

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 55-73.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023460
周昕越1( ), 蒋庆雪1, 贾会丽2, 马琳1, 樊璐1, 王学敏1(
), 蒋庆雪1, 贾会丽2, 马琳1, 樊璐1, 王学敏1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-09
修回日期:2024-01-12
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-07-15
通讯作者:
王学敏
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: wangxuemin@caas.cn基金资助:
Xin-yue ZHOU1( ), Qing-xue JIANG1, Hui-li JIA2, Lin MA1, Lu FAN1, Xue-min WANG1(
), Qing-xue JIANG1, Hui-li JIA2, Lin MA1, Lu FAN1, Xue-min WANG1( )
)
Received:2023-11-09
Revised:2024-01-12
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-07-15
Contact:
Xue-min WANG
摘要:
BBX家族转录因子参与光形态建成、成花生理、避荫反应、种子生长发育、激素信号转导及对逆境胁迫的响应等植物重要生长发育过程。紫花苜蓿是耐盐性较强的牧草饲料作物,其品质优良,有“牧草之王”的美誉。发掘并探索紫花苜蓿MsBBX20基因响应非生物胁迫的分子机理,有助于揭示紫花苜蓿抗逆生物学基础,为紫花苜蓿抗逆分子育种提供新的基因资源。通过RT-PCR、3′/5′RACE PCR技术克隆得到MsBBX20基因cDNA序列,生物信息学分析发现其CDS全长834 bp,编码278个氨基酸,该基因编码的蛋白质为锌指结构蛋白家族成员。利用qRT-PCR技术分析MsBBX20在紫花苜蓿不同组织和不同非生物胁迫下的表达模式。通过基因枪轰击技术,在洋葱表皮瞬时表达MsBBX20进行亚细胞定位。克隆得到大小为1737 bp的MsBBX20启动子序列并分析了顺式作用元件,该启动子可驱动GUS报告基因在烟草的叶、茎和根中高效表达。将MsBBX20启动子序列与包含GUS基因的pCAMBIA-1301载体连接,瞬时转化烟草并通过组织化学染色对不同组织进行GUS活性分析。构建pCAMBIA3301-MsBBX20植物超表达载体,通过农杆菌介导的方法遗传转化野生型拟南芥,获得超表达MsBBX20的拟南芥株系。用不同浓度盐溶液(150、200和300 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理拟南芥转基因株系并分析其MDA含量和抗氧化酶活性。进化分析表明紫花苜蓿MsBBX20蛋白与红三叶TpBBX20的亲缘关系最近。MsBBX20蛋白定位于细胞核。MsBBX20基因在花中表达量最高,且MsBBX20可以响应干旱、盐、冷、脱落酸、赤霉素、光照等多种非生物胁迫。遗传转化获得MsBBX20过表达拟南芥株系,并选择3个高表达阳性株系进行功能验证。在不同浓度NaCl处理条件下,过量表达MsBBX20的拟南芥株系的丙二醛(MDA)含量显著低于对照,而超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和过氧化物酶(POD)活性均显著高于对照。克隆获得紫花苜蓿锌指蛋白转录因子基因MsBBX20,该基因在花中表达量最高,能够响应多种非生物逆境胁迫和外源激素处理,表明MsBBX20可能参与紫花苜蓿的多个逆境响应过程。进一步的研究证明MsBBX20可能通过调节植物的抗氧化酶系统,缓解逆境造成的植物细胞氧化损伤,提高转基因拟南芥对盐胁迫的抗性,进而增强植株的耐盐性。
周昕越, 蒋庆雪, 贾会丽, 马琳, 樊璐, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX20基因克隆及耐盐功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 55-73.
Xin-yue ZHOU, Qing-xue JIANG, Hui-li JIA, Lin MA, Lu FAN, Xue-min WANG. Cloning and salt-tolerance functional analysis of alfalfa MsBBX20 gene[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 55-73.
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5'→3′) | 用途Function |
|---|---|---|
| BBX-3′-RACE | GGACCCAGATTCATCATCCACCA | 基因克隆Gene cloning |
| BBX-5′-RACE | CAGAGCCAATACTGGTGGATGATGA | |
| BBX-ORF-F | ATGAAGATCCAATGTGATGTGTGTG | |
| BBX-ORF-R | TTATCGAAAGTGTCTAGATTTTTTTATG | |
| BBX-Real-up | CCACCAGTATTGGCTCTGAACC | |
| BBX-Real-low | CCTGTGTCACTAGCCATGTTGTCT | |
| MsBBX20-SP1 | AGGGTAGTCTTTGGAGTTGAGGTGA | 启动子克隆Promoter cloning |
| MsBBX20-SP2 | TTGTTGGCACGGTGGATGGTATGAT | |
| MsBBX20-SP3 | CCTCAGCTTTCTCACACACATCAC | |
| BBX-1301-EcoRⅠ | TATGACCATGATTACGAATTCCGTACCTCACTAGTACCCAATTACA | |
| BBX-1301-NcoⅠ | ACCCTCAGATCTACCATGGCCTCAGCTTTCTCACACACATCACA | |
| BBX-PA7-GFP-Xho | TACTCGAGATGAAGATCCAATGTGATGTGT | |
| BBX-PA7-GFP-SpeⅠ | GCACTAGTTCGAAAGTGTCTAGATTTTTTTA | |
| BBX-3301-BglⅡ | TGACCATGGTAGATCTGATGAAGATCCAATGTGATGTGTGTG | |
| BBX-3301-BstEⅡ | ATTCGAGCTGGTCACCTTATCGAAAGTGTCTAGATTTTTTTATG | |
| 35S-3301-F | AACAGAACTCGCCGTAAAGACT | |
| MsActin2-F | 内参基因Reference genes | |
| MsActin2-R | ||
| AtActin-F | GGACAAGTTATCACCATCGG | |
| AtActin-R | ATTGGGCAGTTTCTTTGGTAGC |
表1 所用引物信息
Table 1 Primer information used in the experiment
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5'→3′) | 用途Function |
