

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 139-154.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021499
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
姜瑛1( ), 魏畅1(
), 魏畅1( ), 焦秋娟1, 申凤敏1, 李鸽子2, 张雪海2, 杨芳3, 柳海涛1(
), 焦秋娟1, 申凤敏1, 李鸽子2, 张雪海2, 杨芳3, 柳海涛1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-28
修回日期:2022-03-09
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-08-12
通讯作者:
柳海涛
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: liuhaitaoky@henau.edu.cn基金资助:
Ying JIANG1( ), Chang WEI1(
), Chang WEI1( ), Qiu-juan JIAO1, Feng-min SHEN1, Ge-zi LI2, Xue-hai ZHANG2, Fang YANG3, Hai-tao LIU1(
), Qiu-juan JIAO1, Feng-min SHEN1, Ge-zi LI2, Xue-hai ZHANG2, Fang YANG3, Hai-tao LIU1( )
)
Received:2021-12-28
Revised:2022-03-09
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
Hai-tao LIU
About author:First author contact:JIANG Ying、WEI Chang These authors contributed equally to this work.
摘要:
为探究镉(Cd)胁迫条件下,施硅(Si)对玉米幼苗生长以及根系构型分级的影响,寻求可缓解Cd对玉米毒害的有效途径,本研究采用水培试验,在Cd胁迫条件下施加不同浓度Si,测定玉米的Cd浓度及含量、生长相关指标、光合指标、根系构型,并将根系构型按根系直径进行分级比较其变化特征。结果表明,Cd胁迫条件下玉米幼苗的生长发育受到抑制,叶绿素含量上升,光合参数显著降低,总根长、根表面积、根体积、根尖数和分枝数,包括Ⅰ~Ⅲ级径级区间的根长,和Ⅰ~Ⅱ级径级区间的根表面积以及根体积显著下降。施加不同浓度Si后,玉米幼苗整株Cd含量降低了12.65%~88.07%,Cd毒害在不同程度上得到缓解,表现为株高、主根长、生物量和耐受指数的提高;总叶绿素含量在Si浓度为0.25 mmol·L-1时提高了11.76%,Cd胁迫下气孔导度、胞间CO2浓度和蒸腾速率分别在Si浓度为1.00 mmol·L-1时显著提高;总根长、分枝数、Ⅰ级径级区间的根长、根表面积和根体积在Si浓度为1.00 mmol·L-1时达到最大,当Si浓度为1.50 mmol·L-1时,根表面积和根体积达到峰值。相关性分析表明Ⅰ~Ⅲ级径级区间内的总根长和根表面积,以及Ⅰ~Ⅱ级径级区间的根体积与Cd转运系数呈显著负相关;生长耐受性综合评价表明,总体上1.00 mmol·L-1外源Si缓解50 μmol·L-1玉米Cd毒害的效果最佳。结果表明,施Si可通过降低玉米幼苗根系对Cd的吸收、积累和转运,减少地上部的Cd浓度及积累,从而减小Cd对光合系统的影响,提高玉米幼苗生物量,并进一步促进光合产物向地下部的分配,减轻Cd对根系构型的影响,提高玉米耐Cd能力,缓解Cd对玉米的毒害作用。
姜瑛, 魏畅, 焦秋娟, 申凤敏, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 杨芳, 柳海涛. 外源硅对镉胁迫下玉米生理参数及根系构型分级的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 139-154.
Ying JIANG, Chang WEI, Qiu-juan JIAO, Feng-min SHEN, Ge-zi LI, Xue-hai ZHANG, Fang YANG, Hai-tao LIU. Effects of exogenous silicon application on physiological parameters, root architecture and diameter distribution of maize under cadmium stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 139-154.
生长指标 Growth index | CK | Cd50 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | Si0.25 | Si0.5 | Si1 | Si1.5 | Si2 | Si4 | ||
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 47.00± 2.67a | 29.80± 0.79d | 33.50± 0.72c | 32.83± 2.19c | 38.73± 1.42b | 38.87± 1.07b | 33.53± 1.52c | 29.90± 1.06d |
| 主根长Main root length (cm) | 29.70± 1.30a | 21.37± 1.59cde | 18.67± 0.74e | 22.53± 1.47bcd | 22.07± 0.76bcd | 23.33± 3.13bc | 24.97± 1.88b | 19.97± 0.49de |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot weight (g) | 4.31± 0.46a | 1.78± 0.12b | 2.01± 0.33b | 1.83± 0.43b | 2.28± 0.29b | 2.45± 0.53b | 1.86± 0.31b | 0.92± 0.47c |
