

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 69-78.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021179
孙晓梵1( ), 张一龙1, 李培英1,2,3(
), 张一龙1, 李培英1,2,3( ), 孙宗玖1,2,3
), 孙宗玖1,2,3
收稿日期:2021-05-07
修回日期:2021-06-09
出版日期:2022-06-20
发布日期:2022-05-11
通讯作者:
李培英
作者简介:E-mail: 823797457@qq.com基金资助:
Xiao-fan SUN1( ), Yi-long ZHANG1, Pei-ying LI1,2,3(
), Yi-long ZHANG1, Pei-ying LI1,2,3( ), Zong-jiu SUN1,2,3
), Zong-jiu SUN1,2,3
Received:2021-05-07
Revised:2021-06-09
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-05-11
Contact:
Pei-ying LI
摘要:
为探讨干旱下施氮肥是否可以提高狗牙根抗旱性,以新农1号狗牙根为材料,干旱前进行不施氮(0 mmol·L-1)、低氮(1.5 mmol·L-1)、中氮(7.5 mmol·L-1)、高氮(15.0 mmol·L-1) 4种施氮处理,盆栽试验控制水分缓慢干旱,在干旱0、7、14 d、复水7 d,测定草坪质量、叶片相对含水量、相对电导率、丙二醛含量、抗氧化酶活性[超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)]、过氧化氢以及渗透调节物质可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸、可溶性糖含量,并对干旱7、14 d下狗牙根抗旱性响应指标进行热图聚类及主成分分析。结果表明,不同施氮量对狗牙根草坪质量的影响因干旱程度不同而有所不同。正常灌溉和中度干旱下高氮处理(15 mmol·L-1)下狗牙根表现出较好的草坪质量,而中氮处理(7.5 mmol·L-1) 能显著提高其重度干旱下草坪质量。与干旱对照相比,干旱处理下施中氮可使狗牙根叶片相对含水量、CAT活性、SOD活性、可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸和可溶性糖含量依次显著提高60.98%、154.40%、163.73%、61.75%、144.71%和31.53%,维持较高的草坪质量。且复水后中氮和高氮处理狗牙根草坪质量恢复较快,可能是由于在干旱胁迫时受到损伤较小。综上认为,干旱前施中氮,可以一定程度缓解干旱胁迫对狗牙根幼苗造成的伤害。
孙晓梵, 张一龙, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同施氮量对干旱下狗牙根抗氧化酶活性及渗透调节物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 69-78.
Xiao-fan SUN, Yi-long ZHANG, Pei-ying LI, Zong-jiu SUN. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on antioxidant activity and content of substances involved in osmotic adjustment in Cynodon dactylon under drought stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 69-78.
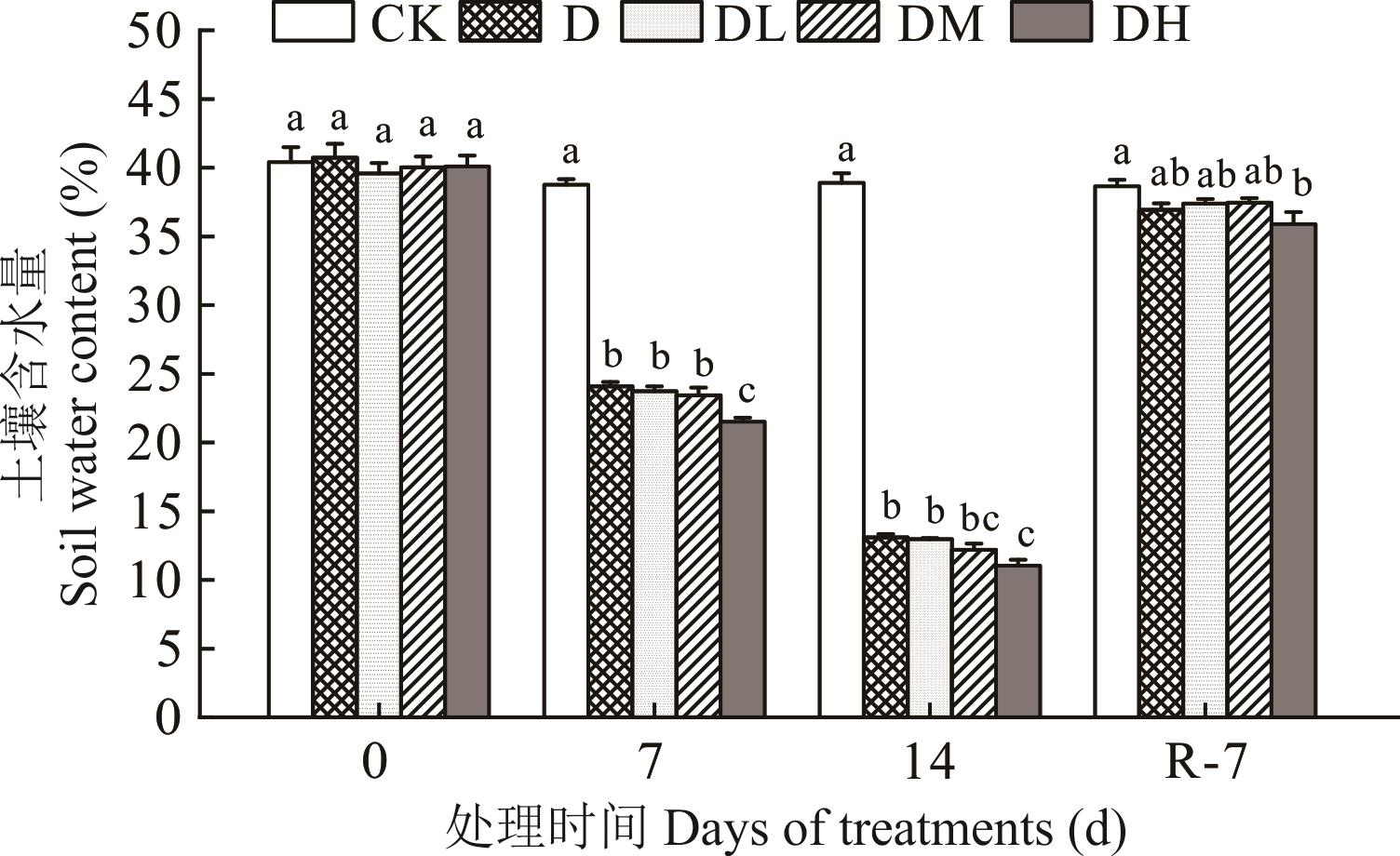
图1 干旱及复水对土壤含水量的影响不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),大写字母CK、D、DL、DM、DH分别表示正常灌溉+无氮、干旱+无氮、低氮+干旱、中氮+干旱、高氮+干旱,数字0、7、14、R-7分别代表第0、7、14天及复水7天后的处理天数,下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments (P<0.05). CK, D, DL, DM, DH indicate normal irrigation+No-n, drought+No-n, low-n+drought, medium-n+drought, high-n+drought respectively, the numbers 0, 7, 14 and R-7 represent the treatment days after day 0, 7, 14 and the 7th day after re-watering respectively. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of drought and re-watering on soil water content

图2 干旱及复水下不同施氮量对狗牙根幼苗草坪质量和叶片相对含水量的影响
Fig.2 Effects of different nitrogen rates on turf quality and leaf relative water content of bermudagrass seedlings under drought and re-watering

图3 干旱及复水下不同施氮量对狗牙根幼苗相对电导率及丙二醛含量的影响
