANG, Wen-ting CHAI, Shan-shan ZHAO, Chun-lai ZHANG( )
)
Received:2025-03-04
Revised:2025-05-06
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2025-11-13
Contact:
Chun-lai ZHANG
摘要:
藜麦的生长发育易受逆境胁迫,影响藜麦产业的发展。SGT1作为Skp1-4的抑制因子,通过分子伴侣或调控泛素化对植物抗逆反应进行调控,其中Skp1-4参与调控细胞周期、信号转导和基因表达等生物过程。鉴定藜麦SGT1基因,明确藜麦SGT1基因对生物及非生物胁迫的应答情况。利用生物信息学方法,鉴定出藜麦SGT1基因,并对其理化性质、序列特征、系统发育树、蛋白互作网络及表达模式等方面进行研究。从藜麦基因组鉴定出2个SGT1基因,分别命名为CqSGT1a和CqSGT1b,位于Chr06和Chr07上,藜麦SGT1蛋白主要富含碱性氨基酸,亚细胞定位在细胞核,无信号肽结构,二级结构以α-螺旋为主,属于疏水性蛋白,无跨膜结构,具有TPR-SGS-CS结构域。CqSGT1启动子区域存在藜麦生长发育和抵御逆境胁迫的光系统和激素等响应元件。CqSGT1基因与BvSGT1基因亲缘关系最近。qPCR技术分析表明,藜麦SGT1在花和籽粒中表达量较高,推测其表达与花和籽粒形成发育有关;低温初期表达水平上调,随之被抑制;水杨酸(SA)正向调控SGT1的表达,3 h时响应最显著。SGT1于2403(抗病材料)中响应霜霉病菌侵染,抗病材料中SGT1的表达量于接种后2 h显著上调,后期先降后升,在24 h时的响应最为强烈,表明SGT1a/b基因在藜麦霜霉病中发挥正调控作用。CqSGT1基因具有组织表达特异性,并且均响应低温、SA胁迫及霜霉病菌侵染,在藜麦器官生长发育和抗逆过程中发挥重要作用。
窦苗苗, 姜晓东, 孙慧琼, 徐宏申, 王锡亮, 杨博慧, 柴文婷, 赵珊珊, 张春来. 藜麦CqSGT1基因克隆、表达模式与DNA变异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 223-240.
Miao-miao DOU, Xiao-dong JIANG, Hui-qiong SUN, Hong-shen XU, Xi-liang WANG, Bo-hui YANG, Wen-ting CHAI, Shan-shan ZHAO, Chun-lai ZHANG. Cloning, expression profiling and DNA variation analysis of the disease-resistance gene CqSGT1 in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa)[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(1): 223-240.
基因名称 Gene name | 正向序列 Forward primer (5′→3′) | 反向序列 Reverse primer (5′→3′) | 用途 Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | ACGGAAAGGAACTGCGTGTA | GGCTGCTTGTGCATTGGTAG | qRT-PCR, SemiRT-PCR |
| CqSGT1b | TTACCTACGAAAAGGGACCGC | TGCTTGTGCATTGGTAGGCT | qRT-PCR, SemiRT-PCR |
| CqEF1α | GACAAGCGTGTGATCGAGAG | TCGGCCTTAAGTTTGTCGAG | qRT-PCR, SemiRT-PCR |
| TI-CqSGT1a/b | ATGGCGACGGATCTCGAGACCAAG | TTAGTATTCCCATTTCTTCATCTC | 基因克隆Gene clone |
pCAMBIA1300-Cq SGT1a/b | CGC | CGC | 瞬时表达Transient expression |
| M13 | GTTGTAAAACGACGGCCAG | CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC | 基因克隆和瞬时表达Gene clone and transient expression |
表1 PCR基因分析所用的引物
Table1 Primers used for gene analysis of PCR
基因名称 Gene name | 正向序列 Forward primer (5′→3′) | 反向序列 Reverse primer (5′→3′) | 用途 Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | ACGGAAAGGAACTGCGTGTA | GGCTGCTTGTGCATTGGTAG | qRT-PCR, SemiRT-PCR |
| CqSGT1b | TTACCTACGAAAAGGGACCGC | TGCTTGTGCATTGGTAGGCT | qRT-PCR, SemiRT-PCR |
| CqEF1α | GACAAGCGTGTGATCGAGAG | TCGGCCTTAAGTTTGTCGAG | qRT-PCR, SemiRT-PCR |
| TI-CqSGT1a/b | ATGGCGACGGATCTCGAGACCAAG | TTAGTATTCCCATTTCTTCATCTC | 基因克隆Gene clone |
pCAMBIA1300-Cq SGT1a/b | CGC | CGC | 瞬时表达Transient expression |
| M13 | GTTGTAAAACGACGGCCAG | CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC | 基因克隆和瞬时表达Gene clone and transient expression |
