

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (7): 107-119.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024304
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
富贵1,2,4( ), 刘玉萍3,4,5, 苏旭3,4,5(
), 刘玉萍3,4,5, 苏旭3,4,5( ), 曲荣举3, 才让扎西3
), 曲荣举3, 才让扎西3
收稿日期:2024-07-31
修回日期:2024-09-12
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-05-12
通讯作者:
苏旭
作者简介:E-mail: xusu8527972@126.com基金资助:
Gui FU1,2,4( ), Yu-ping LIU3,4,5, Xu SU3,4,5(
), Yu-ping LIU3,4,5, Xu SU3,4,5( ), Rong-ju QU3, Zha-xi CAIRANG3
), Rong-ju QU3, Zha-xi CAIRANG3
Received:2024-07-31
Revised:2024-09-12
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-05-12
Contact:
Xu SU
摘要:
扇穗茅是青藏高原特有的一种具有重要生态和经济价值的禾本科草本植物,开发稳定高效的微卫星(SSR)分子标记可为其遗传多样性、系统发育和物种分布格局等研究提供重要的技术手段。本研究基于Pacbio测序平台获得扇穗茅全长转录组30624条Unigene序列,利用MISA软件搜索到14089个SSR重复序列,SSR发生频率为33.85%;通过对SSR位点特征分析发现,SSR位点包含6种核苷酸重复类型,其中单、二、三核苷酸占所有核苷酸类型的97.35%,为主要重复类型;3种主导基序类型中,三核苷酸所形成的基元类型数目最多,共检测到10个基元类型,其中CCG/CGG基元类型占优,共形成1736个SSR位点,占三核苷酸总SSR位点的31.32%;随机挑选12个不同居群的扇穗茅样本对合成的160对引物进行PCR扩增和琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,最终获得扩增稳定、具特异性的15对SSR引物。基于扇穗茅27个居群、81个个体,对15对SSR引物多态性进行了分析,共扩增出132个观测等位基因,平均每对引物扩增出8.8个观测等位基因,有效等位基因数(Ne)、Shannon’s信息指数(I)、多态性信息含量(PIC)、观测杂合度(Ho)、期望杂合度(He)平均值分别为4.7799、1.6959、0.7270、0.8575和0.7648。基于Nei’s遗传距离利用UPGMA方法进行聚类分析,结果表明,扇穗茅居群间和居群内个体间存在明显的系统亲缘关系,不同居群间遗传距离可能和地理距离相关。本研究开发的15对SSR引物遗传多样性丰富,可为扇穗茅种质资源遗传变异研究提供更加有效的标记选择。
富贵, 刘玉萍, 苏旭, 曲荣举, 才让扎西. 扇穗茅全长转录组SSR特征分析及分子标记开发[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 107-119.
Gui FU, Yu-ping LIU, Xu SU, Rong-ju QU, Zha-xi CAIRANG. Analysis of SSR characterization in full-length transcriptome and development of SSR molecular markers for Littledalea racemosa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(7): 107-119.
居群编号 Population No. | 样本数量 Sample size | 采样地 Sampling location | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POP2 | 3 | 青海省兴海县Xinghai County, Qinghai Province | 35°20′32.5″ | 99°5′8.2″ | 4164 |
| POP8 | 3 | 青海省玛沁县Maqin County, Qinghai Province | 34°32′58.1″ | 99°8′47.4″ | 4396 |
| POP12 | 3 | 青海省玛多县Maduo County, Qinghai Province | 34°8′22.7″ | 97°40′25.8″ | 4727 |
| POP13 | 3 | 青海省玛沁县 Maqin County, Qinghai Province | 34°30′36″ | 99°9′0″ | 4353 |
| POP20 | 3 | 青海省曲麻莱县Qumalai County, Qinghai Province | 34°9′1.3″ | 95°53′55.2″ | 4513 |
| POP25 | 3 | 青海省曲麻莱县Qumalai County, Qinghai Province | 35°31′16.3″ | 93°54′47.8″ | 4625 |
| POP62 | 3 | 青海省兴海县Xinghai County, Qinghai Province | 35°29′26.6″ | 99°29′57.3″ | 4455 |
| POP65 | 3 | 青海省兴海县Xinghai County, Qinghai Province | 35°23′3.1″ | 99°18′2.4″ | 4377 |
| POP66 | 3 | 青海省玛多县Maduo County, Qinghai Province | 35°20′49.8″ | 99°6′6.2″ | 4171 |
| POP68 | 3 | 青海省玛多县Maduo County, Qinghai Province | 35°7′38.4″ | 99°4′2.3″ | 4200 |
| POP69 | 3 | 青海省玛多县Maduo County, Qinghai Province | 35°5′51.6″ | 99°6′7.8″ | 4117 |
| POP72 | 3 | 青海省玛沁县Maqin County, Qinghai Province | 34°23′54.0″ | 99°12′2.5″ | 4293 |
| POP73 | 3 | 青海省玛沁县Maqin County, Qinghai Province | 34°30′13.1″ | 99°10′9.4″ | 4363 |
| POP88 | 3 | 青海省曲麻莱县Qumalai County, Qinghai Province | 34°9′31.8″ | 95°55′14.0″ | 4582 |
| POP95 | 3 | 西藏类乌齐县Riwoqê County, Xizang | 30°51′14.2″ | 96°37′19.0″ | 4552 |
| POP101 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 33°49′48.6″ | 92°20′2.6″ | 4613 |
| POP104 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 33°59′19.5″ | 92°20′46.4″ | 4655 |
| POP106 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°6′12.8″ | 92°21′34.0″ | 4740 |
| POP111 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°25′21.4″ | 92°43′23.4″ | 4568 |
| POP115 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°38′56.9″ | 92°53′52.3″ | 4829 |
| POP118 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°50′47.0″ | 92°56′56.1″ | 4623 |
| POP119 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°57′21.3″ | 92°57′9.9″ | 4558 |
| POP120 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°5′17.8″ | 93°1′32.9″ | 4690 |
| POP122 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°18′35.8″ | 93°17′42.6″ | 4536 |