| 地下部鲜重Root weight (g) | 1.50± 0.21a | 0.95± 0.08bc | 1.13± 0.15abc | 1.19± 0.38abc | 1.22± 0.20abc | 1.49± 0.27a | 1.28± 0.10ab | 0.85± 0.22c |
| 地上部干重Shoot dry weight (g) | 0.31± 0.02a | 0.15± 0.01cd | 0.17± 0.03cd | 0.16± 0.04cd | 0.20± 0.02bc | 0.22± 0.04b | 0.17± 0.03cd | 0.12± 0.01d |
| 地下部干重Root dry weight (g) | 0.08± 0.01bc | 0.06± 0.00c | 0.07± 0.01bc | 0.09± 0.02bc | 0.10± 0.01ab | 0.11± 0.01a | 0.09± 0.01ab | 0.08± 0.02bc |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.26± 0.03d | 0.39± 0.05c | 0.45± 0.02bc | 0.53± 0.03b | 0.48± 0.03bc | 0.52± 0.04b | 0.53± 0.04b | 0.65± 0.13a |
| 茎耐受指数Shoot tolerance index (%) | - | 49.66± 4.52bc | 53.82± 9.55bc | 51.68± 12.18bc | 64.70± 7.22ab | 71.20± 12.36a | 53.89± 9.14bc | 39.93± 4.46c |
| 根耐受指数Root tolerance index (%) | - | 73.68± 5.37c | 91.35± 11.38bc | 105.11± 27.94abc | 118.95± 16.89ab | 139.12± 13.63a | 108.98± 11.00ab | 99.55± 28.29bc |
表1 Cd胁迫下不同浓度Si处理对玉米幼苗生长及耐受指数的影响
Table 1 Effects of different Si treatment on the growth and tolerance index of maize seedlings under Cd stress (mean±SD)
生长指标 Growth index | CK | Cd50 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | Si0.25 | Si0.5 | Si1 | Si1.5 | Si2 | Si4 | ||
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 47.00± 2.67a | 29.80± 0.79d | 33.50± 0.72c | 32.83± 2.19c | 38.73± 1.42b | 38.87± 1.07b | 33.53± 1.52c | 29.90± 1.06d |
| 主根长Main root length (cm) | 29.70± 1.30a | 21.37± 1.59cde | 18.67± 0.74e | 22.53± 1.47bcd | 22.07± 0.76bcd | 23.33± 3.13bc | 24.97± 1.88b | 19.97± 0.49de |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot weight (g) | 4.31± 0.46a | 1.78± 0.12b | 2.01± 0.33b | 1.83± 0.43b | 2.28± 0.29b | 2.45± 0.53b | 1.86± 0.31b | 0.92± 0.47c |
| 地下部鲜重Root weight (g) | 1.50± 0.21a | 0.95± 0.08bc | 1.13± 0.15abc | 1.19± 0.38abc | 1.22± 0.20abc | 1.49± 0.27a | 1.28± 0.10ab | 0.85± 0.22c |
| 地上部干重Shoot dry weight (g) | 0.31± 0.02a | 0.15± 0.01cd | 0.17± 0.03cd | 0.16± 0.04cd | 0.20± 0.02bc | 0.22± 0.04b | 0.17± 0.03cd | 0.12± 0.01d |
| 地下部干重Root dry weight (g) | 0.08± 0.01bc | 0.06± 0.00c | 0.07± 0.01bc | 0.09± 0.02bc | 0.10± 0.01ab | 0.11± 0.01a | 0.09± 0.01ab | 0.08± 0.02bc |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.26± 0.03d | 0.39± 0.05c | 0.45± 0.02bc | 0.53± 0.03b | 0.48± 0.03bc | 0.52± 0.04b | 0.53± 0.04b | 0.65± 0.13a |
| 茎耐受指数Shoot tolerance index (%) | - | 49.66± 4.52bc | 53.82± 9.55bc | 51.68± 12.18bc | 64.70± 7.22ab | 71.20± 12.36a | 53.89± 9.14bc | 39.93± 4.46c |