基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 染色体位置 Chromosome location | 氨基酸长度Length of amino acids (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 等电点 Isoelectric point (pI) | 不稳定系数Instability coefficient | 脂溶系数 Liposolubility coefficient | 亲水性均值 Grand average of hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | AUR62021095 | Chr06 | 358 | 39906.09 | 5.18 | 36.21 | 75.03 | -0.515 |
| CqSGT1b | AUR62031443 | Chr07 | 358 | 39890.07 | 5.42 | 34.77 | 73.66 | -0.563 |
表2 藜麦中SGT1基因的基本信息
Table 2 Basic information of SGT1 family genes in C. quinoa
基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 染色体位置 Chromosome location | 氨基酸长度Length of amino acids (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 等电点 Isoelectric point (pI) | 不稳定系数Instability coefficient | 脂溶系数 Liposolubility coefficient | 亲水性均值 Grand average of hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | AUR62021095 | Chr06 | 358 | 39906.09 | 5.18 | 36.21 | 75.03 | -0.515 |
| CqSGT1b | AUR62031443 | Chr07 | 358 | 39890.07 | 5.42 | 34.77 | 73.66 | -0.563 |
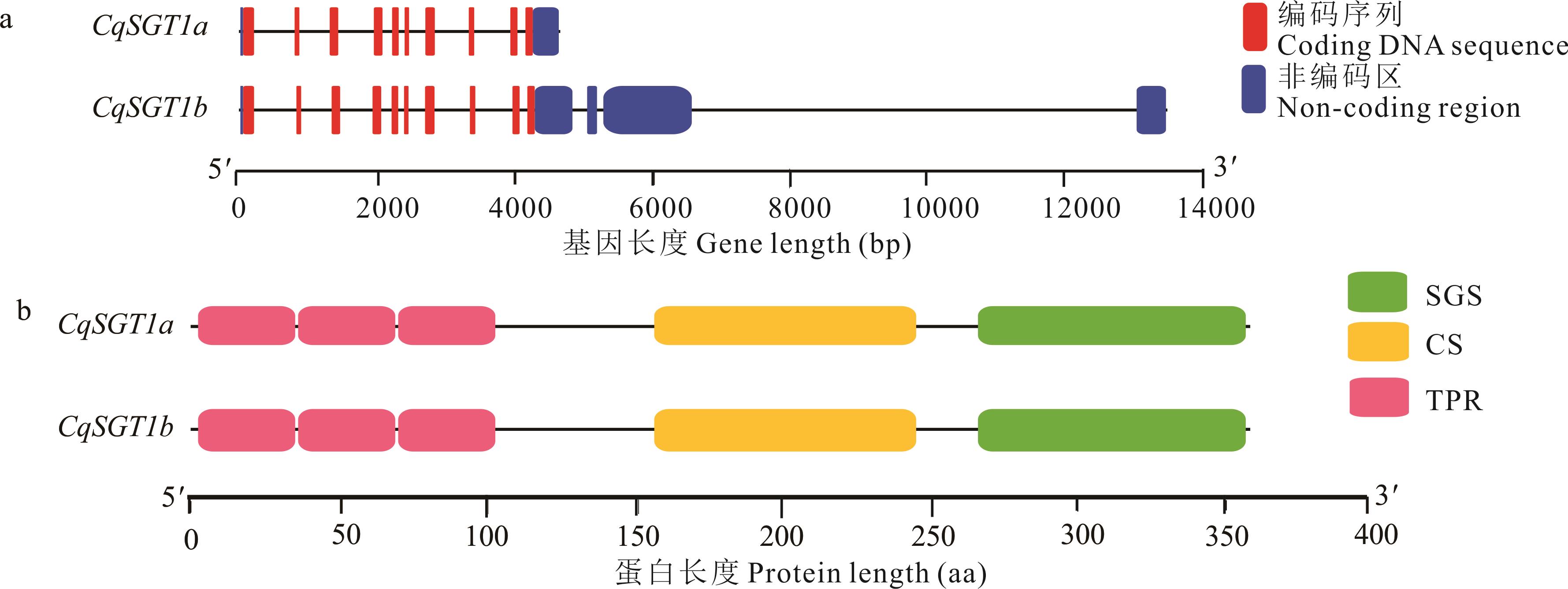
图2 藜麦SGT1基因结构及蛋白功能分析a: 藜麦SGT1基因结构Gene structures of SGT1 genes in C. quinoa; b: 藜麦SGT1蛋白的保守结构域Conservative domain of SGT1 proteins in C. quinoa. TPR: 四肽重复序列区域结构域Tetratricopeptide repeat-sequenceregion domain; CS: 半胱氨酸和组氨酸富集结构域与SGT1蛋白结构域CHORD and SGT1 domain; SGS: 甘氨酸-丝氨酸重复结构域Glycine-serine repeat domain. 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Analysis of the gene structure and protein function of SGT1 in C.quinoa
蛋白质名称 Protein name | α-螺旋 α-helix | 延伸链 Extended strand | β-转角 β-turn | 无规则卷曲 Random coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | 41.62 | 13.41 | 4.19 | 40.78 |
| CqSGT1b | 45.81 | 12.57 | 3.63 | 37.99 |
表3 藜麦中SGT1蛋白的二级结构
Table 3 Secondary structures of SGT1 proteins in C. quinoa (%)
蛋白质名称 Protein name | α-螺旋 α-helix | 延伸链 Extended strand | β-转角 β-turn | 无规则卷曲 Random coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | 41.62 | 13.41 | 4.19 | 40.78 |
| CqSGT1b | 45.81 | 12.57 | 3.63 | 37.99 |
蛋白质 名称 Protein name | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 磷酸化位点 Phosphorylation sites | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丝氨酸Serine | 苏氨酸Threonine | 酪氨酸Tyrosine | |||
| CqSGT1a | 无Nothing | 细胞核Nucleus | 16 | 11 | 6 |
| CqSGT1b | 无Nothing | 细胞核Nucleus | 17 | 12 | 6 |
表4 藜麦CqSGT1蛋白的信号肽、亚细胞定位预测和磷酸化位点
Table 4 Signal peptid, subcellular localization prediction and phosphorylation sites of CqSGT1 proteins in C. quinoa
蛋白质 名称 Protein name | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 磷酸化位点 Phosphorylation sites | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丝氨酸Serine | 苏氨酸Threonine | 酪氨酸Tyrosine | |||
| CqSGT1a | 无Nothing | 细胞核Nucleus | 16 | 11 | 6 |