Fig.3 Effects of different nitrogen rates on relative electric conductivity and MDA content of bermudagrass seedlings under drought and re-watering
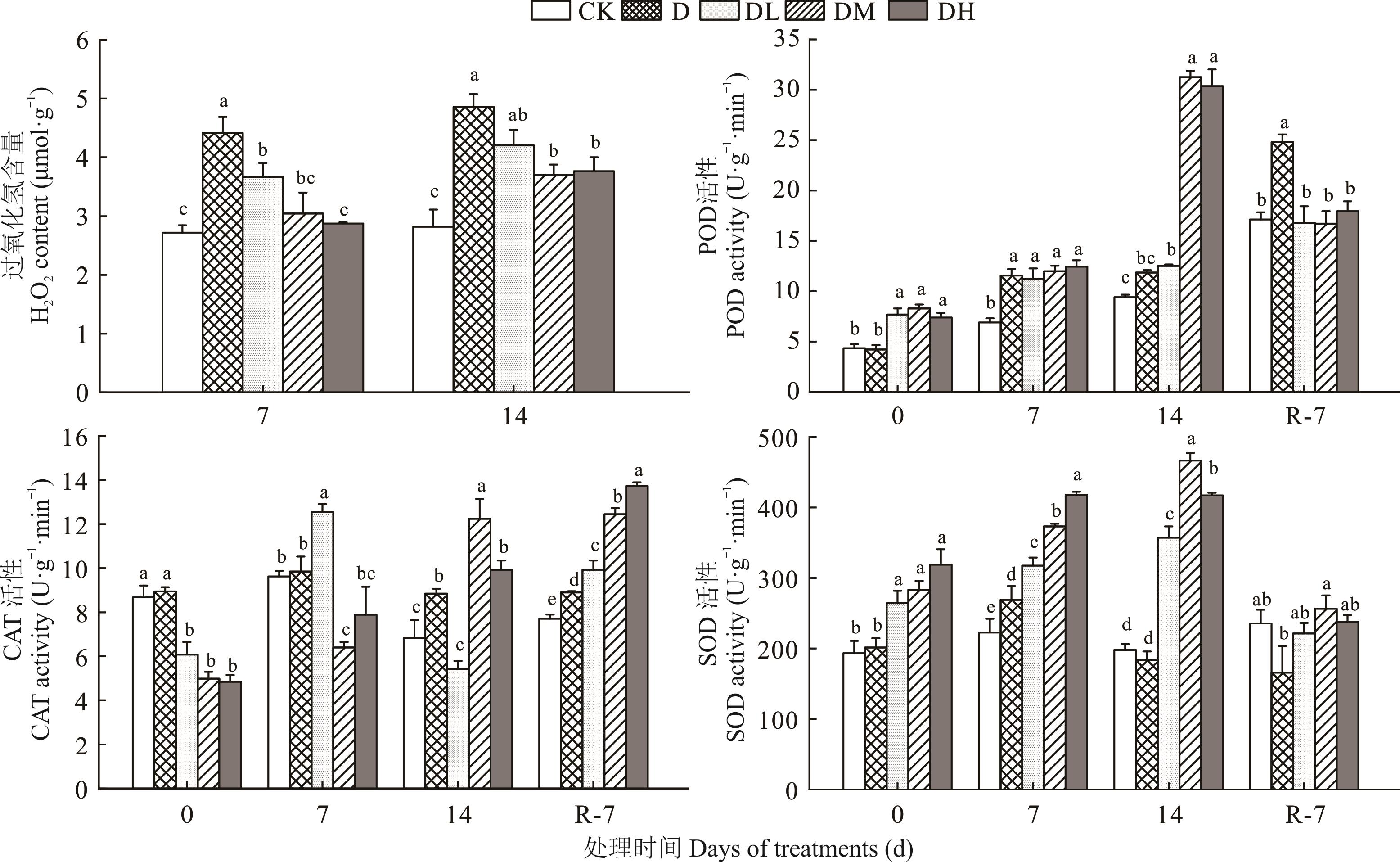
图4 干旱及复水下不同施氮量对狗牙根幼苗H2O2含量及抗氧化酶活性的影响
Fig.4 Effects of different nitrogen rates on H2O2 content and antioxidant enzyme activities of bermudagrass seedlings under drought and re-watering

图5 干旱胁迫及复水下不同施氮量对狗牙根幼苗可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸和可溶性糖含量的影响
Fig.5 Effects of different nitrogen rates on soluble protein, proline and soluble sugar content of bermudagrass seedlings under drought and re-watering

图6 干旱下不同施氮量对狗牙根幼苗各指标热图聚类分析以及主成分分析
Fig.6 Heat map cluster analysis and principal component analysis of different nitrogen application rates on the indexes of bermudagrass seedlings under drought
| 1 | Chai Q, Jin F, Merewitz E, et al. Growth and physiological traits associated with drought survival and post-drought recovery in perennial turfgrass species. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 2010, 135(2): 125-133. |
| 2 | He L. Water-saving measures in landscaping design in arid area. The Journal of Hebei Forestry Science and Technology, 2013(12): 61-63. |
| 何磊. 干旱区园林绿化设计中的节水措施. 河北林业科技, 2013(12): 61-63. | |
| 3 | Qin F F, Shen Y X, Li L H, et al. Effect of drought stress on the photosynthetic characteristics and water use efficiency of three dominant forage grasses in Sinkiang. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(10): 86-94. |
| 覃凤飞, 沈益新, 李兰海, 等. 干旱胁迫对新疆三个优势牧草种的光合特性与水分利用效率的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(10): 86-94. | |
| 4 | Wei X R, Zhang Z W, Zhou Y, et al. Effects of melatonin on growth and antioxidant system of perennial ryegrass seedlings under cold and drought stresses. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1337-1345. |
| 尉欣荣, 张智伟, 周雨, 等. 褪黑素对低温和干旱胁迫下多年生黑麦草幼苗生长和抗氧化系统的调节作用. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1337-1345. | |
| 5 | Wang Y L. Physiology responses of kiwifruit seedlings to re-watering and exogenous application of abscisicacid under drought conditions. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2010. |
| 王岩磊. 复水与外源脱落酸处理对干旱胁迫下猕猴桃幼苗抗旱性的影响. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2010. | |
| 6 | Wu W, Zhao J. Advances on plants’ nitrogen assimilation and utilization. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(13): 75-78. |
| 吴巍, 赵军. 植物对氮素吸收利用的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(13): 75-78. | |