| POP125 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°32′49.4″ | 93°57′24.3″ | 4628 |
| POP126 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°38′19.2″ | 94°4′9.4″ | 4772 |
| POP127 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°43′11.1″ | 94°6′57.3″ | 4468 |
表1 供试材料及原产地详细信息
Table 1 Materials and detailed information of origins
居群编号 Population No. | 样本数量 Sample size | 采样地 Sampling location | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POP2 | 3 | 青海省兴海县Xinghai County, Qinghai Province | 35°20′32.5″ | 99°5′8.2″ | 4164 |
| POP8 | 3 | 青海省玛沁县Maqin County, Qinghai Province | 34°32′58.1″ | 99°8′47.4″ | 4396 |
| POP12 | 3 | 青海省玛多县Maduo County, Qinghai Province | 34°8′22.7″ | 97°40′25.8″ | 4727 |
| POP13 | 3 | 青海省玛沁县 Maqin County, Qinghai Province | 34°30′36″ | 99°9′0″ | 4353 |
| POP20 | 3 | 青海省曲麻莱县Qumalai County, Qinghai Province | 34°9′1.3″ | 95°53′55.2″ | 4513 |
| POP25 | 3 | 青海省曲麻莱县Qumalai County, Qinghai Province | 35°31′16.3″ | 93°54′47.8″ | 4625 |
| POP62 | 3 | 青海省兴海县Xinghai County, Qinghai Province | 35°29′26.6″ | 99°29′57.3″ | 4455 |
| POP65 | 3 | 青海省兴海县Xinghai County, Qinghai Province | 35°23′3.1″ | 99°18′2.4″ | 4377 |
| POP66 | 3 | 青海省玛多县Maduo County, Qinghai Province | 35°20′49.8″ | 99°6′6.2″ | 4171 |
| POP68 | 3 | 青海省玛多县Maduo County, Qinghai Province | 35°7′38.4″ | 99°4′2.3″ | 4200 |
| POP69 | 3 | 青海省玛多县Maduo County, Qinghai Province | 35°5′51.6″ | 99°6′7.8″ | 4117 |
| POP72 | 3 | 青海省玛沁县Maqin County, Qinghai Province | 34°23′54.0″ | 99°12′2.5″ | 4293 |
| POP73 | 3 | 青海省玛沁县Maqin County, Qinghai Province | 34°30′13.1″ | 99°10′9.4″ | 4363 |
| POP88 | 3 | 青海省曲麻莱县Qumalai County, Qinghai Province | 34°9′31.8″ | 95°55′14.0″ | 4582 |
| POP95 | 3 | 西藏类乌齐县Riwoqê County, Xizang | 30°51′14.2″ | 96°37′19.0″ | 4552 |
| POP101 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 33°49′48.6″ | 92°20′2.6″ | 4613 |
| POP104 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 33°59′19.5″ | 92°20′46.4″ | 4655 |
| POP106 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°6′12.8″ | 92°21′34.0″ | 4740 |
| POP111 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°25′21.4″ | 92°43′23.4″ | 4568 |
| POP115 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°38′56.9″ | 92°53′52.3″ | 4829 |
| POP118 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°50′47.0″ | 92°56′56.1″ | 4623 |
| POP119 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 34°57′21.3″ | 92°57′9.9″ | 4558 |
| POP120 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°5′17.8″ | 93°1′32.9″ | 4690 |
| POP122 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°18′35.8″ | 93°17′42.6″ | 4536 |
| POP125 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°32′49.4″ | 93°57′24.3″ | 4628 |
| POP126 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°38′19.2″ | 94°4′9.4″ | 4772 |
| POP127 | 3 | 青海省格尔木市 Geermu City, Qinghai Province | 35°43′11.1″ | 94°6′57.3″ | 4468 |
| 统计项目Statistical items | 数目Number |
|---|---|
| Unigene数量 Number of Unigene | 30624 |
| Unigene序列总长度 Total length of Unigene sequence (bp) | 94880976 |
| 含SSR位点Unigene序列总数 Total number of Unigene sequence with SSR loci | 10367 |
| SSR位点数 Number of SSR loci | 14089 |
| 含1个以上SSR位点数的Unigene The number of Unigene with more than 1 SSR loci | 2710 |
| 复合型SSR位点数 Number of composite SSR loci | 927 |
| SSR出现频率 The occurrence frequency of SSR loci (%) | 46.01 |
| SSR发生频率 The incidence of SSR loci (%) | 33.85 |
表2 转录组SSR位点分布信息描述
Table 2 The description of distribution information for SSR loci intranscriptome
| 统计项目Statistical items | 数目Number |
|---|---|
| Unigene数量 Number of Unigene | 30624 |
| Unigene序列总长度 Total length of Unigene sequence (bp) | 94880976 |
| 含SSR位点Unigene序列总数 Total number of Unigene sequence with SSR loci | 10367 |
| SSR位点数 Number of SSR loci | 14089 |
| 含1个以上SSR位点数的Unigene The number of Unigene with more than 1 SSR loci | 2710 |
| 复合型SSR位点数 Number of composite SSR loci | 927 |