| CqSGT1b | 无Nothing | 细胞核Nucleus | 17 | 12 | 6 |
元件名称 Element name | 核心序列 Core sequence | 元件功能 Element function | 数量Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | CqSGT1b | |||
| chs-CMA1a | TTACTTAA | 部分光响应元件Part of light responsive element | 1 | - |
| 3-AF1 binding site | TAAGAGAGGAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | - |
| HD-Zip 3 | GTAAT(G/C)ATTAC | 蛋白质结合位点Protein binding site | 1 | - |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导必不可少的顺式作用调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction | 4 | 1 |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 2 | - |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 参与光响应的部分保守DNA模块Part of conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness | 3 | 4 |
| G-box | CACGAC | 参与光反应的顺式作用调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 | - |
| GA-motif | ATAGATAA | 部分光响应元件Part of light responsive element | 1 | - |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 部分光响应元件Part of light responsive element | 1 | - |
| P-box | CCTTTTG | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element | 2 | 2 |
| Gap-box | CAAATGAA(A/G)A | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | - |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用调节件Cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | 1 | - |
| ATCT-motif | AATCTAATCC | 参与光响应的部分保守DNA模块Part of conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness | 1 | - |
| TATA-box | AATCTAATCC | 转录起始-30核心启动子元件Core promoter element around-30 of transcription start | 64 | 53 |
| MBSI | AAAAAAC(G/C)GTTA | MYB结合位点参与类黄酮生物合成基因的调控元件MYB-binding site as a regulatory element involved in the control of flavonoid biosynthetic genes | - | 1 |
| CAAT-box | CAAAT | 启动子和增强子区域调控元件Promoter and enhancer region regulatory elements | - | 12 |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 部分光响应元件Part of light responsive element | - | 2 |
| O2-site | GTTGACGTGA | 参与玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调控的顺式调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolism regulation | - | 1 |
| MRE | AACCTAA | MYB结合位点(参与光响应)MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness | - | 1 |
| Circadian | AACCTAA | 参与昼夜节律控制的顺式作用调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in circadian control | - | 1 |
表5 藜麦中SGT1基因的顺式作用元件
Table 5 Cis-acting elements of SGT1 genes in C. quinoa
元件名称 Element name | 核心序列 Core sequence | 元件功能 Element function | 数量Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | CqSGT1b | |||
| chs-CMA1a | TTACTTAA | 部分光响应元件Part of light responsive element | 1 | - |
| 3-AF1 binding site | TAAGAGAGGAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | - |
| HD-Zip 3 | GTAAT(G/C)ATTAC | 蛋白质结合位点Protein binding site | 1 | - |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导必不可少的顺式作用调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction | 4 | 1 |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 2 | - |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 参与光响应的部分保守DNA模块Part of conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness | 3 | 4 |
| G-box | CACGAC | 参与光反应的顺式作用调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | 1 | - |
| GA-motif | ATAGATAA | 部分光响应元件Part of light responsive element | 1 | - |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 部分光响应元件Part of light responsive element | 1 | - |
| P-box | CCTTTTG | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element | 2 | 2 |
| Gap-box | CAAATGAA(A/G)A | 光响应元件Light responsive element | 1 | - |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用调节件Cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | 1 | - |
| ATCT-motif | AATCTAATCC | 参与光响应的部分保守DNA模块Part of conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness | 1 | - |
| TATA-box | AATCTAATCC | 转录起始-30核心启动子元件Core promoter element around-30 of transcription start | 64 | 53 |
| MBSI | AAAAAAC(G/C)GTTA | MYB结合位点参与类黄酮生物合成基因的调控元件MYB-binding site as a regulatory element involved in the control of flavonoid biosynthetic genes | - | 1 |
| CAAT-box | CAAAT | 启动子和增强子区域调控元件Promoter and enhancer region regulatory elements | - | 12 |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 部分光响应元件Part of light responsive element | - | 2 |
| O2-site | GTTGACGTGA | 参与玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调控的顺式调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolism regulation | - | 1 |
| MRE | AACCTAA | MYB结合位点(参与光响应)MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness | - | 1 |
| Circadian | AACCTAA | 参与昼夜节律控制的顺式作用调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in circadian control | - | 1 |
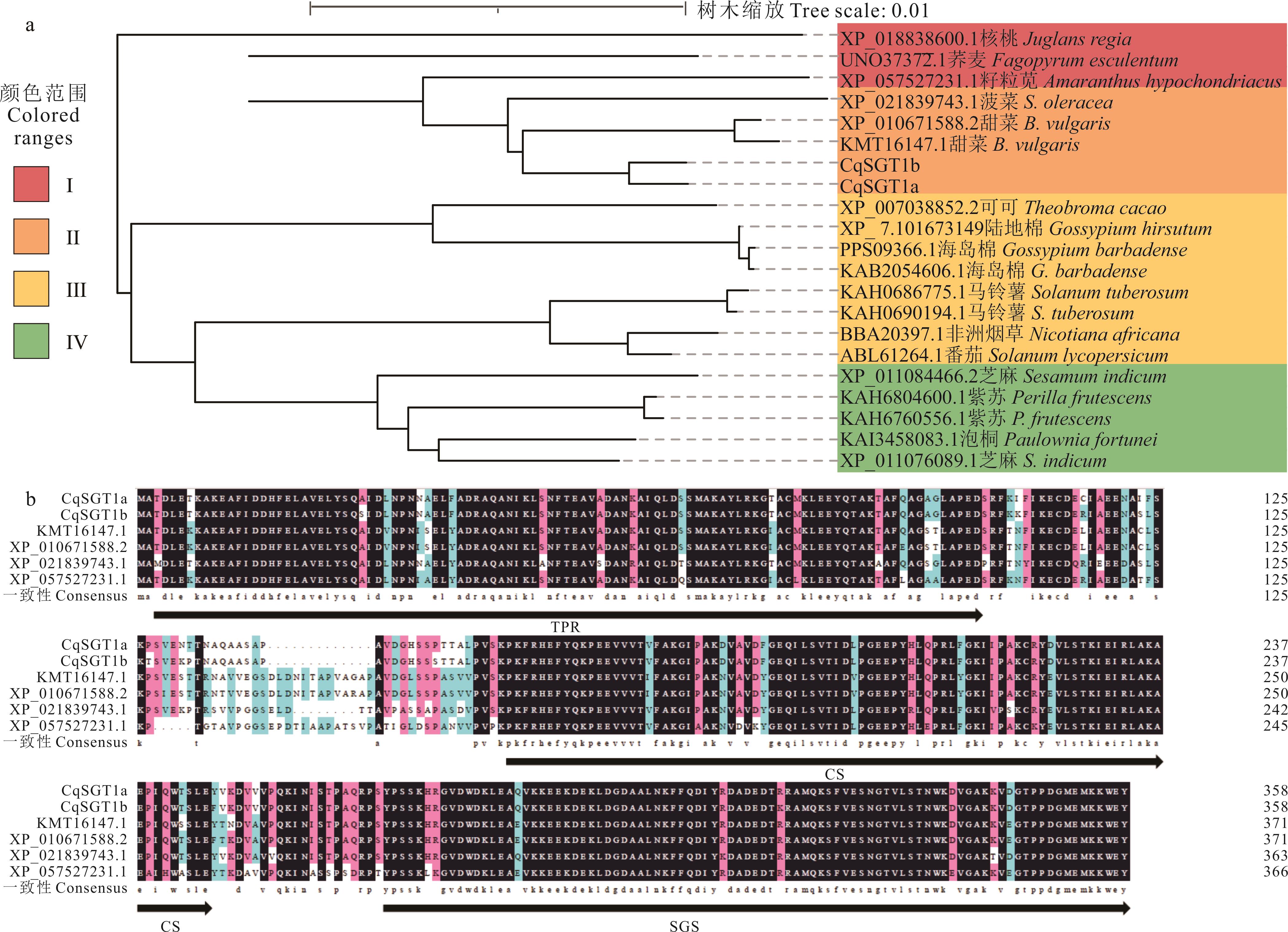
图5 藜麦SGT1蛋白系统发育分析及氨基酸序列比对a: CqSGT1和其他物种的系统发育分析Phylogenetic analysis of CqSGT1 and other species; b: CqSGT1与甜菜、菠菜和籽粒苋的氨基酸序列比对Amino acids alignment amongCqSGT1 and B. vulgaris, S. oleracea and A. hypochondriacus.
Fig.5 Phylogenetic analysis and amino acid sequence alignment of SGT1 in C. quinoa

图6 藜麦SGT1基因的PCR扩增及序列比对a: 2403-CqSGT1扩增结果Amplification results of 2403-CqSGT1 gene; b: pCAMBIA1300-CqSGT1的菌液PCR结果PCR results of bacteria that contain the plasmid pCAMBIA1300-CqSGT1.M: DNA标准分子量DNA Maker; 1: CqSGT1a的PCR结果The PCR results for CqSGT1a;2: CqSGT1b的PCR结果The PCR results for CqSGT1b; 3: pCAMBIA1300-CqSGT1的M13引物PCR扩增PCR amplification of M13 primers for pCAMBIA1300-CqSGT1; 4: pCAMBIA1300-CqSGT1的特异性引物PCR扩增PCR amplification of specific primers for pCAMBIA1300-CqSGT1. 下同The same below.