|---|---|---|
| BBX-3′-RACE | GGACCCAGATTCATCATCCACCA | 基因克隆Gene cloning |
| BBX-5′-RACE | CAGAGCCAATACTGGTGGATGATGA | |
| BBX-ORF-F | ATGAAGATCCAATGTGATGTGTGTG | |
| BBX-ORF-R | TTATCGAAAGTGTCTAGATTTTTTTATG | |
| BBX-Real-up | CCACCAGTATTGGCTCTGAACC | |
| BBX-Real-low | CCTGTGTCACTAGCCATGTTGTCT | |
| MsBBX20-SP1 | AGGGTAGTCTTTGGAGTTGAGGTGA | 启动子克隆Promoter cloning |
| MsBBX20-SP2 | TTGTTGGCACGGTGGATGGTATGAT | |
| MsBBX20-SP3 | CCTCAGCTTTCTCACACACATCAC | |
| BBX-1301-EcoRⅠ | TATGACCATGATTACGAATTCCGTACCTCACTAGTACCCAATTACA | |
| BBX-1301-NcoⅠ | ACCCTCAGATCTACCATGGCCTCAGCTTTCTCACACACATCACA | |
| BBX-PA7-GFP-Xho | TACTCGAGATGAAGATCCAATGTGATGTGT | |
| BBX-PA7-GFP-SpeⅠ | GCACTAGTTCGAAAGTGTCTAGATTTTTTTA | |
| BBX-3301-BglⅡ | TGACCATGGTAGATCTGATGAAGATCCAATGTGATGTGTGTG | |
| BBX-3301-BstEⅡ | ATTCGAGCTGGTCACCTTATCGAAAGTGTCTAGATTTTTTTATG | |
| 35S-3301-F | AACAGAACTCGCCGTAAAGACT | |
| MsActin2-F | 内参基因Reference genes | |
| MsActin2-R | ||
| AtActin-F | GGACAAGTTATCACCATCGG | |
| AtActin-R | ATTGGGCAGTTTCTTTGGTAGC |
生物信息学工具 Bioinformatics tools | 网址 Website | 用途 Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Open reading frame finder | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/ | 开放阅读框分析Open reading frame analysis |
| SMART | https://smart.embl.de/ | 蛋白质保守结构域分析Protein conserved domain analysis |
| Expasy-ProtParam tool | https://web.expasy.org/protparam/ | 蛋白质理化性质分析Analysis of physical and chemical properties of proteins |
| PRABI | https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa%20_sopma.html | 蛋白质二级结构分析Protein secondary structure analysis |
| BLAST | https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi | 同源蛋白序列分析Homologous protein sequence analysis |
| DNAMAN | https://www.lynnon.com/qa.html | 多序列比对Multiple sequence alignment |
| Plant CARE | https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/ | 顺式作用元件分析Cis-acting element analysis |
| MEGA | https://www.megasoftware.net/ | 系统进化树构建Phylogenetic tree construction |
表2 所用生物信息学工具
Table 2 Bioinformatics tools used
生物信息学工具 Bioinformatics tools | 网址 Website | 用途 Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Open reading frame finder | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/ | 开放阅读框分析Open reading frame analysis |
| SMART | https://smart.embl.de/ | 蛋白质保守结构域分析Protein conserved domain analysis |
| Expasy-ProtParam tool | https://web.expasy.org/protparam/ | 蛋白质理化性质分析Analysis of physical and chemical properties of proteins |
| PRABI | https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa%20_sopma.html | 蛋白质二级结构分析Protein secondary structure analysis |
| BLAST | https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi | 同源蛋白序列分析Homologous protein sequence analysis |
| DNAMAN | https://www.lynnon.com/qa.html | 多序列比对Multiple sequence alignment |
| Plant CARE | https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/ | 顺式作用元件分析Cis-acting element analysis |
| MEGA | https://www.megasoftware.net/ | 系统进化树构建Phylogenetic tree construction |
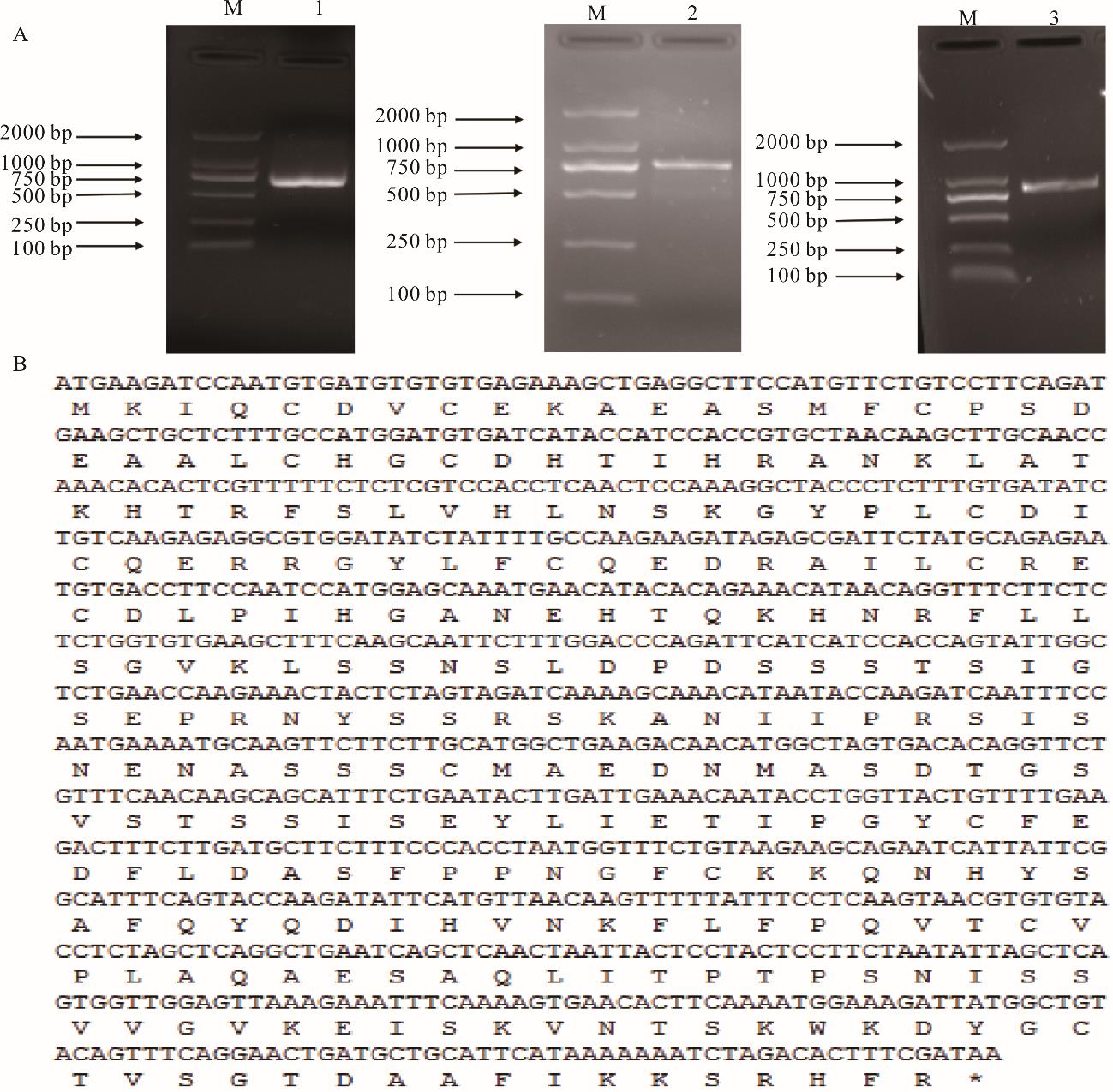
图1 MsBBX20的克隆与cDNA全长及对应蛋白序列A:紫花苜蓿MsBBX20基因RACE-PCR结果;M: DL2000;1:3′-RACE 产物;2:5′-RACE 产物;3:ORF扩增产物。A:Results of RACE-PCR for MsBBX20 gene of M. sativa; M: DL2000 DNA marker; 1: 3′-RACE product; 2: 5′-RACE product; 3: ORF amplified product; B: MsBBX20的cDNA全序列 Full cDNA sequence of MsBBX20.