| SSR出现频率 The occurrence frequency of SSR loci (%) | 46.01 |
| SSR发生频率 The incidence of SSR loci (%) | 33.85 |
重复类型 Repeat types | 数目 Number | 比例 Proportion (%) | 频率 Frequency (%) | 平均分布距离 Average distribution distance (kb) | 总长度 Total length (bp) | 平均长度 Average length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单核苷酸Mono-nucleotide | 5196 | 36.88 | 16.97 | 18.26 | 67040 | 12.90 |
| 二核苷酸Di-nucleotide | 2977 | 21.13 | 9.72 | 31.87 | 25448 | 8.55 |
| 三核苷酸Tri-nucleotide | 5543 | 39.34 | 18.10 | 17.12 | 31536 | 5.69 |
| 四核苷酸Tetra-nucleotide | 269 | 1.91 | 0.88 | 352.73 | 1515 | 5.63 |
| 五核苷酸Penta-nucleotide | 53 | 0.38 | 0.17 | 1790.21 | 243 | 4.58 |
| 六核苷酸Hexa-nucleotide | 51 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 1860.41 | 312 | 6.12 |
| 总计Total | 14089 | 100.00 | 46.00 | 6.73 | 192100 | 13.63 |
表3 扇穗茅SSR位点重复类型分析
Table 3 Analysis of duplication types of SSR loci for L. racemosa
重复类型 Repeat types | 数目 Number | 比例 Proportion (%) | 频率 Frequency (%) | 平均分布距离 Average distribution distance (kb) | 总长度 Total length (bp) | 平均长度 Average length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单核苷酸Mono-nucleotide | 5196 | 36.88 | 16.97 | 18.26 | 67040 | 12.90 |
| 二核苷酸Di-nucleotide | 2977 | 21.13 | 9.72 | 31.87 | 25448 | 8.55 |
| 三核苷酸Tri-nucleotide | 5543 | 39.34 | 18.10 | 17.12 | 31536 | 5.69 |
| 四核苷酸Tetra-nucleotide | 269 | 1.91 | 0.88 | 352.73 | 1515 | 5.63 |
| 五核苷酸Penta-nucleotide | 53 | 0.38 | 0.17 | 1790.21 | 243 | 4.58 |
| 六核苷酸Hexa-nucleotide | 51 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 1860.41 | 312 | 6.12 |
| 总计Total | 14089 | 100.00 | 46.00 | 6.73 | 192100 | 13.63 |
重复类型 Repeat type | 基序类型 Motif type | 数量 Number | 比例 Proportion (%) | 频率 Frequency (%) | 重复类型 Repeat type | 基序类型 Motif type | 数量 Number | 比例 Proportion (%) | 频率 Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
单核苷酸 Mono-nucleotide | A/T | 3829 | 73.69 | 12.50 | 四核苷酸 Tetra-nucleotide | AACC/GGTT | 11 | 4.09 | 0.04 |
| C/G | 1367 | 26.31 | 4.46 | ACTC/AGTG | 11 | 4.09 | 0.04 | ||
二核苷酸 Di-nucleotide | AG/CT | 1983 | 66.61 | 6.48 | AGGC/CCTG | 10 | 3.72 | 0.03 | |
| AC/GT | 603 | 20.26 | 1.97 | CCCG/CGGG | 10 | 3.72 | 0.03 | ||
| AT/AT | 201 | 6.75 | 0.66 | 其他Others (18) | 76 | 28.25 | 0.25 | ||
| CG/CG | 190 | 6.38 | 0.62 | 五核苷酸 Penta-nucleotide | AAACC/GGTTT | 9 | 16.98 | 0.03 | |
三核苷酸 Tri-nucleotide | CCG/CGG | 1736 | 31.32 | 5.67 | AAGAG/CTCTT | 7 | 13.21 | 0.02 | |
| AGC/CTG | 1057 | 19.07 | 3.45 | AGAGG/CCTCT | 7 | 13.21 | 0.02 | ||
| AGG/CCT | 1034 | 18.65 | 3.38 | AGGGG/CCCCT | 7 | 13.21 | 0.02 | ||
| ACC/GGT | 468 | 8.44 | 1.53 | CCCCG/CGGGG | 7 | 13.21 | 0.02 | ||
| AAG/CTT | 385 | 6.95 | 1.26 | AACCC/GGGTT | 3 | 5.66 | 0.01 | ||
| ACG/CGT | 265 | 4.78 | 0.87 | 其他Others (13) | 13 | 24.53 | 0.04 | ||
| ATC/ATG | 227 | 4.10 | 0.74 | 六核苷酸 Hexa-nucleotide | AGAGGG/CCCTCT | 6 | 11.76 | 0.02 | |
| AAC/GTT | 223 | 4.02 | 0.73 | AGCAGG/CCTGCT | 5 | 9.80 | 0.02 | ||
| AAT/ATT | 99 | 1.79 | 0.32 | AAGCAG/CTGCTT | 3 | 5.88 | 0.01 | ||
| ACT/AGT | 49 | 0.88 | 0.16 | ACCTCC/AGGTGG | 3 | 5.88 | 0.01 | ||
四核苷酸 Tetra-nucleotide | AGGG/CCCT | 33 | 12.27 | 0.11 | AACAGC/CTGTTG | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | |
| ATCC/ATGG | 25 | 9.29 | 0.08 | AAGGAG/CCTTCT | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| AAAG/CTTT | 23 | 8.55 | 0.08 | ACCGCC/CGGTGG | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| ACAT/ATGT | 21 | 7.81 | 0.07 | AGGCGC/CCTGCG | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| ACGC/CGTG | 20 | 7.43 | 0.07 | AGGGCG/CCCTCG | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| AGAT/ATCT | 15 | 5.58 | 0.05 | AGGGGG/CCCCCT | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| AAGG/CCTT | 14 | 5.20 | 0.05 | 其他Others (22) | 22 | 43.14 | 0.07 |
表4 SSR位点基序类型分析
Table 4 Analysis of motif types of SSR loci
重复类型 Repeat type | 基序类型 Motif type | 数量 Number | 比例 Proportion (%) | 频率 Frequency (%) | 重复类型 Repeat type | 基序类型 Motif type | 数量 Number | 比例 Proportion (%) | 频率 Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