Fig.6 PCR amplification and sequence alignment of the SGT1 gene in C. quinoa
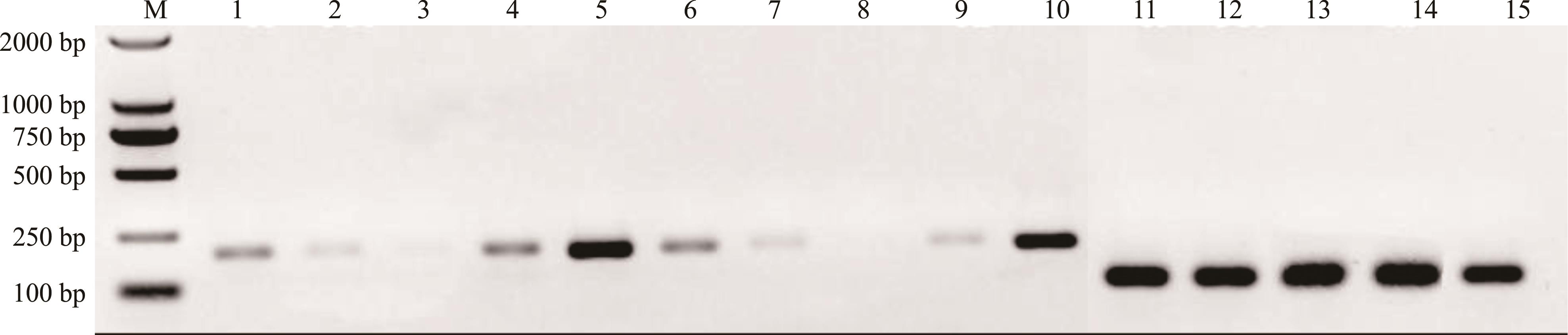
图7 CqSGT1基因在藜麦不同器官中的表达1~5、6~10和11~15表示CqSGT1a、CqSGT1b和CqEF1α分别在茎、幼叶、老叶、根和花的半定量RT-PCR结果。1-5, 6-10 and 11-15 represent semi RT-PCR results of CqSGT1a, CqSGT1b and CqEF1α in stem, young leaves, old leaves, roots and flowers, respectively.
Fig.7 Expression of CqSGT1 genes in different organs of C. quinoa
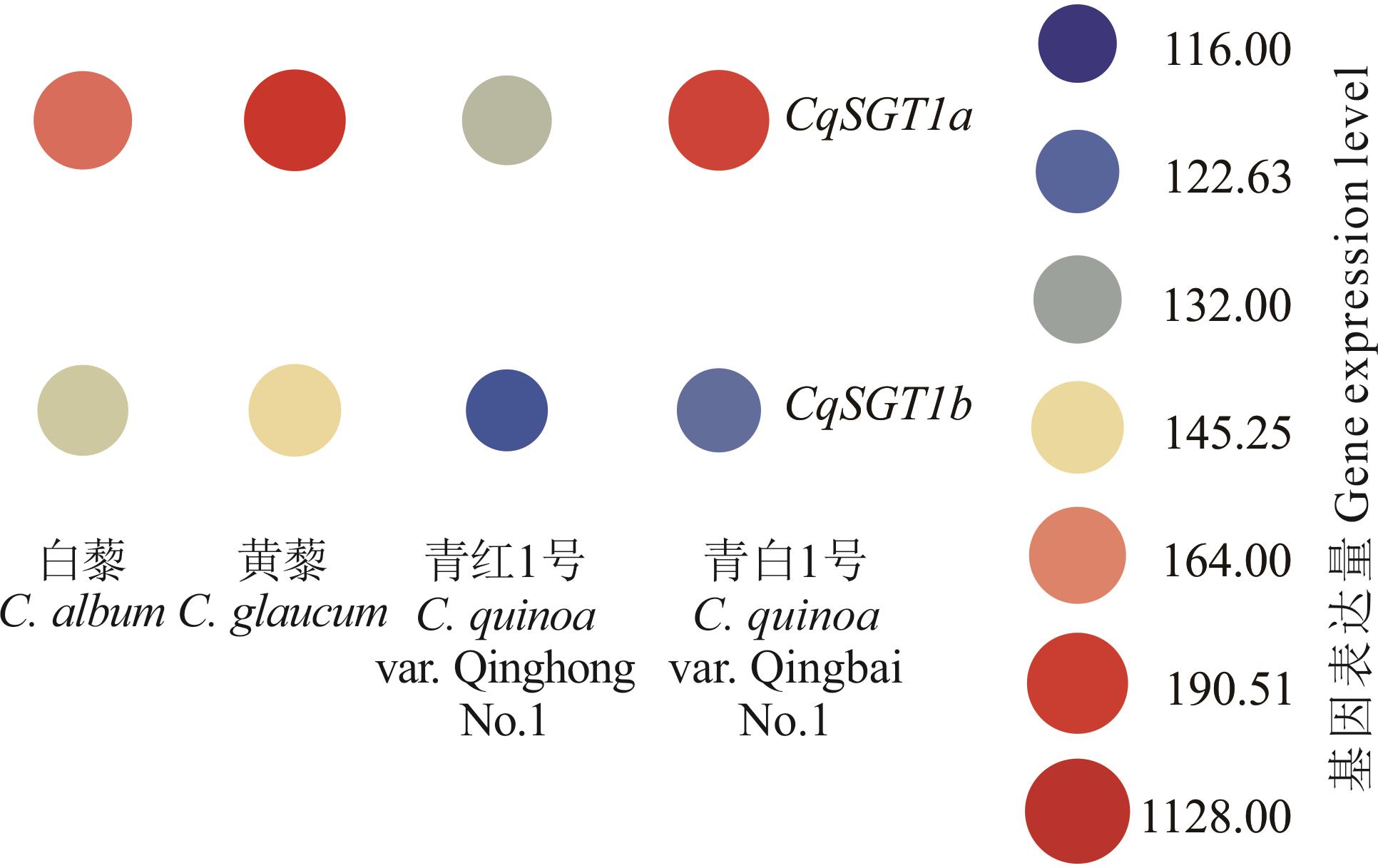
图8 CqSGT1基因在白藜、黄藜、青白1号、青红1号的花后幼嫩籽粒中的表达分析
Fig.8 Expression analysis of the CqSGT1 genes in the young seeds of C. album, C. glaucum, C. quinoa var. Qinghong No.1, and C. quinoa var.Qingbai No.1 after flowering

图9 水杨酸和低温胁迫下CqSGT1基因的表达模式不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.9 Expression pattern of CqSGT1 genes under SA and low temperature stress
基因 Gene | 染色体位置Chromosome location | Ref | Alt | JQ3 | JQ6 | Qingheili-8 | Qingbaili-9 | 影响Effect(其他突变系Other mutant lines) | 改变的密码子 The changed codon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | Chr06:34577463 | GA | G | GA, GA | GA, GA | GA, GA | G,G | 内含子Intron | GTa/Gat |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83675475 | A | AT | N | A, AT | A, AT | N | 上游Upstream | aAt/aAT |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83677523 | A | AC | AC, AC | AC, AC | AC, AC | AC, AC | 内含子Intron | aAc/aAC |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83679761 | CA | C | C, C | C, C | C, C | CA, C | 内含子Intron | cCA/cCa |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83679830 | TTTGTTGTTGTTG | T | TTTGTTGTTGTTG, TTTGTTGTTGTTG | N | N | TTTGTTGTTGTTG, T | 内含子Intron | cTTTGTTGTTGTTGT/cTt |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83689890 | A | ATAGCTGGCACAAACGGTGCCTTGT | A, A | A, ATAGCTGGCACAAACGGTGCCTTGT | A, ATAGCTGGCACAAACGGTGCCTTGT | A, ATAGCTGGCA CAAACGGTGCCTTGT | 下游Downstream | aAt/aATAGCTGGCACAAACGGTGCCTTGTt |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83690874 | A | AT | AT, AT | A, A | A, A | N | 下游Downstream | tAt/tAT |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83691319 | G | GA | GA, GA | GA, GA | GA, GA | GA, GA | 下游Downstream | acGaaa/acGAaa |
表6 藜麦品系间CqSGT1s的DNA变异
Table 6 DNA variation of CqSGT1s among C. quinoa lines
基因 Gene | 染色体位置Chromosome location | Ref | Alt | JQ3 | JQ6 | Qingheili-8 | Qingbaili-9 | 影响Effect(其他突变系Other mutant lines) | 改变的密码子 The changed codon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqSGT1a | Chr06:34577463 | GA | G | GA, GA | GA, GA | GA, GA | G,G | 内含子Intron | GTa/Gat |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83675475 | A | AT | N | A, AT | A, AT | N | 上游Upstream | aAt/aAT |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83677523 | A | AC | AC, AC | AC, AC | AC, AC | AC, AC | 内含子Intron | aAc/aAC |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83679761 | CA | C | C, C | C, C | C, C | CA, C | 内含子Intron | cCA/cCa |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83679830 | TTTGTTGTTGTTG | T | TTTGTTGTTGTTG, TTTGTTGTTGTTG | N | N | TTTGTTGTTGTTG, T | 内含子Intron | cTTTGTTGTTGTTGT/cTt |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83689890 | A | ATAGCTGGCACAAACGGTGCCTTGT | A, A | A, ATAGCTGGCACAAACGGTGCCTTGT | A, ATAGCTGGCACAAACGGTGCCTTGT | A, ATAGCTGGCA CAAACGGTGCCTTGT | 下游Downstream | aAt/aATAGCTGGCACAAACGGTGCCTTGTt |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83690874 | A | AT | AT, AT | A, A | A, A | N | 下游Downstream | tAt/tAT |
| CqSGT1b | Chr07:83691319 | G | GA | GA, GA | GA, GA | GA, GA | GA, GA | 下游Downstream | acGaaa/acGAaa |
| [1] | Gómez-Caravaca A M, Iafelice G, Verardo V, et al. Influence of pearling process on phenolic and saponin content in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). Food Chemistry, 2014, 15(157): 174-178. |