Fig.1 Cloning and full-length cDNA sequence of MsBBX20
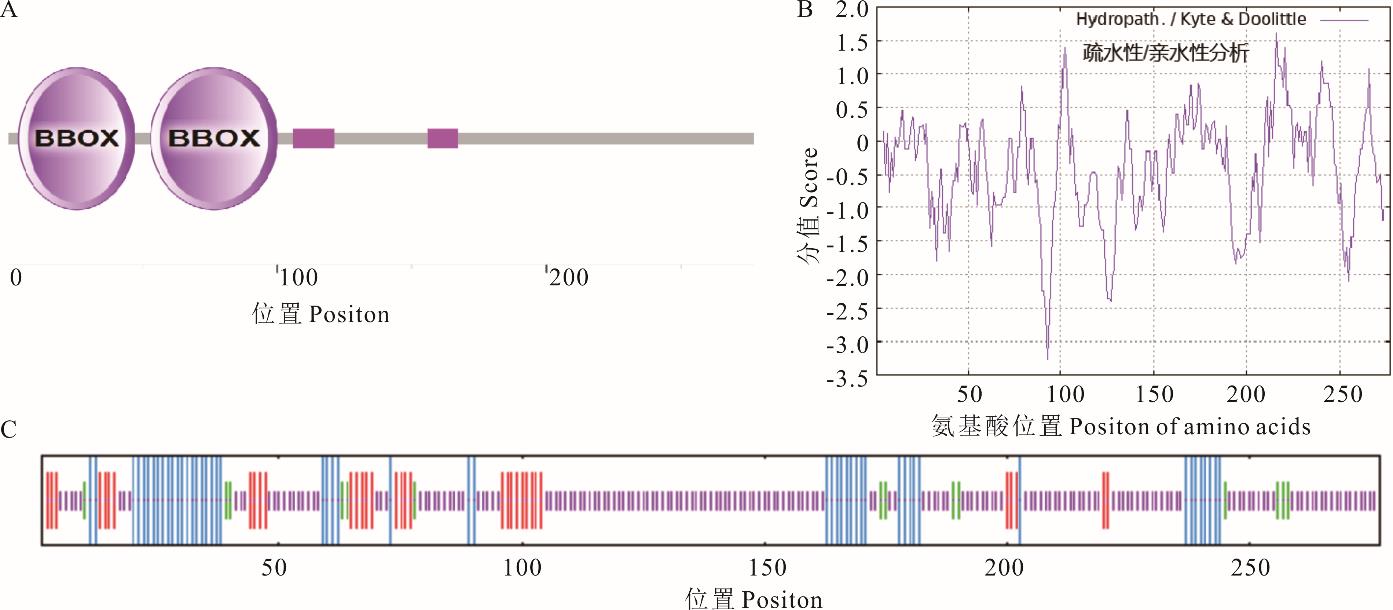
图2 MsBBX20蛋白结构特征分析A: MsBBX20蛋白保守结构域 MsBBX20 protein conserved domain; B: MsBBX20蛋白的亲疏水性 The hydrophilicity of MsBBX20 protein; C: MsBBX20蛋白的二级结构;蓝色:α螺旋;绿色:β折叠;紫色:无规则卷曲;红色:延伸链。Secondary structure of MsBBX20 protein; Blue: Alpha helix; Green: Beta fold; Purple: Random curling; Red: Extended chain.
Fig.2 Structural characterization analysis of MsBBX20 protein

图3 MsBBX20编码氨基酸多序列比对Ms:紫花苜蓿;Mt:蒺藜苜蓿;Ca:鹰嘴豆;Gs:野大豆;Tp:红三叶;Va:赤豆;Gm:大豆;Ps:豌豆。下同。Ms: M. sativa; Mt: M. truncatula; Ca: C. arietinum; Gs: G. soja; Tp: T. pratense; Va: V. angularis; Gm: G. max; Ps: P. sativum. The same below.
Fig.3 Multiple sequence alignment of MsBBX20 encoded amino acids
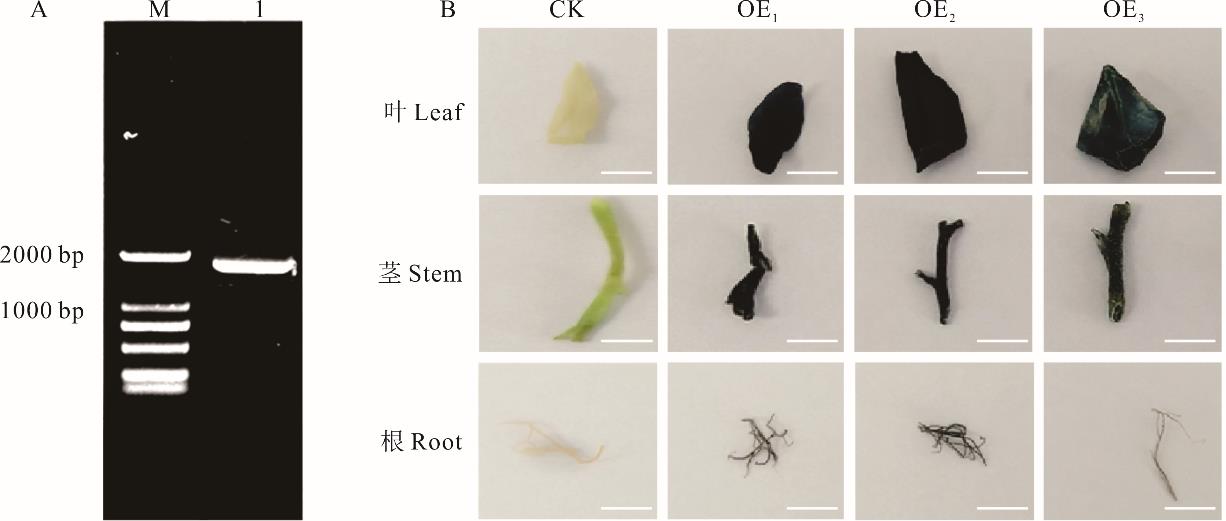
图6 MsBBX20基因启动子的克隆与表达分析A: MsBBX20基因启动子的克隆,M: DL2000;1:MsBBX20基因启动子长度。A: Cloning of the promoter of MsBBX20 gene, M: DL2000; 1: MsBBX20 gene promoter length. B: MsBBX20:GUS转基因烟草的GUS染色;图中比例尺为1 cm; CK为未转基因烟草组织,OE1~OE3为MsBBX20:GUS转基因烟草的不同组织。B: MsBBX20:GUS staining of transgenic tobacco; the scale in the figure is 1 cm; CK is an unmodified tobacco tissue, and OE1-OE3 are different tissues of MsBBX20:GUS transgenic tobacco.