| 根耐受指数Root tolerance index (%) | - | 73.68± 5.37c | 91.35± 11.38bc | 105.11± 27.94abc | 118.95± 16.89ab | 139.12± 13.63a | 108.98± 11.00ab | 99.55± 28.29bc |

图2 Cd胁迫下不同浓度Si处理对玉米幼苗组织内Cd浓度、Cd含量以及转运系数的影响图中误差线代表标准偏差,不同小写字母代表各处理间差异达到显著水平 (P<0.05),下同。The error lines in the figure represent standard deviation, and different lowercase letters represent the difference among treatment has reached significant level (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.2 Effects of different Si treatment on Cd concentration, Cd accumulation and translocation factors of maize seedling tissue under Cd stress
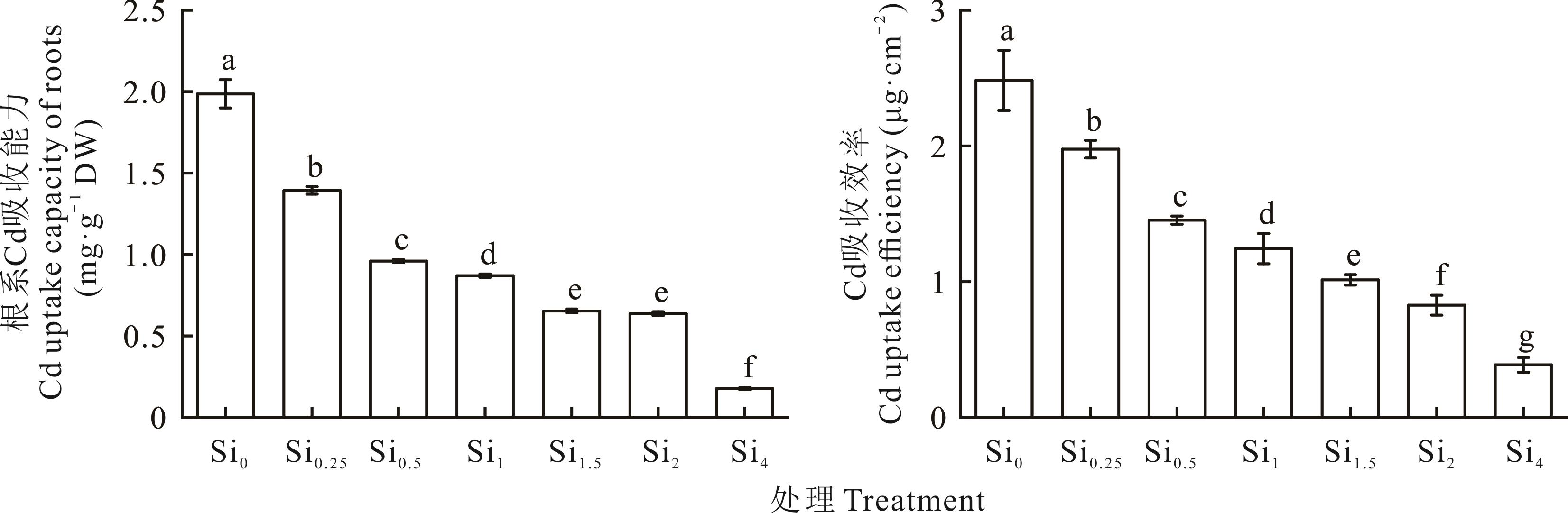
图3 Cd胁迫下不同浓度Si处理对玉米幼苗根系Cd吸收能力和Cd吸收效率的影响
Fig.3 Effects of different Si treatment on Cd uptake capacity of roots and Cd uptake efficiency of maize seedling under Cd stress
项目 Item | CK | Cd50 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | Si0.25 | Si0.5 | Si1 | Si1.5 | Si2 | Si4 | ||
| 总根长RL (cm) | 966.95±120.15a | 367.71±32.39b | 380.44±64.23b | 393.17±142.11b | 484.58±115.19b | 433.66±43.93b | 436.79±41.96b | 206.38±19.77c |
| 各分级总根长RL of each class (cm) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 794.09±104.54a | 266.37±14.84b | 290.32±43.70b | 290.55±129.39b | 358.25±98.33b | 297.63±39.49b | 284.08±28.68b | 115.60±17.26c |
| Ⅱ | 146.80±17.46a | 86.01±20.61bcd | 67.94±20.62d | 79.36±14.49bcd | 101.85±14.47b | 97.94±5.46bc | 130.00±15.51a | 71.24±5.93cd |
| Ⅲ | 16.10±2.26b | 9.43±1.67c | 11.83±2.01bc | 13.17±1.46bc | 15.30±2.37bc | 22.39±7.32a | 13.67±4.06bc | 10.61±1.19bc |
| Ⅳ | 9.60±3.06b | 5.85±1.59b | 10.31±0.66b | 10.02±2.99b | 9.13±2.70b | 15.49±5.20a | 8.93±3.13b | 8.83±0.89b |
| 根表面积SA (cm2) | 100.56±10.31a | 47.73±3.24de | 52.42±8.81cde | 56.09±14.61bcd | 68.12±13.74bc | 72.87±9.37b | 68.21±4.97bc | 36.29±4.09e |
| 各分级根表面积SA of each class (cm2) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 42.73±5.91a | 15.93±0.73b | 19.04±2.73b | 19.20±8.51b | 25.10±7.50b | 22.21±2.28b | 20.62±2.25b | 6.66±1.09c |
| Ⅱ | 32.49±3.91a | 18.75±4.14cd | 15.48±5.06d | 17.75±3.50cd | 23.11±3.12bc | 22.60±1.28bc | 28.80±3.31ab | 15.20±2.07d |
| Ⅲ | 6.05±0.87b | 3.57±0.59b | 4.45±0.78b | 4.93±0.53b | 5.69±0.82b | 8.62±2.93a | 5.15±1.56b | 4.08±0.48b |
| Ⅳ | 7.43±2.33b | 4.68±1.38b | 8.12±0.60b | 8.83±3.00ab | 7.27±2.23b | 12.82±4.35a | 7.38±2.04b | 7.24±1.03b |
| 根体积RV (cm3) | 0.83±0.07ab | 0.49±0.03d | 0.57±0.10cd | 0.65±0.11bcd | 0.76±0.13bc | 0.99±0.23a | 0.85±0.05ab | 0.51±0.07d |
| 各分级根体积RV of each class (cm3) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.23±0.04a | 0.09±0.01cd | 0.12±0.02bc | 0.12±0.05bc | 0.17±0.05b | 0.15±0.01b | 0.14±0.02bc | 0.04±0.01d |