| 7 | Zhao T T, Zhen S L, Wan N X, et al. Effects of early application of nitrogen on drought-resistance capability of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(5): 185-190. |
| 赵婷婷, 郑顺林, 万年鑫, 等. 早期施氮对马铃薯苗期抗旱能力的影响. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(5): 185-190. | |
| 8 | Zhang R H, Guo D W, Zhang X H, et al. Effects of nitrogen on photosynthesis and antioxidant enzyme activities of maize leaf under drought stress. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2012, 20(6): 118-122. |
| 张仁和, 郭东伟, 张兴华, 等. 干旱胁迫下氮肥对玉米叶片生理特性的影响. 玉米科学, 2012, 20(6): 118-122. | |
| 9 | Ahmadi S, Ebadi A, Jahanbakhsh S, et al. Changes in enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidant defense mechanisms of canola seedlings at different drought stress and nitrogen levels. Turkish Journal of Agriculture & Forestry, 2015, 39(5): 601-612. |
| 10 | Zhao Y P, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on physiological characteristics of Perilla frutescens seedlings under different drought stress.Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2020, 32(4): 61-66. |
| 赵永平, 张毅, 朱亚, 等. 施氮对不同干旱胁迫条件下紫苏幼苗生理特性的影响. 江西农业学报, 2020, 32(4): 61-66. | |
| 11 | Hu Z M, Yu G R, Fan J W, et al. Precipitation-use efficiency along a 4500-km grassland transect. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2010, 19(6): 842-851. |
| 12 | Chang Z, Liu Y, Dong H, et al. Effects of cytokinin and nitrogen on drought tolerance of creeping bentgrass. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0154005. |
| 13 | Li J J, Chen Y J, Zhang L, et al. Effects of water-nitrogen interaction on physiological-biochemical indexes and turf quality of Poa pratensis L.Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2016, 38(4): 42-48. |
| 李静静, 陈雅君, 张璐, 等. 水氮交互作用对草地早熟禾生理生化与坪用质量的影响. 中国草地学报, 2016, 38(4): 42-48. | |
| 14 | Sun X N, Zhao J Y, Sun F L, et al. Nitrogen rate effects on the establishment of bermudagrass from stolons. Forestry and Ecological Sciences, 2019, 34(4): 431-435. |
| 孙熙喏, 赵佳愉, 孙福来, 等. 氮素用量对狗牙根营养体建坪效果的影响. 林业与生态科学, 2019, 34(4): 431-435. | |
| 15 | Hang C Y. Soil science. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 黄昌勇. 土壤学. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 16 | Hanson A D, Rathinasabapathi B, Rivoal J, et al. Osmoprotective compounds in the Plumbaginaceae: A natural experiment in metabolic engineering of stress tolerance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91(1): 306-310. |
| 17 | Zou Q. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 邹琦. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 18 | Wang Y J. Study on population quality and individual physiological functions of super high-yield summer maize. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2008. |