Fig.6 Cloning and expression analysis of MsBBX20 gene promoter
元件名称 Element name | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Amount | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| AE-box | AGAAACTT/AGAAACAT/AGAAACAA | 3 | 光响应模块的一部分Part of a module for light response |
| CATT-motif | GCATTC | 2 | 光响应元件的一部分Part of a light responsive element |
| G-Box | CACGTT | 2 | 参与光反应的顺式作用调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 1 | 参与脱落酸响应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting elements involved in the abscisic acid response |
| HSE | CCGAAA | 1 | 参与低温响应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness |
| MBS | CGGTCA | 1 | MYB结合位点MYB binding site |
| MRE | AACCTAA | 1 | 光诱导的MYB响应元件MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness |
| Sp1 | CC(G/A)CCC | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsive element |
| TATC-box | TATCCCA | 1 | 参与赤霉素反应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in gibberellin-responsiveness |
| TC-rich repeats | ATTCTCTAAC | 1 | 参与防御和胁迫反应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness |
| Circadian | CAANNNNATC | 2 | 参与昼夜节律顺行调控元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in circadian control |
表3 MsBBX20基因启动子部分顺式作用元件分析
Table 3 Analysis of cis-acting elements in the promoter region of the MsBBX20 gene
元件名称 Element name | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Amount | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| AE-box | AGAAACTT/AGAAACAT/AGAAACAA | 3 | 光响应模块的一部分Part of a module for light response |
| CATT-motif | GCATTC | 2 | 光响应元件的一部分Part of a light responsive element |
| G-Box | CACGTT | 2 | 参与光反应的顺式作用调节元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 1 | 参与脱落酸响应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting elements involved in the abscisic acid response |
| HSE | CCGAAA | 1 | 参与低温响应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness |
| MBS | CGGTCA | 1 | MYB结合位点MYB binding site |
| MRE | AACCTAA | 1 | 光诱导的MYB响应元件MYB binding site involved in light responsiveness |
| Sp1 | CC(G/A)CCC | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsive element |
| TATC-box | TATCCCA | 1 | 参与赤霉素反应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in gibberellin-responsiveness |
| TC-rich repeats | ATTCTCTAAC | 1 | 参与防御和胁迫反应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness |
| Circadian | CAANNNNATC | 2 | 参与昼夜节律顺行调控元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in circadian control |
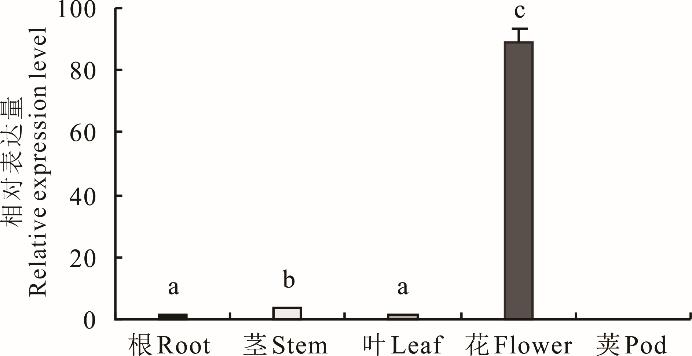
图7 MsBBX20在紫花苜蓿各组织部位的表达量不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the P<0.05 level.
Fig.7 Expression of MsBBX20 in various tissue parts of M. sativa
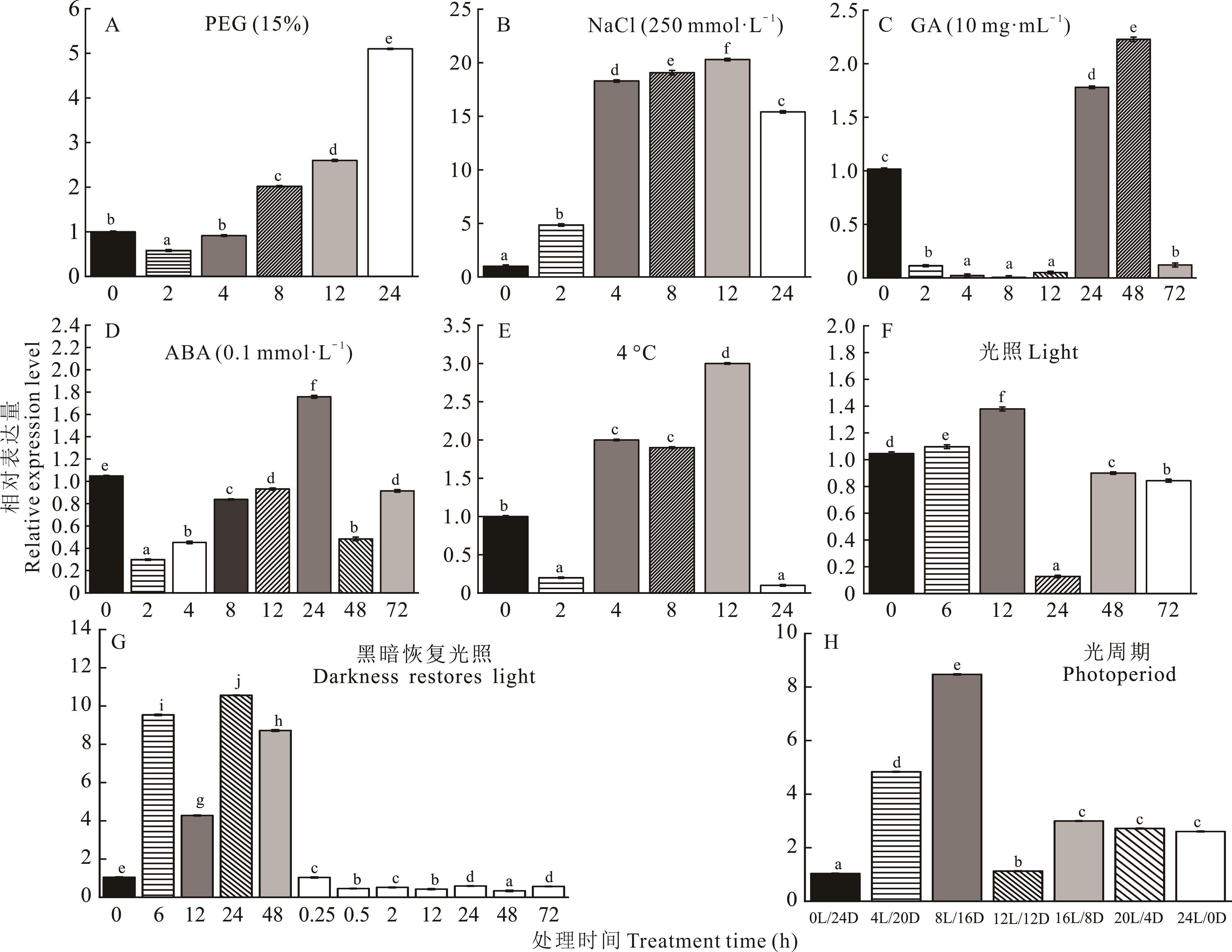