| Ⅱ | 0.59±0.07a | 0.33±0.07cd | 0.29±0.10d | 0.33±0.07cd | 0.43±0.06bc | 0.43±0.03bc | 0.52±0.06ab | 0.27±0.05d |
| Ⅲ | 0.18±0.03b | 0.11±0.02b | 0.13±0.02b | 0.15±0.02b | 0.17±0.02b | 0.27±0.09a | 0.16±0.05b | 0.13±0.02b |
| Ⅳ | 0.54±0.17bc | 0.36±0.12c | 0.61±0.09bc | 0.84±0.36ab | 0.55±0.19bc | 1.03±0.33a | 0.61±0.13bc | 0.60±0.19bc |
| 平均直径RD (mm) | 0.33±0.01e | 0.41±0.01d | 0.44±0.00cd | 0.47±0.07bcd | 0.45±0.02cd | 0.54±0.07ab | 0.50±0.01abc | 0.56±0.03a |
| 根尖数RT | 1759.67±91.54a | 598.33±118.45bc | 513.33±74.57c | 564.00±190.84bc | 723.00±97.15bc | 603.33±147.55bc | 735.33±53.68b | 623.67±46.19bc |
| 分枝数RF | 3768.67±659.30a | 1111.67±62.77bc | 1225.67±282.53bc | 1313.67±507.38bc | 1578.67±391.95b | 1512.33±282.17b | 1451.00±178.10b | 641.00±142.45c |
表2 Cd胁迫下不同浓度Si处理对玉米幼苗根系结构和根系分级的影响
Table 2 Effects of different Si treatment on root structure and root of different root diameters classes of maize seedlings under Cd stress (mean±SD)
项目 Item | CK | Cd50 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si0 | Si0.25 | Si0.5 | Si1 | Si1.5 | Si2 | Si4 | ||
| 总根长RL (cm) | 966.95±120.15a | 367.71±32.39b | 380.44±64.23b | 393.17±142.11b | 484.58±115.19b | 433.66±43.93b | 436.79±41.96b | 206.38±19.77c |
| 各分级总根长RL of each class (cm) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 794.09±104.54a | 266.37±14.84b | 290.32±43.70b | 290.55±129.39b | 358.25±98.33b | 297.63±39.49b | 284.08±28.68b | 115.60±17.26c |
| Ⅱ | 146.80±17.46a | 86.01±20.61bcd | 67.94±20.62d | 79.36±14.49bcd | 101.85±14.47b | 97.94±5.46bc | 130.00±15.51a | 71.24±5.93cd |
| Ⅲ | 16.10±2.26b | 9.43±1.67c | 11.83±2.01bc | 13.17±1.46bc | 15.30±2.37bc | 22.39±7.32a | 13.67±4.06bc | 10.61±1.19bc |
| Ⅳ | 9.60±3.06b | 5.85±1.59b | 10.31±0.66b | 10.02±2.99b | 9.13±2.70b | 15.49±5.20a | 8.93±3.13b | 8.83±0.89b |
| 根表面积SA (cm2) | 100.56±10.31a | 47.73±3.24de | 52.42±8.81cde | 56.09±14.61bcd | 68.12±13.74bc | 72.87±9.37b | 68.21±4.97bc | 36.29±4.09e |
| 各分级根表面积SA of each class (cm2) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 42.73±5.91a | 15.93±0.73b | 19.04±2.73b | 19.20±8.51b | 25.10±7.50b | 22.21±2.28b | 20.62±2.25b | 6.66±1.09c |
| Ⅱ | 32.49±3.91a | 18.75±4.14cd | 15.48±5.06d | 17.75±3.50cd | 23.11±3.12bc | 22.60±1.28bc | 28.80±3.31ab | 15.20±2.07d |
| Ⅲ | 6.05±0.87b | 3.57±0.59b | 4.45±0.78b | 4.93±0.53b | 5.69±0.82b | 8.62±2.93a | 5.15±1.56b | 4.08±0.48b |
| Ⅳ | 7.43±2.33b | 4.68±1.38b | 8.12±0.60b | 8.83±3.00ab | 7.27±2.23b | 12.82±4.35a | 7.38±2.04b | 7.24±1.03b |
| 根体积RV (cm3) | 0.83±0.07ab | 0.49±0.03d | 0.57±0.10cd | 0.65±0.11bcd | 0.76±0.13bc | 0.99±0.23a | 0.85±0.05ab | 0.51±0.07d |
| 各分级根体积RV of each class (cm3) | ||||||||