单核苷酸 Mono-nucleotide | A/T | 3829 | 73.69 | 12.50 | 四核苷酸 Tetra-nucleotide | AACC/GGTT | 11 | 4.09 | 0.04 |
| C/G | 1367 | 26.31 | 4.46 | ACTC/AGTG | 11 | 4.09 | 0.04 | ||
二核苷酸 Di-nucleotide | AG/CT | 1983 | 66.61 | 6.48 | AGGC/CCTG | 10 | 3.72 | 0.03 | |
| AC/GT | 603 | 20.26 | 1.97 | CCCG/CGGG | 10 | 3.72 | 0.03 | ||
| AT/AT | 201 | 6.75 | 0.66 | 其他Others (18) | 76 | 28.25 | 0.25 | ||
| CG/CG | 190 | 6.38 | 0.62 | 五核苷酸 Penta-nucleotide | AAACC/GGTTT | 9 | 16.98 | 0.03 | |
三核苷酸 Tri-nucleotide | CCG/CGG | 1736 | 31.32 | 5.67 | AAGAG/CTCTT | 7 | 13.21 | 0.02 | |
| AGC/CTG | 1057 | 19.07 | 3.45 | AGAGG/CCTCT | 7 | 13.21 | 0.02 | ||
| AGG/CCT | 1034 | 18.65 | 3.38 | AGGGG/CCCCT | 7 | 13.21 | 0.02 | ||
| ACC/GGT | 468 | 8.44 | 1.53 | CCCCG/CGGGG | 7 | 13.21 | 0.02 | ||
| AAG/CTT | 385 | 6.95 | 1.26 | AACCC/GGGTT | 3 | 5.66 | 0.01 | ||
| ACG/CGT | 265 | 4.78 | 0.87 | 其他Others (13) | 13 | 24.53 | 0.04 | ||
| ATC/ATG | 227 | 4.10 | 0.74 | 六核苷酸 Hexa-nucleotide | AGAGGG/CCCTCT | 6 | 11.76 | 0.02 | |
| AAC/GTT | 223 | 4.02 | 0.73 | AGCAGG/CCTGCT | 5 | 9.80 | 0.02 | ||
| AAT/ATT | 99 | 1.79 | 0.32 | AAGCAG/CTGCTT | 3 | 5.88 | 0.01 | ||
| ACT/AGT | 49 | 0.88 | 0.16 | ACCTCC/AGGTGG | 3 | 5.88 | 0.01 | ||
四核苷酸 Tetra-nucleotide | AGGG/CCCT | 33 | 12.27 | 0.11 | AACAGC/CTGTTG | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | |
| ATCC/ATGG | 25 | 9.29 | 0.08 | AAGGAG/CCTTCT | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| AAAG/CTTT | 23 | 8.55 | 0.08 | ACCGCC/CGGTGG | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| ACAT/ATGT | 21 | 7.81 | 0.07 | AGGCGC/CCTGCG | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| ACGC/CGTG | 20 | 7.43 | 0.07 | AGGGCG/CCCTCG | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| AGAT/ATCT | 15 | 5.58 | 0.05 | AGGGGG/CCCCCT | 2 | 3.92 | 0.01 | ||
| AAGG/CCTT | 14 | 5.20 | 0.05 | 其他Others (22) | 22 | 43.14 | 0.07 |
引物 编号 NO. | 重复基元 Repetition type | 正向引物 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5′-3′) | 产物大小 Product size (bp) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR57 | (GTTGG)5 | TGATGATTGGAGCGAGCGAAGT | GAGAAGCGAAAAAAAGGGAGGC | 291~318 | 57.5 |
| SR78 | (GTAG)5 | GGGTCCTTTACCTGACTCCTC | CACCCAATCGCAAACAGC | 163~247 | 56.5 |
| SR87 | (CAAT)5 | TCCCGCAAGGAAAAAGAG | CAGCACAAACGAAAAATAAAAATA | 371~399 | 51.0 |
| SR91 | (GAGCCT)5 | ATCGCCCGTGTCTCCTGTTTC | CGCAAGAAAACATCTCCACACAAGT | 349~385 | 57.5 |
| SR106 | (GGTT)7 | CAAAGTCGTGGGTCAGGTGTC | CCACAAGAACCAGCCAATACAAA | 254~298 | 57.5 |
| SR108 | (TGTA)10 | AGGCACAACTAATAGCAAGCA | CAATCGCTAACGCTGACG | 139~197 | 55.0 |
| SR112 | (GCCT)6 | GCAGCCGCCGACTACCTACT | AAACCACCGCGAAGACAACA | 233~261 | 59.5 |
| SR119 | (ATTT)5 | GGACCTGACCATCCATCTAAACT | TCGTTCTCGGTCGCTTTGT | 176~196 | 57.5 |
| SR120 | (CTAT)10 | CGGCTGCTCTTGGTTGATG | CGGTTAGGTGGGCTGGTTC | 202~254 | 60.5 |
| SR121 | (TGAC)6 | GACAACGGAAATGTGCCTGAG | TGGGTGGAGTTCCCTTTAGTTT | 229~281 | 57.5 |
| SR125 | (ACGC)9 | GCCGTCGCCAGTTCATTC | CTGCCTGACTCCAAGAGGAAATA | 265~301 | 59.5 |
| SR127 | (GTAT)5 | GGGAATGGACAGATTGGTTGA | GCTGACTGGTAACACGAAAGAAAA | 148~192 | 60.5 |
| SR129 | (ACGC)9 | GCCGTCGCCAGTTCATTC | CTGCCTGACTCCAAGAGGAAATA | 266~302 | 59.5 |
| SR130 | (AGAT)5 | CAGGTCCAGATGCCAAGC | GACAACAGAATACTACATTACACGG | 255~279 | 57.5 |
| SR131 | (AGAT)5 | GAACCCGCTCACTCTCTGAATGG | TCACCCAGACTTGGAAGCAAACTA | 422~516 | 59.5 |
表5 15对扇穗茅多态性SSR引物信息
Table 5 Information of 15 pairs of polymorphic SSR primers developed for L. racemosa
引物 编号 NO. | 重复基元 Repetition type | 正向引物 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5′-3′) | 产物大小 Product size (bp) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR57 | (GTTGG)5 | TGATGATTGGAGCGAGCGAAGT | GAGAAGCGAAAAAAAGGGAGGC | 291~318 | 57.5 |
| SR78 | (GTAG)5 | GGGTCCTTTACCTGACTCCTC | CACCCAATCGCAAACAGC | 163~247 | 56.5 |
| SR87 | (CAAT)5 | TCCCGCAAGGAAAAAGAG | CAGCACAAACGAAAAATAAAAATA | 371~399 | 51.0 |
| SR91 | (GAGCCT)5 | ATCGCCCGTGTCTCCTGTTTC | CGCAAGAAAACATCTCCACACAAGT | 349~385 | 57.5 |