图8 MsBBX20在不同逆境胁迫处理下的相对表达量A:干旱胁迫(15% PEG6000)处理下MsBBX20基因的相对表达量 The relative expression level of the MsBBX20 gene under drought stress (15% PEG6000) treatment; B:盐胁迫(250 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理下MsBBX20基因的相对表达量 The relative expression level of the MsBBX20 gene under salt stress (250 mmol·L-1 NaCl) treatment; C:赤霉素(10 mg·mL-1 GA)胁迫处理下MsBBX20基因的相对表达量 The relative expression level of the MsBBX20 gene under gibberellin stress (10 mg·mL-1 GA) treatment; D:脱落酸(0.1 mmol·L-1 ABA)胁迫处理下MsBBX20基因的相对表达量 The relative expression level of the MsBBX20 gene under abscisic acid stress (0.1 mmol·L-1 ABA) treatment; E:4 ℃冷胁迫处理下MsBBX20基因的相对表达量 The relative expression level of the MsBBX20 gene under cold stress (4 ℃) treatment; F:持续光照处理下MsBBX20基因的相对表达量 The relative expression level of the MsBBX20 gene under continuous light treatment; G:黑暗恢复光照处理下MsBBX20基因的相对表达量 The relative expression level of the MsBBX20 gene under the treatment of dark recovery followed by light illumination; H:不同光周期处理下MsBBX20基因的相对表达量 The relative expression level of the MsBBX20 gene under different light periods treatment;横坐标L和D分别表示光照(Light)和黑暗(Dark) The horizontal coordinates L and D represent light and dark, respectively. 不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the P<0.05 level.
Fig.8 Relative expression levels of MsBBX20 under different adverse stress conditions
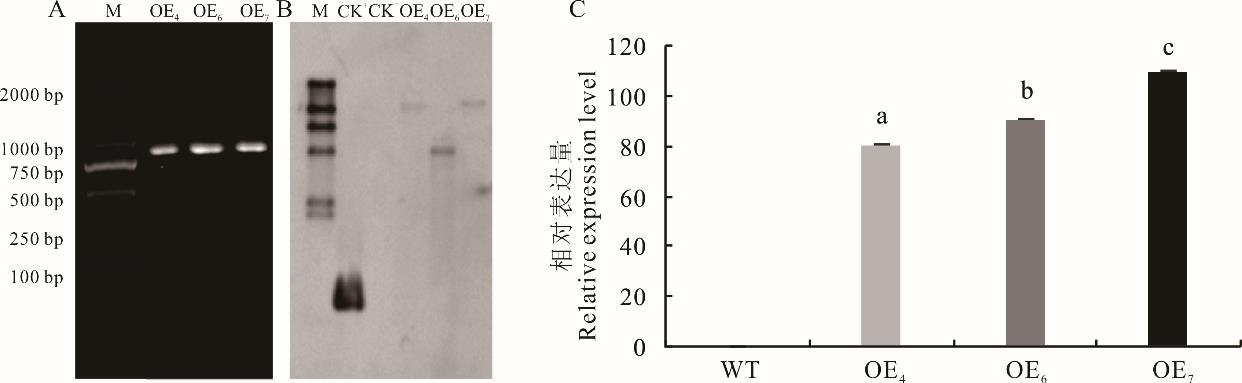
图9 MsBBX20过表达转化拟南芥株系的分子检测与Southern-blot杂交分析A:转化拟南芥植株的PCR检测 M: DL2000;OE4、OE6和OE7:转基因拟南芥株系。A: PCR detection of transformed A. thaliana plants, M: DL2000; OE4, OE6 and OE7: transgenic Arabidopsis strains. B:转基因拟南芥的Southern杂交检测,CK+:阳性对照,CK-:阴性对照,B: Southern hybridization test of transgenic A. thaliana, CK+: Positive control, CK-: Negative control. C:转基因拟南芥MsBBX20基因的相对表达量。C: Relative expression of transgenic A. thalianaMsBBX20 gene. WT表示野生型拟南芥植株;不同小写字母表示差异达显著水平(P<0.05)。 WT indicates wild-type Arabidopsis plants; Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the P<0.05 level.
Fig.9 Molecular detection and Southern-blot hybridization analysis of A. thaliana transgenic lines overexpressing MsBBX20

图10 NaCl胁迫下转MsBBX20基因拟南芥植株生长情况A:盐胁迫(150 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理4 d的萌发情况 Germination after 4 days of salt stress (150 mmol·L-1 NaCl) treatment; B:盐胁迫(150 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理7 d的侧根生长情况 Lateral root growth after 7 days of salt stress (150 mmol·L-1 NaCl) treatment; C:盐胁迫(200 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理0~10 d的萌发情况 Germination after treatment with salt stress (200 mmol·L-1 NaCl) for 0-10 days; D:盐胁迫(200和300 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理7 d的生长情况 Growth under salt stress (200 and 300 mmol·L-1 NaCl) for 7 days; E:盐胁迫(150 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理7 d的侧根数量统计 Lateral root number statistics after 7 days of salt stress (150 mmol·L-1 NaCl) treatment; F:盐胁迫(200 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理下植株鲜重 Plant fresh weight under salt stress (200 mmol·L-1 NaCl); G:盐胁迫(300 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理下植株叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content of plants treated with salt stress (300 mmol·L-1 NaCl); H:盐胁迫(300 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理7 d后的植株存活率。Plant survival rate for 7 days after salt stress (300 mmol·L-1 NaCl). 不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the P<0.05 level.