| Ⅰ | 0.23±0.04a | 0.09±0.01cd | 0.12±0.02bc | 0.12±0.05bc | 0.17±0.05b | 0.15±0.01b | 0.14±0.02bc | 0.04±0.01d |
| Ⅱ | 0.59±0.07a | 0.33±0.07cd | 0.29±0.10d | 0.33±0.07cd | 0.43±0.06bc | 0.43±0.03bc | 0.52±0.06ab | 0.27±0.05d |
| Ⅲ | 0.18±0.03b | 0.11±0.02b | 0.13±0.02b | 0.15±0.02b | 0.17±0.02b | 0.27±0.09a | 0.16±0.05b | 0.13±0.02b |
| Ⅳ | 0.54±0.17bc | 0.36±0.12c | 0.61±0.09bc | 0.84±0.36ab | 0.55±0.19bc | 1.03±0.33a | 0.61±0.13bc | 0.60±0.19bc |
| 平均直径RD (mm) | 0.33±0.01e | 0.41±0.01d | 0.44±0.00cd | 0.47±0.07bcd | 0.45±0.02cd | 0.54±0.07ab | 0.50±0.01abc | 0.56±0.03a |
| 根尖数RT | 1759.67±91.54a | 598.33±118.45bc | 513.33±74.57c | 564.00±190.84bc | 723.00±97.15bc | 603.33±147.55bc | 735.33±53.68b | 623.67±46.19bc |
| 分枝数RF | 3768.67±659.30a | 1111.67±62.77bc | 1225.67±282.53bc | 1313.67±507.38bc | 1578.67±391.95b | 1512.33±282.17b | 1451.00±178.10b | 641.00±142.45c |
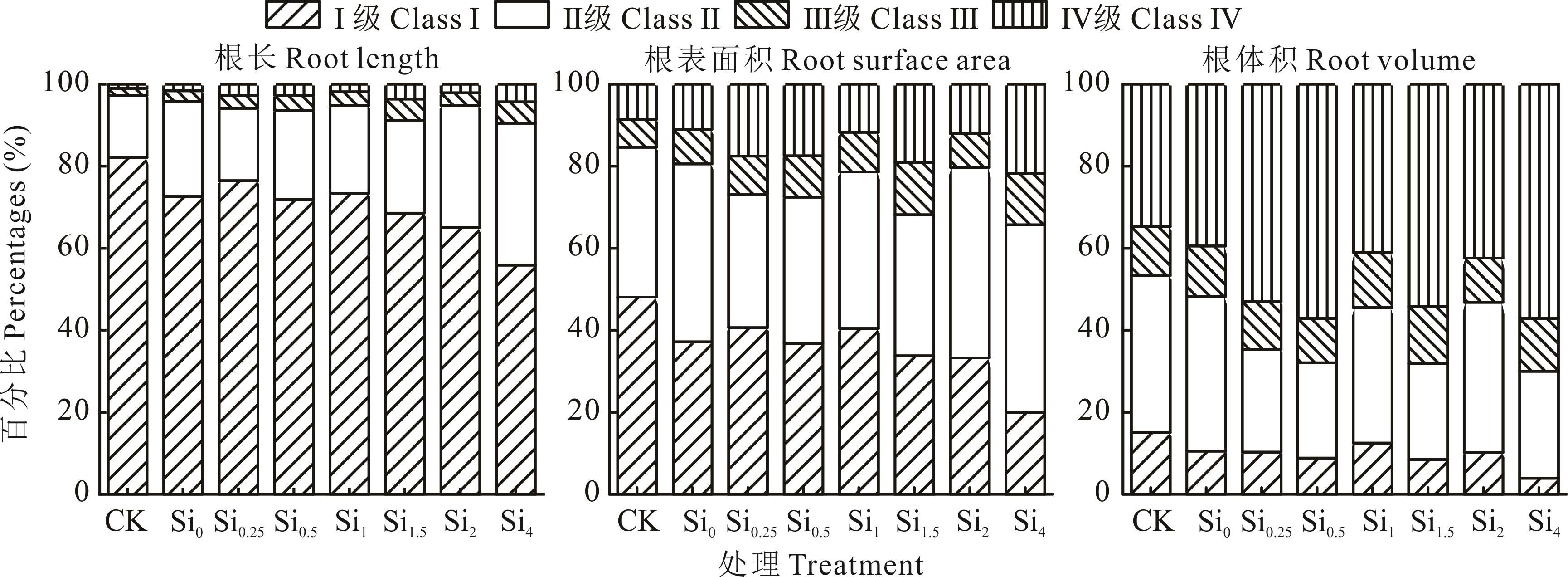
图6 Cd胁迫下不同浓度Si处理对玉米幼苗根长、根表面积以及根体积在不同径级区间所占百分比的影响
Fig.6 Effects of different Si treatment on maize seedling percentage of root length, root surface area and root volume in different root diameters under Cd stress
项目 Item | Cd处理 Cd treatment (μmol·L-1) | Si处理 Si treatment (mmol·L-1) | 平均值 Average value | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0.82 | 1 |
| Cd50Si0 | 50 | 0 | 0.31 | 7 |
| Cd50Si0.25 | 50 | 0.25 | 0.45 | 4 |
| Cd50Si0.5 | 50 | 0.50 | 0.43 | 5 |
| Cd50Si1 | 50 | 1.00 | 0.53 | 2 |
| Cd50Si1.5 | 50 | 1.50 | 0.49 | 3 |
| Cd5 Si2 | 50 | 2.00 | 0.36 | 6 |
| Cd50Si4 | 50 | 4.00 | 0.07 | 8 |
表3 Cd胁迫下不同浓度Si处理后玉米幼苗生长耐受性综合评价
Table 3 Effects of different Si treatment on comprehensive evaluation of tolerance of maize seedlings under Cd stress
项目 Item | Cd处理 Cd treatment (μmol·L-1) | Si处理 Si treatment (mmol·L-1) | 平均值 Average value | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0.82 | 1 |
| Cd50Si0 | 50 | 0 | 0.31 | 7 |
| Cd50Si0.25 | 50 | 0.25 | 0.45 | 4 |
| Cd50Si0.5 | 50 | 0.50 | 0.43 | 5 |
| Cd50Si1 | 50 | 1.00 | 0.53 | 2 |
| Cd50Si1.5 | 50 | 1.50 | 0.49 | 3 |
| Cd5 Si2 | 50 | 2.00 | 0.36 | 6 |
| Cd50Si4 | 50 | 4.00 | 0.07 | 8 |
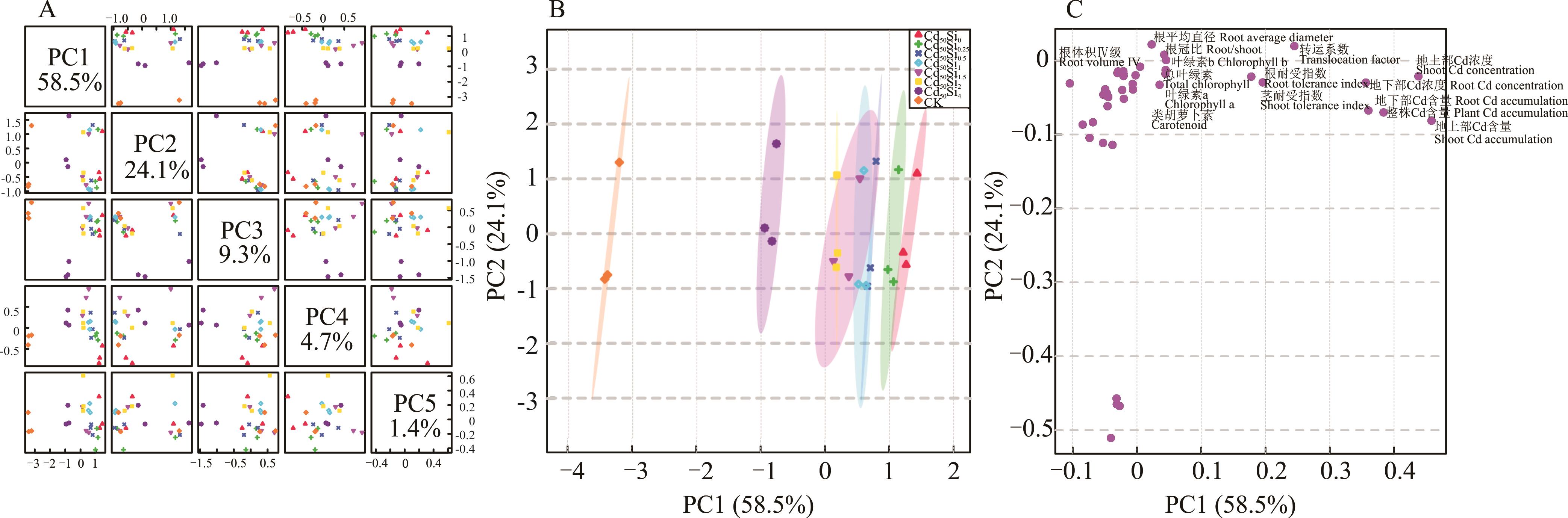
图7 Cd胁迫下不同浓度Si处理诱导玉米幼苗各指标变化的主成分分析
Fig.7 Principal component analysis of the changes of each index of maize seedlings induced by Si at different concentrations under Cd stress

图8 Cd胁迫下不同浓度Si处理诱导玉米幼苗各指标变化的相关性分析和热图A中颜色的深浅代表系数的大小,0以上代表正相关,0以下代表负相关,颜色越深,相关性越大。In figure A, the different color represents the value of coefficient, the value above zero represents positively correlated, and the value below zero represents negatively correlated. The darker the color, the larger the correlation.