| SR106 | (GGTT)7 | CAAAGTCGTGGGTCAGGTGTC | CCACAAGAACCAGCCAATACAAA | 254~298 | 57.5 |
| SR108 | (TGTA)10 | AGGCACAACTAATAGCAAGCA | CAATCGCTAACGCTGACG | 139~197 | 55.0 |
| SR112 | (GCCT)6 | GCAGCCGCCGACTACCTACT | AAACCACCGCGAAGACAACA | 233~261 | 59.5 |
| SR119 | (ATTT)5 | GGACCTGACCATCCATCTAAACT | TCGTTCTCGGTCGCTTTGT | 176~196 | 57.5 |
| SR120 | (CTAT)10 | CGGCTGCTCTTGGTTGATG | CGGTTAGGTGGGCTGGTTC | 202~254 | 60.5 |
| SR121 | (TGAC)6 | GACAACGGAAATGTGCCTGAG | TGGGTGGAGTTCCCTTTAGTTT | 229~281 | 57.5 |
| SR125 | (ACGC)9 | GCCGTCGCCAGTTCATTC | CTGCCTGACTCCAAGAGGAAATA | 265~301 | 59.5 |
| SR127 | (GTAT)5 | GGGAATGGACAGATTGGTTGA | GCTGACTGGTAACACGAAAGAAAA | 148~192 | 60.5 |
| SR129 | (ACGC)9 | GCCGTCGCCAGTTCATTC | CTGCCTGACTCCAAGAGGAAATA | 266~302 | 59.5 |
| SR130 | (AGAT)5 | CAGGTCCAGATGCCAAGC | GACAACAGAATACTACATTACACGG | 255~279 | 57.5 |
| SR131 | (AGAT)5 | GAACCCGCTCACTCTCTGAATGG | TCACCCAGACTTGGAAGCAAACTA | 422~516 | 59.5 |

图2 基于78号引物的88号居群3个样本毛细管电泳图88-1、88-2和88-3分别代表88号居群3个不同样本,横轴代表3个样本扩增片段长度。88-1, 88-2, and 88-3 represent three different samples in 88 population, respectively, and the horizontal axis represents the length of the amplified fragments of the three samples.
Fig.2 The capillary electrophoresis spectrum diagram for three samples in 88 population based on 78 SSR primers
引物编号 NO. | 观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles (Ne) | Shannon’s信息指数 Shannon’s information index (I) | 观测杂合度 Observed heterozygosity (Ho) | 期望杂合度 Expected heterozygosity (He) | 多态性信息含量 Polymorphic information content (PIC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR57 | 6 | 4.5441 | 1.5808 | 0.9825 | 0.7868 | 0.7435 |
| SR78 | 13 | 7.9152 | 2.2157 | 1.0000 | 0.8800 | 0.8610 |
| SR87 | 7 | 2.9388 | 1.3745 | 0.6341 | 0.6679 | 0.6210 |
| SR91 | 6 | 2.7487 | 1.2149 | 0.9870 | 0.6404 | 0.5670 |
| SR106 | 9 | 4.1166 | 1.6314 | 0.9589 | 0.7623 | 0.7190 |
| SR108 | 12 | 5.1392 | 1.9508 | 0.9333 | 0.8122 | 0.7840 |
| SR112 | 8 | 2.6828 | 1.2844 | 0.8312 | 0.6314 | 0.5830 |
| SR119 | 5 | 1.9719 | 0.9952 | 0.3793 | 0.5015 | 0.4620 |
| SR120 | 11 | 6.6667 | 2.1061 | 0.9400 | 0.8586 | 0.8340 |
| SR121 | 10 | 4.8518 | 1.8239 | 0.9667 | 0.8073 | 0.7690 |
| SR125 | 8 | 5.6082 | 1.8138 | 0.7067 | 0.8272 | 0.7970 |
| SR127 | 7 | 4.7393 | 1.7108 | 0.9661 | 0.7957 | 0.7610 |
| SR129 | 8 | 4.8313 | 1.6973 | 0.7083 | 0.7986 | 0.7620 |
| SR130 | 7 | 5.2630 | 1.7644 | 0.9744 | 0.8205 | 0.7830 |
| SR131 | 15 | 7.6809 | 2.2747 | 0.8947 | 0.8814 | 0.8570 |
| 平均值±标准差Mean±standard deviation | 8.8000±2.8586 | 4.7799±1.7557 | 1.6959±0.3670 | 0.8575±0.1770 | 0.7648±0.1073 | 0.7270±0.1125 |
表6 扇穗茅15对SSR引物群体扩增分析
Table 6 Amplification analysis of 15 pairs of SSR primers in L. racemosa
引物编号 NO. | 观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles (Ne) | Shannon’s信息指数 Shannon’s information index (I) | 观测杂合度 Observed heterozygosity (Ho) | 期望杂合度 Expected heterozygosity (He) | 多态性信息含量 Polymorphic information content (PIC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR57 | 6 | 4.5441 | 1.5808 | 0.9825 | 0.7868 | 0.7435 |
| SR78 | 13 | 7.9152 | 2.2157 | 1.0000 | 0.8800 | 0.8610 |
| SR87 | 7 | 2.9388 | 1.3745 | 0.6341 | 0.6679 | 0.6210 |
| SR91 | 6 | 2.7487 | 1.2149 | 0.9870 | 0.6404 | 0.5670 |
| SR106 | 9 | 4.1166 | 1.6314 | 0.9589 | 0.7623 | 0.7190 |
| SR108 | 12 | 5.1392 | 1.9508 | 0.9333 | 0.8122 | 0.7840 |
| SR112 | 8 | 2.6828 | 1.2844 | 0.8312 | 0.6314 | 0.5830 |
| SR119 | 5 | 1.9719 | 0.9952 | 0.3793 | 0.5015 | 0.4620 |
| SR120 | 11 | 6.6667 | 2.1061 | 0.9400 | 0.8586 | 0.8340 |
| SR121 | 10 | 4.8518 | 1.8239 | 0.9667 | 0.8073 | 0.7690 |
| SR125 | 8 | 5.6082 | 1.8138 | 0.7067 | 0.8272 | 0.7970 |
| SR127 | 7 | 4.7393 | 1.7108 | 0.9661 | 0.7957 | 0.7610 |
| SR129 | 8 | 4.8313 | 1.6973 | 0.7083 | 0.7986 | 0.7620 |
| SR130 | 7 | 5.2630 | 1.7644 | 0.9744 | 0.8205 | 0.7830 |
| SR131 | 15 | 7.6809 | 2.2747 | 0.8947 | 0.8814 | 0.8570 |
| 平均值±标准差Mean±standard deviation | 8.8000±2.8586 | 4.7799±1.7557 | 1.6959±0.3670 | 0.8575±0.1770 | 0.7648±0.1073 | 0.7270±0.1125 |