| 王永军. 超高产夏玉米群体质量与个体生理功能研究. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2008. | |
| 19 | Wang Y L. Plant physiology experiment guidance. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 王燕凌. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 20 | Li H S. Principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry experiments. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. | |
| 21 | Zeng L S, Li P Y. Evaluation on drought resistance of 10 bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) germplasms from Xinjiang. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(3): 22-29. |
| 曾令霜, 李培英. 10份新疆狗牙根种质抗旱性评价. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(3): 22-29. | |
| 22 | Wang J M. Effects of nitrogen level of physiology indication of kentucky bluegrass under water stress. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2012. |
| 王晶懋. 水分胁迫下氮素水平对早熟禾生理指标的影响. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2012. | |
| 23 | Song C, Ma K, Qu L, et al. Interactive effects of water, nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth, biomass partitioning and water-use efficiency of Bauhinia faberi seedlings. Journal of Arid Environments, 2010, 74(9): 1003-1012. |
| 24 | Gu Y, Zhao Y, Ji C D. The effect of silicon fertilizer on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of bermudagrass under salt stress. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(3): 30-37. |
| 顾跃, 赵云, 姬承东. 硅肥对盐胁迫下狗牙根生理生化特征的影响. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(3): 30-37. | |
| 25 | Fu J M, Huang B R. Effects of foliar application of nutrients on heat tolerance of creeping bentgrass. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2003, 26(1): 81. |
| 26 | Zhang C L, Zeng G P, Chen J X. Effects of drought stress on the protective enzymes activities and membrane lipid peroxidation in leaves of Brassica parachinensis L. H. Bailey. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2000, 9(4): 23-26, 33. |
| 章崇玲, 曾国平, 陈建勋. 干旱胁迫对菜苔叶片保护酶活性和膜脂过氧化的影响. 植物资源与环境学报, 2000, 9(4): 23-26, 33. | |
| 27 | Ai X Y, Wu Q, Zhou Y F, et al. Effects of nitrogen on photosynthesis and antioxidant enzyme activities of sorghum under drought stress and re-watering.Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2019, 37(5): 99-105, 113. |
| 艾雪莹, 吴奇, 周宇飞, 等. 干旱-复水条件下氮素对高粱光合特性及抗氧化代谢的影响.干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(5): 99-105, 113. | |