Fig.8 Thermography and correlation analysis of the changes of each index of maize seedlings induced by Si at different concentrations under Cd stress
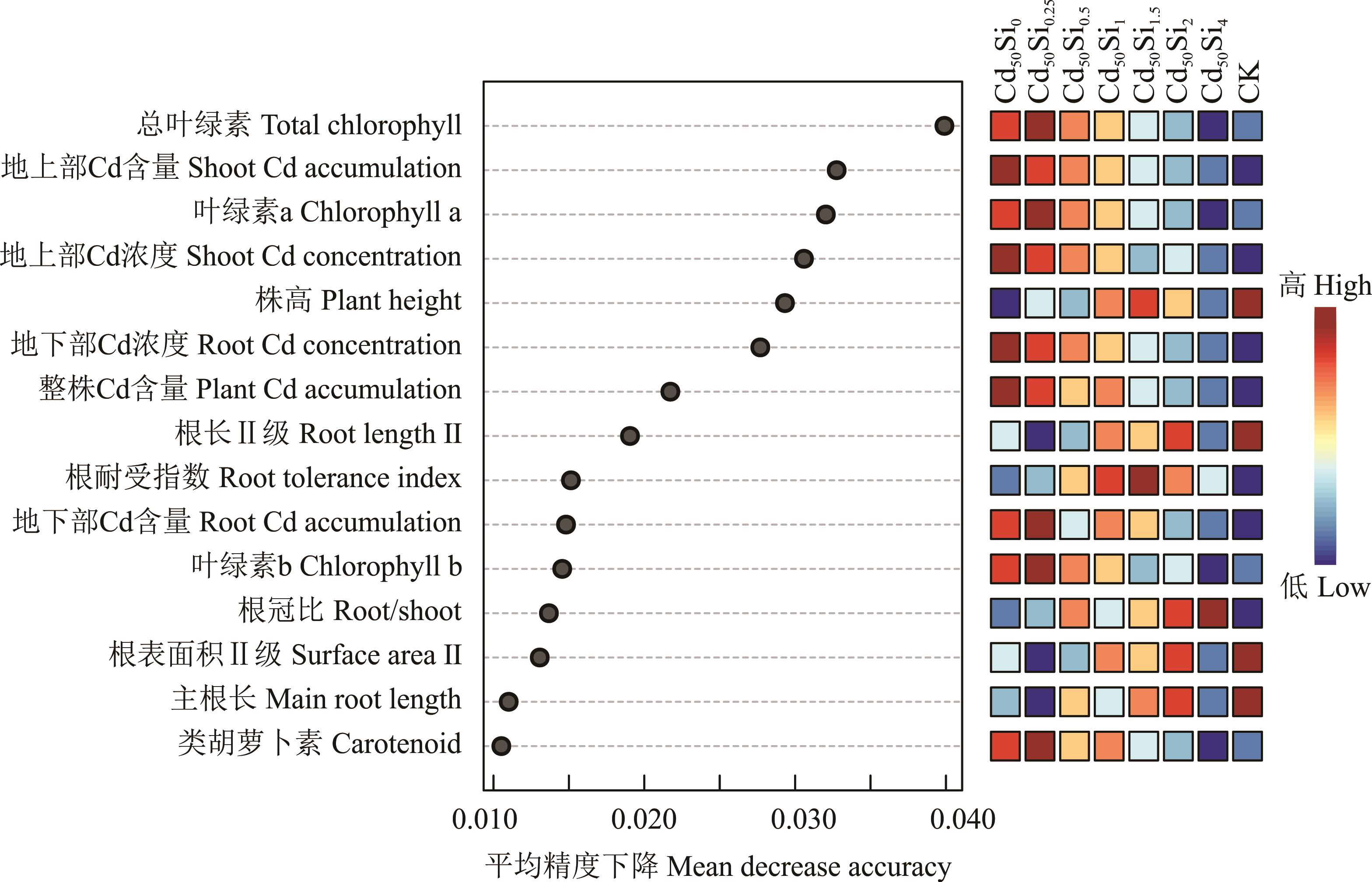
图9 Cd胁迫下不同浓度Si处理诱导玉米幼苗各指标变化的随机森林分析
Fig.9 Random forest plot of the changes of each index of maize seedlings induced by Si at different concentrations under Cd stress
| 1 | Chen N C, Zheng Y J, He X F, et al. Analysis of the report on the national general survey of soil contamination. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(9): 1689-1692. |
| 陈能场, 郑煜基, 何晓峰, 等. 《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》探析. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(9): 1689-1692. | |
| 2 | Liu C F, Shi G R, Yu R G, et al. Eco-physiological mechanisms of silicon-induced alleviation of cadmium toxicity in plants: A review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(23): 7799-7810. |
| 刘彩凤, 史刚荣, 余如刚, 等. 硅缓解植物镉毒害的生理生态机制. 生态学报, 2017, 37(23): 7799-7810. | |
| 3 | Satarug S, Garrett S H, Sens M A, et al. Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2010, 118(2): 182-190. |
| 4 | Nishijo M, Nakagawa H, Suwazono Y, et al. Causes of death in patients with Itai-itai disease suffering from severe chronic cadmium poisoning: A nested case-control analysis of a follow-up study in Japan. BMJ Open, 2017, 7(7): e015694. |
| 5 | Malcovska S M, Ducaiova Z, Maslanakova I, et al. Effect of silicon on growth, photosynthesis, oxidative status and phenolic compounds of maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium excess. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2014, 225(8): 2056. |
| 6 | Chen J J, Yu W, Zu Y Q, et al. Variety difference of Cd accumulation and translocation in Zea mays. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(10): 1671-1676. |
| 陈建军, 于蔚, 祖艳群, 等. 玉米(Zea mays)对镉积累与转运的品种差异研究. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(10): 1671-1676. | |
| 7 | Qu D Y, Zhang L G, Gu W R, et al. Effects of chitosan on root growth and leaf photosynthesis of maize seedlings under cadmium stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(5): 1300-1309. |
| 曲丹阳, 张立国, 顾万荣, 等. 壳聚糖对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗根系生长及叶片光合的影响. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(5): 1300-1309. | |
| 8 | Zhang C C, Chang J T, Gao S L, et al. Effects of silicon on yield and physiological characteristics of rice plants under cadmium and zinc stress. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 26(6): 936-941. |
| 张翠翠, 常介田, 高素玲, 等. 硅处理对镉锌胁迫下水稻产量及植株生理特性的影响. 核农学报, 2012, 26(6): 936-941. | |
| 9 | Wang H, Zhao S C, Xia W J, et al. Effect of cadmium stress on photosynthesis, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2008(1): 36-42. |
| 汪洪, 赵士诚, 夏文建,等. 不同浓度镉胁迫对玉米幼苗光合作用、脂质过氧化和抗氧化酶活性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008(1): 36-42. | |
| 10 | Qu D Y, Gu W R, Li L J, et al. Regulation of chitosan on the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in Zea mays seedling leaves under cadmium stress. Plant Science Journal, 2018, 36(2): 291-299. |
| 曲丹阳, 顾万荣, 李丽杰,等. 壳聚糖对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗叶片AsA-GSH循环的调控效应. 植物科学学报, 2018, 36(2): 291-299. | |
| 11 | Wu Z C, Zhao X H, Sun X C, et al. Antioxidant enzyme systems and the ascorbate-glutathione cycle as contributing factors to cadmium accumulation and tolerance in two oilseed rape cultivars (Brassica napus L.) under moderate cadmium stress. Chemosphere, 2015, 138(11): 526-536. |
| 12 | Yu K L, Zou J, Zou J H. Effects of cadmium stress on antioxidant enzyme system and absorption of mineral elements in maize seedlings. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(6): 1050-1056. |
| 宇克莉, 邹婧, 邹金华. 镉胁迫对玉米幼苗抗氧化酶系统及矿质元素吸收的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(6): 1050-1056. | |
| 13 | Xu H X, Weng X Y, Mao W H, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and excitation energy distribution in leaves of rice. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(4): 338-342. |
| 徐红霞, 翁晓燕, 毛伟华, 等. 镉胁迫对水稻光合、叶绿素荧光特性和能量分配的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(4): 338-342. | |
| 14 | Yu K L, Meng Q M, Zou J H. Effects of Cd2+ on seedling growth, chlorophyll contents and ultrastructures in maize. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2010, 25(3): 118-123. |
| 宇克莉, 孟庆敏, 邹金华. 镉对玉米幼苗生长、叶绿素含量及细胞超微结构的影响. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(3): 118-123. | |