Fig.10 Growth of transgenic Arabidopsis plants with MsBBX20 gene under NaCl stress
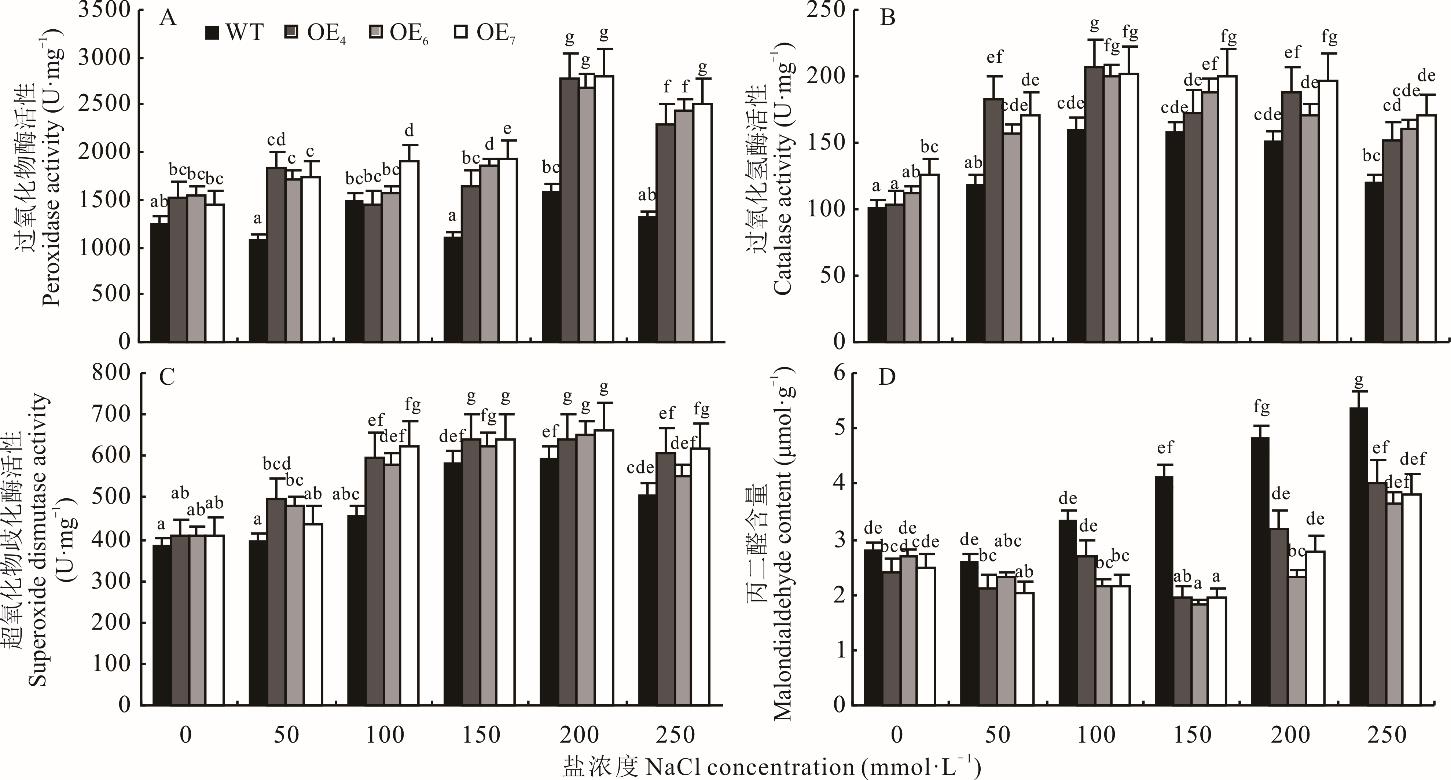
图11 盐胁迫下转MsBBX20基因的拟南芥植株生理指标变化情况A:不同NaCl浓度胁迫下转基因拟南芥和WT的POD活性测定 Determination of POD activity of transgenic A. thaliana and WT under different NaCl concentrations of stress; B:不同NaCl浓度胁迫下转基因拟南芥和WT的CAT活性测定 Determination of CAT activity of transgenic A. thaliana and WT under different NaCl concentrations of stress; C:不同NaCl浓度胁迫下转基因拟南芥和WT的SOD活性测定 Determination of SOD activity of transgenic A. thaliana and WT under different NaCl concentrations of stress; D:不同NaCl浓度胁迫下转基因拟南芥和WT的MDA含量测定。Determination of MDA content of transgenic A. thaliana and WT under different NaCl concentrations of stress. 不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the P<0.05 level.
Fig.11 Changes of physiological indicators in A. thaliana plants transgenic for MsBBX20 under salt stress
| 1 | Radović J, Sokolović D, Marković J. Alfalfa-most important perennial forage legume in animal husbandry. Biotechnology in Animal Husbandry, 2009, 25(5/6): 465-475. |
| 2 | Ren J Z, Wang S X. Performance of alfalfa in different grassland types in central Gansu Province. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 1959(4): 1-9. |
| 任继周, 王素香. 甘肃中部的紫花苜蓿在不同草原类型上的表现. 甘肃农业大学学报, 1959(4): 1-9. | |
| 3 | Nan L L, Shi S L, Zhang J H. Study on root system development ability of different root-type alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(2): 117-124. |
| 南丽丽, 师尚礼, 张建华. 不同根型苜蓿根系发育能力研究. 草业学报, 2014, 23(2): 117-124. | |
| 4 | Su Y Z. Soil carbon and nitrogen sequestration following the conversion of cropland to alfalfa forage land in northwest China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2007, 92(2): 181-189. |
| 5 | Zhang Q, Liu N F, Xiang Z X, et al. Effects of neutral and alkali salt stresses on the growth and physiological metabolism of kentucky bluegrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(12): 67-76. |
| 张强, 刘宁芳, 向佐湘, 等. 盐碱胁迫对草地早熟禾生长和生理代谢的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(12): 67-76. | |
| 6 | Chou M X, Wei X Y. Review of research advancements on the molecular basis and regulation of symbiotic nodulation of legume. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010, 34(7): 876-888. |
| 丑敏霞, 魏新元. 豆科植物共生结瘤的分子基础和调控研究进展. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(7): 876-888. | |
| 7 | Yang Q C, Sun Y. The history, current situation and development of alfalfa breeding in China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2011, 33(6): 95-101. |
| 杨青川, 孙彦. 中国苜蓿育种的历史、现状与发展趋势. 中国草地学报, 2011, 33(6): 95-101. | |
| 8 | Chen X F, Xu H L, Bi Y X. Research progress on germplasm resources and salt tolerance of alfalfa. China Seed Industry, 2018(9): 16-18. |
| 陈小芳, 徐化凌, 毕云霞. 苜蓿种质资源概况及耐盐性研究进展. 中国种业, 2018(9): 16-18. | |
| 9 | Jing J L, Zhang P, Wang Z Y, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of C2H2-type zinc finger protein transcription factor family in cassava. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(12): 2664-2676. |
| 井建玲, 张鹏, 王振宇, 等. 木薯C2H2型锌指蛋白转录因子家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(12): 2664-2676. | |
| 10 | Gangappa S N, Botto J F. The BBX family of plant transcription factors. Trends in Plant Science, 2014, 19(7): 460-470. |
| 11 | Kumagai T, Ito S, Nakamichi N, et al. The common function of a novel subfamily of B-box zinc finger proteins with reference to circadian-associated events in Arabidopsis thaliana. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2008, 72(6): 1539-1549. |
| 12 | Khanna R, Kronmiler B, Maszle D R, et al. The Arabidopsis B-box zinc finger family. Plant Cell, 2009, 21(11): 3416-3420. |
| 13 | Crocco C D, Botto J F. BBX proteins in green plants: insights into their evolution, structure feature and functional diversification. Gene, 2013, 531(1): 44-52. |
| 14 | Wang Q, Tu X, Zhang J, et al. Heat stress-induced BBX18 negatively regulates the thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Molecular Biology Reports, 2013, 40(3): 2679-2688. |
| 15 | Ma W J, Liu Z, Li Z T, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of BBX gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(11): 2797-2812. |
| 马文婧, 刘震, 李志涛, 等. 马铃薯BBX基因家族的全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 作物学报, 2022, 48(11): 2797-2812. | |
| 16 | Fang B H, Wang W P, Zhao Y, et al. Bioinformatics and expression pattern analysis of BBX gene family in rice. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(20): 6586-6594. |
| 方宝华, 王伟平, 赵杨, 等. 水稻BBX基因家族生物信息学及表达模式分析. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(20): 6586-6594. | |
| 17 | Yin L L, Xing B L, Chen X L, et al. Identification and expression of BBX gene family in soybean. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(6): 35-45. |
| 殷丽丽, 邢宝龙, 陈晓亮, 等. 大豆BBX基因家族的鉴定及表达. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(6): 35-45. | |
| 18 | Wang Y P, Ling L, Zhang W R, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of B-box gene family in wheat. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 47(8): 1437-1449. |
| 王艳朋, 凌磊, 张文睿, 等. 小麦B-box基因家族全基因组鉴定与表达分析. 作物学报, 2021, 47(8): 1437-1449. | |
| 19 | Zhao C J, Xu S Y, Du M X, et al. Identification and expression analysis of BBX gene family in maize. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 677-689. |
| 赵长江, 徐尚缘, 都梦翔, 等. 玉米BBX基因家族鉴定及表达分析. 西北农业学报, 2022, 31(6): 677-689. | |