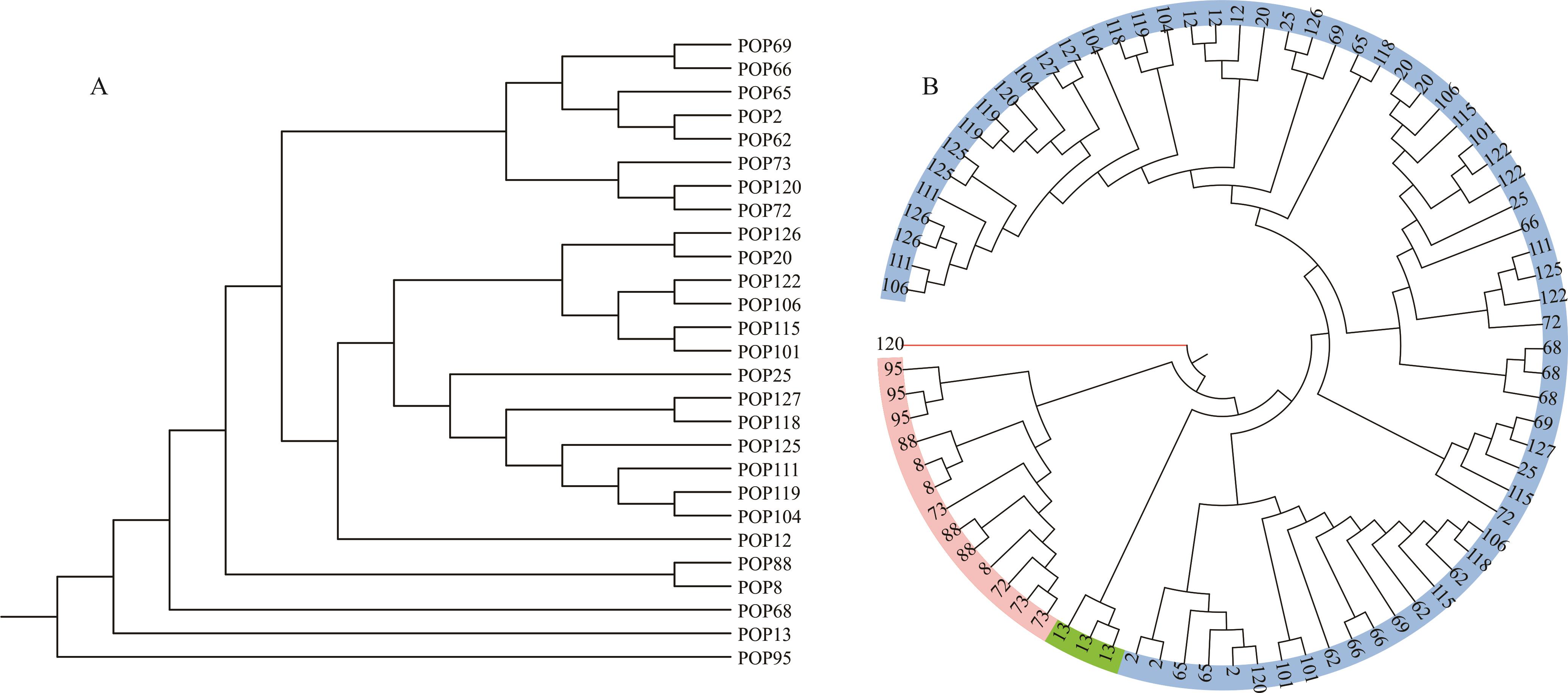
图3 基于SSR标记的扇穗茅 UPGMA 聚类分析A: 居群为单位的聚类,图中编号为居群编号Cluster diagram for population, the numbers in the figure represent the population numbers; B: 个体为单位的聚类,图中数字为同一居群的3个个体Cluster diagram for individuals, the numbers in the figure represent the three samples in same population.
Fig.3 UPGMA dendrogram for L. racemosa based on SSR markers
| 1 | Liu L, Guo B Z. Flora of China (Volume 9, Book 2). Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 377-380. |
| 刘亮, 郭本兆. 中国植物志(第九卷第二分册). 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 377-380. | |
| 2 | Lyu T, Liu Y P, Zhou Y H, et al. Germplasm collection and taxonomic review of Littledalea (Poaceae) in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 57(22): 11-13. |
| 吕婷, 刘玉萍, 周勇辉, 等. 青藏高原扇穗茅属的分类现状及种质资源收集. 湖北农业科学, 2018, 57(22): 11-13. | |
| 3 | Hooker J D. Flora of British India. London: L.Reeve & Co, 1897: 2472-2473. |
| 4 | Geng Y L. Illustration for main plants in China-Poaceae. Beijing: Science Press, 1959: 254-257. |
| 耿以礼. 中国主要植物图说-禾本科. 北京: 科学出版社, 1959: 254-257. | |
| 5 | Tzvelev N N. Planta Asiae centralium. Aedibus: Nauka, 1968: 173-174. |
| 6 | Wu Z Y. Flora of Xizang (Volume 5). Beijing: Science Press, 1987: 138-139. |
| 吴征镒. 西藏植物志(第五卷). 北京: 科学出版社, 1987: 138-139. | |
| 7 | Lu S L. Littledalea, flora of Qinghai (Volume 4). Xining: Qinghai People’s Publishing House, 1999: 72-74. |
| 卢生莲. 扇穗茅属,青海植物志(第四卷). 西宁: 青海人民出版社, 1999: 72-74. | |
| 8 | Zhou Y H. Species delimitation of Littledalea (Poaceae), an endemic genus from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Xining: Qinghai Normal University, 2017. |
| 周勇辉. 青藏高原特有属-扇穗茅属的物种界定研究. 西宁: 青海师范大学, 2017. | |
| 9 | Liu Y P, Lyu T, Zhu D, et al. Sequencing and alignment analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of Littledalea tibetica, an endemic species from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(4): 518-525. |
| 刘玉萍, 吕婷, 朱迪, 等. 青藏高原特有种-藏扇穗茅叶绿体基因组测序及序列分析. 植物研究, 2018, 38(4): 518-525. | |
| 10 | Liu T, Liu Y P, Lyu T, et al. Potential distribution of Littledalea, an endemic genus from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, predicted by Biomod 2 models.Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(6): 1650-1656. |
| 刘涛, 刘玉萍, 吕婷, 等. 基于Biomod 2组合模型预测青藏高原特有属扇穗茅属物种的潜在分布. 草地学报, 2020, 28(6): 1650-1656. | |
| 11 | Yang P, Su X, Liu Y P, et al. Chromosome number and karyotype analysis from different populations of Littledalea racemosa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(7): 1712-1720. |
| 杨萍, 苏旭, 刘玉萍, 等. 扇穗茅不同居群染色体数目及核型分析. 草地学报, 2022, 30(7): 1712-1720. | |
| 12 | Kalia R K, Rar M K, Kalia S, et al. Microsatellite markers: An overview of the recent progress in plants. Euphytica, 2011, 177(3): 309-334. |
| 13 | Gao T X, Cai Y L, Feng Y, et al. Genetic diversity and genetic structure of Prunus pseudocerasus populations from China as revealed by SSR markers. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2016, 43(6): 1148-1156. |
| 高天翔, 蔡宇良, 冯瑛, 等. 中国樱桃14个自然居群遗传多样性和遗传结构的SSR评价. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(6): 1148-1156. | |
| 14 | Gao C C, Yan L P, Wu D J, et al. Analysis of the genetic diversity and population structure of Fraxinus spp. populations based on SSR markers. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2023, 43(6): 69-78. |
| 高铖铖, 燕丽萍, 吴德军, 等. 基于SSR标记的白蜡群体遗传多样性和群体结构分析. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 69-78. | |
| 15 | Yan R J, Schnabel K E, Rowden A A, et al. Population structure and genetic connectivity of squat lobsters (Munida Leach, 1820) associated with vulnerable marine ecosystems in the southwest Pacific Ocean. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2020, 6: 791. |
| 16 | Sun L J, He J J, Wang J, et al. Development of SSR markers based on full-length transcriptome sequencing and genetic diversity analysis of Halogeton glomeratus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 199-210. |