| 28 | Sun H, Zhang Y P, Wu J C, et al. Effect of drought stress and shading on growth and carbon-nitrogen metabolism of Azadirachta indica seedlings.Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(3): 463-470. |
| 孙恒, 张燕平, 吴疆翀, 等. 干旱胁迫和遮光对印楝幼苗生长及碳氮代谢的影响. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(3): 463-470. | |
| 29 | Hoai N T T, Shim I S, Kobayashi K, et al. Accumulation of some nitrogen compounds in response to salt stress and their relationships with salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Plant Growth Regulation, 2003, 41(2): 159-164. |
| [1] | 金祎婷, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 梁国玲, 贾志锋. 全生育期干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 112-126. |
| [2] | 苏世平, 李毅, 刘小娥, 种培芳, 单立山, 后有丽. 外源脯氨酸对缓解红砂干旱胁迫的机理研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 127-138. |
| [3] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 黄书超, 杨琰珊, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 张银翠. 微生物肥料与化肥减量配施对多年生黑麦草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 136-143. |
| [4] | 王志恒, 魏玉清, 赵延蓉, 王悦娟. 基于转录组学比较研究甜高粱幼苗响应干旱和盐胁迫的生理特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 71-84. |
| [5] | 高鹏飞, 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧. 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系特征、结构和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 203-212. |
| [6] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [7] | 赵颖, 辛夏青, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. |
| [8] | 柳福智, 张迎芳, 陈垣. 外源海藻糖对NaHCO3胁迫下甘草幼苗生长调节及总黄酮含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 148-156. |
| [9] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [10] | 罗巧玉, 王彦龙, 陈志, 马永贵, 任启梅, 马玉寿. 水分逆境对发草脯氨酸及其代谢途径的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 75-83. |
| [11] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| [12] | 刘凯强, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 梁国玲, 马祥. 干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦产量及干物质积累与分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 177-188. |
| [13] | 田甜, 王海江, 王金刚, 朱永琪, 史晓艳, 李维弟, 李文瑞玉. 盐胁迫下施加氮素对饲用油菜有机渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 125-136. |
| [14] | 李冬, 申洪涛, 王艳芳, 王悦华, 王丽君, 赵世民, 刘领. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗光合碳同化和内源激素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 130-139. |
| [15] | 张利霞, 常青山, 薛娴, 刘伟, 张巧明, 陈苏丹, 郑轶琦, 李景林, 陈婉东, 李大钊. 酸胁迫对夏枯草叶绿素荧光特性和根系抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 134-142. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||