| [2] | Jiang X D, Li X F, Hao Y P, et al. Gene cloning and express of squalene synthase and β-amyrin synthase from Chenopodium quinoa. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1214-1221. |
| 姜晓东, 李新凤, 郝艳平, 等. 藜麦β-香树酯醇合酶和鲨烯合酶基因的克隆与表达. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1214-1221. | |
| [3] | Jarvis D E, Ho Y S, Lightfoot D J, et al. The genome of Chenopodium quinoa. Nature, 2017, 542(7641): 307-312. |
| [4] | Bazile D, Fuentes F, Mujica A. Historical perspectives and domestication//Bhargava A. Quinoa: botany, production and uses. Wallingford: Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International, 2013: 16-35. |
| [5] | Hinojosa L, González J A, Barrios-Masias F H, et al. Quinoa abiotic stress responses: a review. Plants, 2018, 7(4): 106. |
| [6] | Wang C. Study on resistance evaluation of quinoa germplasms to downy mildew and its resistance mechanisms. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 王昶. 藜麦种质对霜霉病的抗性评价及其抗病机理研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2023. | |
| [7] | Wang C, Li M Q, Yang F R, et al. Diseases investigation and pathogen identification of quinoa downy mildew in Gansu Province. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture, 2023(3): 503-512. |
| 王昶, 李敏权, 杨发荣, 等. 甘肃藜麦霜霉病调查及其病原菌鉴定. 核农学报, 2023(3): 503-512. | |
| [8] | Yuan C L, Li C J, Zhao X B, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of HSP90-RAR1-SGT1-Complex members from Arachis genomes and their responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Frontiers in Genetics, 2021, 12: 689669. |
| [9] | Kitagawa K, Skowyra D, Elledge S J, et al. SGT1 encodes an essential component of the yeast kinetochore assembly pathway and a novel subunit of the SCF ubiquitin ligase complex. Molecular Cell, 1999, 4(1): 21-33. |
| [10] | Wang K, Zhang Z Y. Progress in studying the function of SGT1 in plant disease resistance response. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2008, 9(1): 115-118. |
| 王凯, 张增燕. SGT1在植物抗病反应中的功能研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报, 2008, 9(1): 115-118. | |
| [11] | Zhang D L, Yang X X, Wen Z Y, et al.Proxitome profiling reveals a conserved SGT1-NSL1 signaling module that activates NLR-mediated immunity. Molecular Plant, 2024, 17(9): 1369-1391. |
| [12] | Azevedo C, Sadanandom A, Kitagawa K, et al. The RAR1 interactor SGT1, an essential component of R gene-triggered disease resistance. Science, 2002, 295(5562): 2073-2076. |
| [13] | Wang K, Uppalapati S R, Zhu X H, et al. SGT1 positively regulates the process of plant cell death during both compatible and incompatible plant-pathogen interactions. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2010, 11(5): 597-611. |
| [14] | Makoto I, Ohnishi K, Hikichi Y, et al. Molecular chaperons and co-chaperons, Hsp90, RAR1, and SGT1 negatively regulate bacterial wilt disease caused by Ralstonia solanacearum in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2015, 10: e970410. |
| [15] | Kumar D, Kirt P B. Pathogen-induced SGT1of Arachis diogoi induces cell death and enhanced disease resistance in tobacco and peanut. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 13: 73-84. |
| [16] | Yu G, Xian L, Zhuang H Y, et al. SGT1 is not required for plant LRR-RLK-mediated immunity. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2021, 22(1): 145-150. |
| [17] | Chen Z Q, Wu Q, Tong C, et al. Characterization of the roles of SGT1/RAR1, EDS1/NDR1, NPR1, and NRC/ADR1/NRG1 in Sw-5b-mediated resistance to tomato spotted wilt virus. Viruses, 2021, 13(8): 1447. |
| [18] | Shanmugam A, Thamilarasan S K, Park J I, et al. Characterization and abiotic stress-responsive expression analysis of SGT1 genes in Brassica oleracea. Genome, 2016, 59: 243-251. |
| [19] | Berens M L, Berry H M, Mine A, et al. Evolution of hormone signaling networks in plant defense. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2017, 55(1): 401-425. |