| 孙禄娟, 何建军, 汪军, 等. 基于全长转录组测序的盐生草SSR标记开发及其遗传多样性分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 199-210. | |
| 17 | Nie J R, Zhang W J, Zheng Y, et al. Advances in molecular markers and transcriptomics of Hemarthria compressa.Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2021(6): 1-8. |
| 聂嘉荣, 张文浚, 郑燕, 等. 扁穗牛鞭草分子标记及转录组学研究进展. 草业与畜牧, 2021(6): 1-8. | |
| 18 | Gao J P, Wang D, Cao L Y, et al. Transcriptome sequencing of Codonopsis pilosula and identification of candidate genes involved in polysaccharide biosynthesis. PLoS One, 2015, 10(2): 117-134. |
| 19 | Porebski S, Bailey L G, Baum B R. Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 1997, 15(1): 8-15. |
| 20 | Peakall R, Smouse P E. GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(19): 2537-2539. |
| 21 | Yeh F C, Yang R C, Boyle T, et al. POPGENE Version 1.32 Microsoft windows-based freeware for populations genetic analysis Version 1.31. Edmonton: University of Alberta, and Tim Boyle, Centre for International Forestry Research, 1999. |
| 22 | Kalinowski S T, Taper M L, Marshall T C. Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Molecular Ecology, 2007, 16(5): 1099-1106. |
| 23 | Nei M F, Tajima F, Tateno Y. Accuracy of estimated phylogenetic trees from molecular data. II. Gene frequency data. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 1982, 19(2): 153-170. |
| 24 | Zhang X Y, Zhang X L, Li N, et al. Development and application of genomic SSR markers in Rosa persica. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2024, 44(6): 186-194. |
| 张雪云, 张晓龙, 李娜, 等. 单叶蔷薇基因组SSR标记开发与应用. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 186-194. | |
| 25 | Song Y, Zhang X R, He J X, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of Sophora flavescens Ait. germplasm resources based on cpSSR markers. Crops, 2023, 39(1): 30-37. |
| 宋芸, 张鑫瑞, 贺嘉欣, 等. 基于叶绿体SSR分子标记的苦参种质资源遗传多样性分析. 作物杂志, 2023, 39(1): 30-37. | |
| 26 | Zhao Q J, Xie T, Hu Y Q, et al. Identification of Alpinia officinarum Hance cultivation types based on EST-SSR molecular markers. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023, 21(2): 557-565. |
| 赵全杰, 谢腾, 胡雨晴, 等. 基于EST-SSR分子标记技术的高良姜栽培类型的鉴别. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(2): 557-565. | |
| 27 | Yin H, Li B, Zhang M Z, et al. Analysis of SSR sequence characteristics of Hordeum brevisubulatum transcriptome. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 8: 1-9. |
| 尹航, 李冰, 张明智, 等. 短芒大麦草转录组SSR序列特征分析. 分子植物育种, 2021, 8: 1-9. | |
| 28 | Zhu Y Q, Peng D D, Lin C W, et al. Development of SSR markers based on transcriptome sequence and analysis of genetic diversity in Sorghum sudanense. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(5): 178-189. |
| 朱永群, 彭丹丹, 林超文, 等. 苏丹草转录组SSR分子标记开发及遗传多样性评价. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 178-189. | |
| 29 | Mao X R, Liu Y P, Su X, et al. Characteristics analysis of simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci in Psammochloa villosa (Poaceae) based on transcriptome data.Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(8): 1990-2001. |
| 毛轩睿, 刘玉萍, 苏旭, 等. 沙鞭转录组简单重复序列(SSR)位点特征分析. 草地学报, 2022, 30(8): 1990-2001. | |
| 30 | Fu G, Liu Y P, Su X. Analysis of SSR characteristics for Elsholtzia densa Benth. based on transcriptome data. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2021, 41(4): 654-663. |
| 富贵, 刘玉萍, 苏旭. 基于转录组数据的密花香薷SSR位点特征分析.西北植物学报, 2021, 41(4): 654-663. | |
| 31 | Yin Y, An W, Zhao J H, et al. SSR information in transcriptome and development of molecular markers in Lycium ruthenicum. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2019, 36(2): 422-428. |
| 尹跃, 安巍, 赵建华, 等. 黑果枸杞转录组SSR信息分析及分子标记开发. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(2): 422-428. | |
| 32 | Zhang T Y, Song L, Shen Q. EST-SSR distribution characteristics and markers development of Perilla frutescens. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(9): 114-118. |
| 张天缘, 宋莉, 沈奇. 紫苏EST-SSR分布特征及标记开发. 贵州农业科学, 2017, 45(9): 114-118. | |