| 20 | Min J H, Chuang J S, Lee K H, et al. The CONSTANS-like 4 transcription factor, AtCOL4, positively regulates abiotic stress tolerance through an abscisic acid-dependent manner in Arabidopsis. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2015, 57(3): 313-324. |
| 21 | Deng J, Luo Z L, Zhu F Y, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of B-box zinc-finger protein gene OsBBX26 in rice. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2020, 51(7): 1606-1613. |
| 邓军, 罗正良, 朱菲莹, 等. 水稻B-box锌指蛋白基因OsBBX26的克隆及表达分析. 南方农业学报, 2020, 51(7): 1606-1613. | |
| 22 | Zhang H. Transcriptome analysis of salt tolerance in sweet potato and cloning and functional verification of stress-related genes IbBBX24 and IbCPK28. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 张欢. 甘薯耐盐转录组分析及抗逆相关基因IbBBX24和IbCPK28的克隆与功能验证. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2021. | |
| 23 | Huang S J, Chen C H, Xu M X, et al. Overexpression of Ginkgo BBX25 enhances salt tolerance in transgenic Populus. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 167: 946-954. |
| 24 | Wang Y, Wang J, Li S X. Cloning of MsBBX24 from alfalfa(Medicago sativa)and determination of its role in salt tolerance. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 107-117. |
| 王园, 王晶, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX24基因的克隆及耐盐性分析. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 107-117. | |
| 25 | Li J, Wen H Y, Gao H W, et al. Construction of GoGID gene expression vector in Oriental goat bean and its transformation into alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(1): 167-172. |
| 李俊, 温红雨, 高洪文, 等. 东方山羊豆GoGID基因表达载体构建及紫花苜蓿转化. 草地学报, 2015, 23(1): 167-172. | |
| 26 | Le Z, Shi K, Cui X R, et al. Overexpression of MsNAC51 from alfalfa confers drought tolerance in tobacco. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2023, 205: 105143. |
| 27 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 28 | Zai Z Y, Wang L, Ding H F, et al. Identification and salt stress response of OfWRKY120 gene in Osmanthus fragrans. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 1-11. |
| 宰舟颖, 王柳, 丁卉芬, 等. 桂花OfWRKY120基因鉴定及盐胁迫响应功能研究. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(5): 1-11. | |
| 29 | Li X F, Zhao S Q. Activity detection and application of reporter gene GUS in transgenic plants. Chemistry of Life, 2004, 24(1): 71-74. |
| 李新锋, 赵淑清. 转基因植物中报道基因GUS的活性检测及其应用. 生命的化学, 2004, 24(1): 71-74. | |
| 30 | Zhu Y C, Xue H M, Zhou Q, et al. Cloning and function study of LaDFR1 gene and promoter from Lycoris opalba. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2023, 31(7): 1396-1404. |
| 朱熠辰, 薛惠敏, 周琪, 等. 乳白石蒜LaDFR1基因及启动子克隆与功能研究. 农业生物技术学报, 2023, 31(7): 1396-1404. | |
| 31 | Jin T C, Min F, Li Y D, et al. ROS1-mediated DNA demethylation of AtGSTF14 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023, 21(18): 6031-6036. |
| 金太成, 闵菲, 李一荻, 等. 拟南芥植物中ROS1介导AtGSTF14基因的DNA去甲基化. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(18): 6031-6036. | |
| 32 | Wu X L, Tang W W. Cloning and expression analysis of the Cullin gene in Citrus reticulata. Research Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 11(1): 109-114. |
| 33 | Tao X L, Zhao Y H, Ma L, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of the BrCUC2 gene in Brassica rapa L.Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1274567. |
| 34 | Wang X K. Principles and techniques of plant physiological and biochemical tests. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| 王学奎. 植物生理生化试验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. | |
| 35 | Chang Y Y, Sun H Y, Liu S Y, et al. Identification of BBX gene family and its function in the regulation of microtuber formation in yam. BMC Genomics, 2023, 24(1): 354. |
| 36 | Liu Y, Wang Y X, Liao J, et al. Identification and characterization of the BBX gene family in Bambusa pervariabilis× Dendrocalamopsis grandis and their potential role under adverse environmental stresses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(17): 13465. |
| 37 | Li S, Guo S, Gao X, et al. Genome-wide identification of B-box zinc finger (BBX) gene family in Medicago sativa and their roles in abiotic stress responses. BMC Genomics, 2024, 25(1): 110. |
| 38 | Li T, Du H, Li Y L, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of soybean BBX32 gene and gene editing target design. Soybean Science, 2021, 40(5): 602-611. |
| 李泰, 杜浩, 黎永力, 等. 大豆BBX32基因生物信息学分析及基因编辑靶点设计. 大豆科学, 2021, 40(5): 602-611. | |
| 39 | Xiong C. Functional identification of the keratinoid membrane development regulatory gene WOOLLY and the carotenoid synthesis regulatory gene SLBBX20 in tomato fruits. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. |
| 熊程. 番茄果实角质膜发育调控基因WOOLLY和类胡萝卜素合成调控基因SLBBX20的功能鉴定. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. | |
| 40 | Jiao Y, Liu X Q, Jiang H Y, et al. Research progress of plant tissue-specific promoters. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(1): 18-28. |
| 焦勇, 柳小庆, 江海洋, 等. 植物组织特异性启动子研究进展. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(1): 18-28. | |
| 41 | Wen T L, Liu X M, Ji Y P, et al. Research progress of stress inducible promoters in higher plants. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2014, 34(1): 206-214. |
| 文添龙, 刘雪梅, 冀亚萍, 等. 高等植物胁迫诱导型启动子的研究进展. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(1): 206-214. | |