| [20] | Váczy K Z, Otto M, Gomba-Tóth A, et al. Botrytis cinerea causes different plant responses in grape (Vitis vinifera) berries during noble and grey rot: diverse metabolism versus simple defence. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 1433161. |
| [21] | Yu G, Xian L, Xue H, et al. A bacterial effector protein prevents MAPK-mediated phosphorylation of SGT1to suppress plant immunity. PLoS Pathogens, 2020, 16(9): e1008933. |
| [22] | Peart J R, Lu R, Sadanandom A, et al. Ubiquitin ligase-associated protein SGT1 is required for host and nonhost disease resistance in plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(16): 10865-10869. |
| [23] | Zhu X D, Yang L F, Chen Y Y, et al. Biological functional analysis of common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) FeSGT1 gene in enhancing drought stress resistance. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(6): 1573-1583. |
| 朱旭东, 杨兰锋, 陈媛媛, 等. 甜荞FeSGT1基因克隆及抗旱功能解析. 作物学报, 2023, 49(6): 1573-1583. | |
| [24] | Agarwal G, Garg V, Kudapa H, et al. Genome-wide dissection of AP2/ERF and HSP90 gene families in five legumes and expression profiles in chickpea and pigeonpea. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14: 1563-1577. |
| [25] | Zou C S, Chen A J, Xiao L H, et al. A high-quality genome assembly of quinoa provides insights into the molecular basis of salt bladder-based salinity tolerance and the exceptional nutritional value. Cell Research, 2017, 27(11): 1327-1340. |
| [26] | Xie Y J, Xue J, Jiang X D, et al. Screening of reference genes in Chenopodium quinoa under Peronospora variabilis stress and verification of their stability. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 53(2): 191-198. |
| 解宇洁, 薛婧, 姜晓东, 等. 霜霉病菌胁迫下藜麦内参基因的筛选及其稳定性验证. 福建农林大学(自然科学版), 2024, 53(2): 191-198. | |
| [27] | Koua A P, Oyiga B C, Baig M M, et al. Breeding driven enrichment of genetic variation for key yield components and grain starch content under drought stress in winter wheat. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 684205. |
| [28] | Meldau S, Baldwin I T, Wu J Q. For security and stability: SGT1 in plant defense and development. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2011, 6(10): 1479-1482. |
| [29] | Holt B F, Belkhadir Y, Dangl J L. Antagonistic control of disease resistance protein stability in the plant immune system. Science, 2005, 309(5736): 929-932. |
| [30] | Muskett P, Parker J. Role of SGT1 in the regulation of plant R gene signaling. Microbes and Infection, 2003, 5(11): 969-976. |
| [31] | Chen X Y, Li X B, Duan Y H, et al. A secreted fungal subtilase interferes with rice immunity via degradation of suppressor of G2 allele of skp1. Plant Physiology, 2022, 190(2): 1474-1489. |
| [32] | Wang Y Q, Liu C, Du Y Y, et al. A stripe rust fungal effector PstSIE1 targets TaSGT1 to facilitate pathogen infection. The Plant Journal, 2022, 112(6): 1413-1428. |
| [33] | Steven S R, Huang L, Brandt A S, et al. Development of a virus-induced gene-silencing system for hexaploid wheat and its use in functional analysis of the Lr21-mediated leaf rust resistance pathway. Plant Physiology, 2005, 138(4): 2165-2173. |
| [34] | Li X B. Functional characterization of subtilisin-like protease family genes in Ustilaginoidea virens. Changsha: Central China Agricultural University, 2022. |
| 李夏冰. 稻曲菌枯草杆菌蛋白酶家族基因功能研究. 长沙: 华中农业大学, 2022. | |
| [35] | Ouyang X, Chen J L, Sun Z M, et al. Ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of Ralstonia solanacearum effector RipAW is not essential for induction of plant defense in Nicotiana benthamiana. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14: 1201444. |
| [36] | Zhang C L, Xu D C, Jiang X C. Improvement of disease resistance of sugar beet by molecular breeding. China Beet & Sugar, 2008(2): 23-26. |