| 15 | Ge C L, Luo J F, Liu C, et al. Effect of heavy metals on the photosynthesis and photosynthates transformation in rice. Acta Agriculturae Nucleatae Sinica, 2005,19(3): 214-218. |
| 葛才林, 骆剑峰, 刘冲,等. 重金属对水稻光合作用和同化物输配的影响. 核农学报, 2005,19(3): 214-218. | |
| 16 | Ge C L. Molecular mechanism of heavy metals toxicity and tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2002. |
| 葛才林. 水稻 (Oryza sativa L.)和小麦(Triticum aestivum L.) 的重金属毒害与耐性的分子机理研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2002. | |
| 17 | Wei C, Jiao Q J, Liu H T, et al. Physiological effects of different Cd concentrations on maize root architecture and classification. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 101-113. |
| 魏畅, 焦秋娟, 柳海涛, 等. 镉暴露条件下玉米生长及根系构型分级特征研究. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 101-113. | |
| 18 | He J Y, Wang Y Y, Ren Y F, et al. Effect of cadmium on root morphology and physiological characteristics of rice seedlings. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(5): 1863-1868. |
| 何俊瑜, 王阳阳, 任艳芳, 等. 镉胁迫对不同水稻品种幼苗根系形态和生理特性的影响. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(5): 1863-1868. | |
| 19 | Ma J F. Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2004, 50(1): 11-18. |
| 20 | Epstein E. Silicon: Its manifold roles in plants. Annals of Applied Biology, 2009, 155(2): 155-160. |
| 21 | Chen D M, Chen D Q, Xue R R, et al. Effects of boron, silicon and their interactions on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 367: 447-455. |
| 22 | Zhang J L, Zhu C H, Dou P, et al. Effect of phosphorus and silicon application on the uptake and utilization of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium by maize seedlings. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(5): 677-688. |
| 张嘉莉, 朱从桦, 豆攀, 等. 硅、磷配施对玉米苗期生长及氮磷钾积累的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(5): 677-688. | |
| 23 | Shi Z Y, Yang S Q, Han D, et al. Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.) by reducing cadmium ion uptake and enhancing antioxidative capacity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(8): 7638-7646. |
| 24 | Wu J W, Geilfus C M, Pitann B, et al. Silicon-enhanced oxalate exudation contributes to alleviation of cadmium toxicity in wheat. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2016, 131: 10-18. |
| 25 | Zhu X F, Zheng C, Hu Y T, et al. Cadmium-induced oxalate secretion from root apex is associated with cadmium exclusion and resistance in Lycopersicon esculentum. Plant Cell and Environment, 2011, 34(7): 1055-1064. |
| 26 | Ma J, Cai H M, He C W, et al. A hemicellulose-bound form of silicon inhibits cadmium ion uptake in rice (Oryza sativa) cells. New Phytologist, 2015, 206(3): 1063-1074. |
| 27 | Vaculik M, Landberg T, Grege M, et al. Silicon modifies root anatomy, and uptake and subcellular distribution of cadmium in young maize plants. Annals of Botany, 2012, 110(2): 433-443. |
| 28 | Greger M, Kabir A H, Landberg T, et al. Silicate reduces cadmium uptake into cells of wheat. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 211: 90-97. |
| 29 | Wang X K, Huang J L. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2015. |
| 王学奎, 黄见良. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015. | |
| 30 | Shi G R, Xia S L, Ye J, et al. PEG-simulated drought stress decreases cadmium accumulation in castor bean by altering root morphology. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2015, 111(3): 127-134. |
| 31 | Zadeh L A. Fuzzy sets. Information & Control, 1965, 8(3): 338-353. |
| 32 | Huang H L, Li M, Rizwan M, et al. Synergistic effect of silicon and selenium on the alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 401: 123393. |
| 33 | Shi Y, Zhang Y, Han W H, et al. Silicon enhances water stress tolerance by improving root hydraulic conductance in Solanum lycopersicum L. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 196. |
| 34 | Feng J P, Shi Q H, Wang X F, et al. Silicon supplementation ameliorated the inhibition of photosynthesis and nitrate metabolism by cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Cucumis sativus L. Scientia Horticulturae, 2010, 123(4): 521-530. |
| 35 | Yang C G, Dou H, Liang Y C, et al. Influence of silicon on cadmium availability and cadmium uptake by maize in cadmium-contaminated soil. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 38(1): 116-121. |
| 杨超光, 豆虎, 梁永超, 等. 硅对土壤外源镉活性和玉米吸收镉的影响. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(1): 116-121. | |