| 33 | Liu X L, Zhang A L, Zhao Y, et al. SSR information analysis and primers selecting for Salvia yunnanensis. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2017, 28(9): 2224-2225. |
| 刘小莉, 张爱丽, 赵燕, 等. 云南鼠尾草SSR位点信息分析和引物初筛. 时珍国医国药, 2017, 28(9): 2224-2225. | |
| 34 | Liu X Y, Wei Y K, Li G B. Development and characterization of microsatellite markers for the east Asia Salvia group using transcriptome sequencing. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(22): 7445-7452. |
| 刘欣雨, 魏宇昆, 李桂彬. 丹参转录组的微卫星位点(SSR)特征及属内通用引物的开发. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(22): 7445-7452. | |
| 35 | Haydar K, Crytsal M Y L, Wieland M. Survey of simple sequence repeats in completed fungal genomes. Molecular Biology&Evolution, 2005, 22(3): 639-649. |
| 36 | Shen X B, Zhu Y J, Xu G B. Distribution characteristics of SSR loci and development of molecular markers in Taxus fauna. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2021, 41(4): 139-147. |
| 申响保, 朱妍洁, 徐刚标. 密叶红豆杉SSR位点分布特征及分子标记开发.中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(4): 139-147. | |
| 37 | Zheng C Y. Development of SSR molecular markers and analyses of genetic diversity in Xanthopappus subacaulis (Asteraceae). Xining: Qinghai Normal University, 2023. |
| 郑长远. 黄缨菊SSR分子标记开发及遗传多样性研究. 西宁: 青海师范大学, 2023. | |
| 38 | Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney R K, et al. Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2003, 106(3): 411-422. |
| 39 | Kantety R V, LaRota M, Matthews D E, et al. Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat. Plant Molecular Biology, 2002, 48(5/6): 501-510. |
| 40 | Sun J J, Zhou T, Zhang R T, et al. Comparative transcriptomes and development of expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat markers for two closely related oak species. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 2019, 57(5): 440-450. |
| 41 | Botstein D, White R L, Skolnick M, et al. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. American Journal of Human Genetics, 1980, 32(3): 314. |
| [1] | 马婷, 陈奋奇, 王勇, 哈雪, 李亚君, 马晖玲. NaCl胁迫下鹰嘴紫云英根系基因差异表达及相关通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 104-123. |
| [2] | 冯雅琪, 陈嘉慧, 张静妮, 隋超, 陈基伟, 刘志鹏, 周强, 刘文献. 基于重测序紫花苜蓿高蛋白、高产关联InDel分子标记开发[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 137-149. |
| [3] | 符勇耀, 蔡莉, 李丰耀, 杨文俊, 徐文姬, 姜思佳, 杨利平. 兰州百合多倍体离体诱导及其分子细胞鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 172-181. |
| [4] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [5] | 曾兵, 尚盼盼, 沈秉娜, 王胤晨, 屈明好, 袁扬, 毕磊, 杨兴云, 李文文, 周晓丽, 郑玉倩, 郭文强, 冯彦龙, 曾兵. 淹水胁迫下鸭茅根系基因差异表达及相关通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 93-111. |
| [6] | 田甜, 李军乔, 马斌, 王鑫慈, 曲俊儒. 基于SSR分子标记的自然状态下蕨麻采样策略研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 181-197. |
| [7] | 张浩, 胡海英, 李惠霞, 贺海明, 马霜, 马风华, 宋柯辰. 荒漠草原优势植物牛枝子对干旱胁迫的生理响应与转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 188-205. |
| [8] | 董佳琦, 杨艳婷, 范文强, 王佳妮, 石凤翎. 扁蓿豆种内杂种鉴定及其F1和F2代主要农艺性状优势分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 229-239. |
| [9] | 崔婷, 王勇, 马晖玲. 外源IAA作用下草地早熟禾中调控Cd长距离运输的关键基因表达及其代谢通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 146-156. |
| [10] | 杨瑞鑫, 李勇, 蔡小芳, 韩铖星, 郭艳丽. 不同物理形态的开食料对羔羊瘤胃转录组的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 159-170. |
| [11] | 尚盼盼, 曾兵, 屈明好, 李明阳, 杨兴云, 郑玉倩, 沈秉娜, 毕磊, 杨成, 曾兵. 红三叶响应淹水胁迫的相关通路及差异表达基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 112-128. |
| [12] | 孙禄娟, 何建军, 汪军成, 姚立蓉, 司二静, 杨轲, 李葆春, 马小乐, 尚勋武, 孟亚雄, 王化俊. 基于全长转录组测序的盐生草SSR标记开发及其遗传多样性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 199-210. |
| [13] | 王志恒, 魏玉清, 赵延蓉, 王悦娟. 基于转录组学比较研究甜高粱幼苗响应干旱和盐胁迫的生理特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 71-84. |
| [14] | 潘静, 张俊超, 陈有军, 周青平. 基于SCoT标记的披碱草属种质遗传多样性分析及指纹图谱构建[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 48-60. |
| [15] | 杨志民, 邢瑞, 丁鋆嘉, 庄黎丽. 基于转录组测序的高羊茅分蘖与株高相关差异表达基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 145-163. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||