| 42 | Qi X K, Meng X X, Zhao Z M, et al. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of BBX gene family in Populus pilocarpa. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2023, 46(5): 41-49. |
| 齐小坤, 孟祥熹, 赵志明, 等. 毛果杨BBX基因家族鉴定与生物信息学分析. 河北农业大学学报, 2023, 46(5): 41-49. | |
| 43 | Yang N, Cong Q, Wang X R, et al. Identification of EgrBBX gene family in Eucalyptus grandis and analysis of its expression under abiotic stress treatment. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2020, 28(4): 658-671. |
| 杨宁, 从青, 王晓荣, 等. 巨桉EgrBBX基因家族鉴定及其在非生物逆境处理下的表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2020, 28(4): 658-671. | |
| 44 | Du X F, Wei X H, Wang B Q, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of quinoa BBX family. PeerJ, 2022, 10: e14463. |
| 45 | Yue Y, Ruihan H, Song C, et al. The B-box transcription factor PabBBX27 in the regulation of chlorophyll biosynthesis and photosynthesis in poplar (Populus alba×P. berolinensis). Industrial Crops and Products, 2023, 203: 117159. |
| 46 | Wang Z M, Zhang F J, Xu X. Advances on physiological and biochemical indexes of salt tolerance in plant. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(7): 1493-1496. |
| 王智明, 张峰举, 许兴. 植物耐盐生理生化指标研究进展. 湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(7): 1493-1496. | |
| 47 | Fu C, Sun Y G, Fu G R. Advances in molecular mechanisms of salt tolerance in halophytes. Bulletin of Biotechnology, 2013, 26(1): 1-7. |
| 付畅, 孙玉刚, 傅桂荣. 盐生植物耐盐分子机制的研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2013, 26(1): 1-7. | |
| 48 | Ding Y, Wu G, Guo C K. Research progress of chlorophyll degradation mechanisms in plants. Bulletin of Biotechnology, 2016, 32(11): 1-9. |
| 丁跃, 吴刚, 郭长奎. 植物叶绿素降解机制研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(11): 1-9. | |
| 49 | Liu Y, Xing L J, Li J H, et al. Rice B-box zinc finger protein OsBBX25 is involved in the abiotic respones. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2012, 47(4): 366-378. |
| 刘焱, 邢立静, 李俊华, 等. 水稻含有B-box锌指结构域的OsBBX25蛋白参与植物对非生物胁迫的响应. 植物学报, 2012, 47(4): 366-378. | |
| 50 | He X L, Zhao L L, Li Y P. Effects of AM fungi on the growth and protective enzymes of cotton under NaCl stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(1): 188-193. |
| 贺学礼, 赵丽莉, 李英鹏. NaCl胁迫下AM真菌对棉花生长和叶片保护酶系统的影响. 生态学报, 2005, 25(1): 188-193. | |
| 51 | Dai Y Q, Lu Y, Zhou Z, et al. B-box containing protein 1 from Malus domestica (MdBBX1) is involved in the abiotic stress response. PeerJ, 2022, 10: e12852. |
| 52 | Jia S S, Wen X J, Wang Y C, et al. Identification and expression analysis of BBX transcription factor family of Betula alba and preliminary study of BpBBX24 stress resistance. Chinese Journal of Plant Physiology, 2023, 59(1): 138-152. |
| 贾珊珊, 文雪静, 王玉成, 等. 白桦BBX转录因子家族鉴定、表达分析及BpBBX24抗逆功能初探. 植物生理学报, 2023, 59(1): 138-152. | |
| 53 | Zhen Q H, Ma H, Liu Y M, et al. Effects of different NaCl treatments on growth and antioxidant enzyme activity of licorice. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information, 2023(9): 58-64. |
| 甄千慧, 马红, 刘伊铭, 等. 不同NaCl处理对甘草生长及抗氧化酶活性的影响. 农业科技与信息, 2023(9): 58-64. | |
| 54 | Hu X W, Jin H X, Zhu D H. Research progress of drought and salt tolerance mechanism in plants. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(24): 137-142. |
| 胡兴旺, 金杭霞, 朱丹华. 植物抗旱耐盐机理的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(24): 137-142. | |
| 55 | Jefferson R A, Kavanagh T A, Bevan M W. GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. The EMBO Journal, 1987, 6(13): 3901-3907. |
| 56 | Sergio L, Paola A D, Cantore V, et al. Effect of salt stress on growth parameters, enzymatic antioxidant system, and lipid per‐oxidation in wild chicory (Cichorium intybus L.). Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2012, 34(6): 2349-2358. |
| [1] | 王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93. |
| [2] | 张盈盈, 胡丹丹, 马春晖, 张前兵. 苜蓿叶片结构和光合特性对菌磷添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 133-144. |
| [3] | 王峥, 常伟, 李俊诚, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿还田对饲料玉米产量和氮素吸收转运的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 63-73. |
| [4] | 高金柱, 赵东豪, 高乐, 苏喜浩, 何学青. 硝酸铈与脱落酸处理对紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [5] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [6] | 王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 包爱科. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. |
| [7] | 孔海明, 宋家兴, 杨静, 李倩, 杨培志, 曹玉曼. 紫花苜蓿CAMTA基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [8] | 孟晨, 鲁雪莉, 宋亦汝, 张成省, 李义强, 项海芹, 徐宗昌. 11份益母草种质材料苗期耐盐性评价与鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 196-203. |
| [9] | 王萌, 鲁雪莉, 王菊英, 张梦超, 宋奕汝, 孟晨, 张莉, 徐宗昌. 小黑麦种质萌发期苗期耐盐资源评价与筛选[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 58-68. |
| [10] | 何升然, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 汪雪, 王静. 紫花苜蓿/甜高粱间作对根际土壤特性及微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 92-105. |
| [11] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [12] | 李显炀, 刘昊, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿WRKY转录因子家族鉴定与表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. |
| [13] | 张译尹, 李雪颖, 王斌, 宋珂辰, 兰剑, 胡海英. 盐胁迫对不同种质小黑麦幼苗水分利用效率和渗透调节的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 87-98. |
| [14] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [15] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||