| 张春来, 徐德昌, 姜孝成. 分子育种提高甜菜抗病性. 中国甜菜糖业, 2008(2): 23-26. | |
| [37] | Guo W L, Chen B H, Guo Y Y, et al. Improved powdery mildew resistance of transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana overexpressing the Cucurbita moschata CmSGT1 gene. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 955. |
| [38] | Forner-Giner M Á, Rodríguez-Gamir J, Primo-Millo E, et al. Hydraulic and chemical responses of citrus seedlings to drought and osmotic stress. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2011, 30(3): 353-366. |
| [39] | Luna C M, Pastori G M, Driscoll S, et al. Drought controls on H2O2 accumulation, catalase (CAT) activity and CAT gene expression in wheat. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2005, 56(411): 417-423. |
| [40] | Baczek-Kwinta R, Filek W, Grzesiak S, et al. The effect of soil drought and rehydration on growth and antioxidative activity in flag leaves of triticale. Biologia Plantarum, 2006, 50(1): 55-60. |
| [41] | Mhamdi A, Queval G, Chaouch S, et al. Catalase function in plants: a focus on Arabidopsis mutants as stress-mimic models. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(15): 4197-4220. |
| [42] | Jiang J M, Chen J T, Luo L, et al. Expression analysis reveals that sorghum disease resistance protein SbSGT1 is regulated by auxin. Biology, 2022, 11(1): 67. |
| [43] | Li R Q, Zheng W Y, Yang R F, et al. OsSGT1promotes melatonin-ameliorated seed tolerance to chromium stress by affecting the OsABI5-OsAPX1 transcriptional module in rice. The Plant Journal, 2022, 112(1): 151-171. |
| [44] | Noël L D, Cagna G, Stuttmann J, et al. Interaction between SGT1 and cytosolic/nuclear HSC70 chaperons regulates Arabidopsis immune responses. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(12): 4061-4076. |
| [1] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [2] | 王昶, 闵庚梅, 张丽娟, 陆建英, 牛早霞, 魏玉明, 杨发荣. 藜麦霜霉病及其综合防控研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 194-205. |
| [3] | 赵媛媛, 蒲小剑, 徐成体, 王伟, 傅云洁. 蒺藜苜蓿MtBMI1基因克隆及抗旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 139-153. |
| [4] | 周昕越, 王丽萍, 蒋庆雪, 马晓冉, 仪登霞, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿低温诱导蛋白MsLTI65的分离及其对不同逆境的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 89-104. |
| [5] | 汪欣瑶, 彭亚萍, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草HgS5基因的克隆与抗旱性鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 184-195. |
| [6] | 李永龙, 周生辉, 薛梦瑶, 高远, 巨乐, 陈奕冰, 付松林, 郝建昊, 李恒, 张昆, 左志芳. 结缕草ZjWRKY63基因的克隆及转基因拟南芥的耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 157-169. |
| [7] | 边林, 张岩, 霍晓伟, 代蕊, 郭娜, 伊风艳, 高翠萍, 张志强. 紫花苜蓿CKX基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 125-135. |
| [8] | 秦楠, 曹瑞鹏, 高婧涵, 彭玉飞, 田淼, 吕红, 任璐, 殷辉, 赵晓军. 藜麦种子可培养内生真菌鉴定及分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 98-113. |
| [9] | 贺龙义, 谭萌萌, 车海涛, 张红鹰, 朱雨欣, 张彦妮. 细叶百合LpDREB9基因克隆及耐旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 161-173. |
| [10] | 吴毅, 冯雅岚, 王添宁, 琚吉浩, 肖慧淑, 马超, 张均. 小麦及其祖先物种Hsp70基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 53-67. |
| [11] | 张震欢, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草AKR基因家族成员的鉴定及根系盐胁迫响应基因HgAKR42639的耐盐分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 68-83. |
| [12] | 孔海明, 宋家兴, 杨静, 李倩, 杨培志, 曹玉曼. 紫花苜蓿CAMTA基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [13] | 黎泽斌, 邱永争, 刘延杰, 喻金秋, 王柏吉, 刘千宁, 王月, 崔国文. 紫花苜蓿BZR基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 106-122. |
| [14] | 周昕越, 蒋庆雪, 贾会丽, 马琳, 樊璐, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX20基因克隆及耐盐功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 55-73. |
| [15] | 胡尚钦, 汪军成, 姚立蓉, 司二静, 马小乐, 杨轲, 张宏, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草根系基因HgAKR6C的克隆与初步功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 61-74. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||