| 36 | Ozyigit I I, Baktibekova D, Hocaoglu-Ozyigit A, et al. The effects of cadmium on growth, some anatomical and physiological parameters of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). International Journal of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, 2021, 4(2): 235-253. |
| 37 | Shen C X, Yu Z L, Que Z Q. Physiological and morphological responses of the rice TP309 to short-term cadmium stress. Journal of Yichun University, 2019, 41(12): 5-9. |
| 沈春修, 於紫蕾, 却志群. 水稻品种台北309对短期镉胁迫的生理及形态响应. 宜春学院学报, 2019, 41(12): 5-9. | |
| 38 | Zhang L, Li J M, Wang H X. Physiological and ecological responses of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) root to cadmium stress. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2002, 33(1): 61-65. |
| 张玲, 李俊梅, 王焕校. 镉胁迫下小麦根系的生理生态变化. 土壤通报, 2002, 33(1): 61-65. | |
| 39 | Chen C F. The effect and mechanism of silicon on alleviating cadmium contamination of Chinese cabbage. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Soil Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry), 2007. |
| 陈翠芳. 硅对减轻黑叶白菜镉污染的效应及其机制. 北京: 中国科学院大学 (广州地球化学研究所), 2007. | |
| 40 | Dai Z, Wang C Y, Li N, et al. Effects of combined application of selenium and silicon on cadmium and mineral elements in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) under cadmium stress. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(1): 108-117. |
| 代邹, 王春雨, 李娜, 等. 硒、硅配施对镉胁迫下杂交稻中镉及矿质元素的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(1): 108-117. | |
| 41 | Nwugo C C, Huerta A J. Effects of silicon nutrition on cadmium uptake, growth and photosynthesis of rice plants exposed to low-level cadmium. Plant and Soil, 2008, 311(1/2): 73-86. |
| 42 | Wang P T, Zhao J, Yu H H. Reactive oxygen species signaling in stomata. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2014, 49(4): 490-503. |
| 王棚涛, 赵晶, 余欢欢. 气孔运动中的活性氧信号. 植物学报, 2014, 49(4): 490-503. | |
| 43 | Wang X M, Zhao X X, Huang L S, et al. The Na+ and K+ accumulative effect of four different salt tolerance genotypes in rice under salt stress. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(11): 2140-2146. |
| 王旭明, 赵夏夏, 黄露莎, 等. 盐胁迫下4个不同耐盐基因型水稻Na+、K+积累效应. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(11): 2140-2146. | |
| 44 | Israelsson M, Siegel R S, Young J, et al. Guard cell ABA and CO2 signaling network updates and Ca2+ sensor priming hypothesis. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2006, 9(6): 654-663. |
| 45 | Farooq M A, Ali S, Hameed A, et al. Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes; suppressed cadmium uptake and oxidative stress in cotton. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 96: 242-249. |
| 46 | Rahman S U, Qi X B, Kamran M, et al. Silicon elevated cadmium tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by endorsing nutrients uptake and antioxidative defense mechanisms in the leaves. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 166: 148-159. |
| 47 | Farquhar G D, Sharkey T D. Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis. Annual Reviews Plant Physiology, 1982, 33: 317-345. |
| 48 | Zhou Z, Zhang B, Liu H T, et al. Zinc effects on cadmium toxicity in two wheat varieties (Triticum aestivum L.) differing in grain cadmium accumulation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 183: 109562. |
| 49 | Hossain M T, Mori R, Soga K, et al. Growth promotion and an increase in cell wall extensibility by silicon in rice and some other Poaceae seedlings. Journal of Plant Research, 2002, 115(1117): 23-27. |
| 50 | Cunha K P V D, Nascimento C W A D. Silicon effects on metal tolerance and structural changes in maize (Zea mays L.) grown on a cadmium and zinc enriched soil. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2009, 197: 323-330. |
| 51 | Fan X Y, Wen X H, Huang F, et al. Effects of silicon on morphology, ultrastructure and exudates of rice root under heavy metal stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 38(8): 197. |
| [1] | 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| [2] | 李影正, 程榆林, 徐璐璐, 李万松, 严旭, 李晓锋, 何如钰, 周阳, 郑军军, 汪星宇, 张德龙, 程明军, 夏运红, 何建美, 唐祈林. 不同玉米品种(系)的全株、果穗与秸秆青贮特性比较[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 144-156. |
| [3] | 田吉鹏, 刘蓓一, 顾洪如, 丁成龙, 程云辉, 玉柱. 乳酸菌及丙酸钙对全株玉米和燕麦青贮饲料发酵品质和霉菌毒素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 157-166. |
| [4] | 蒋紫薇, 刘桂宇, 安昊云, 石薇, 常生华, 张程, 贾倩民, 侯扶江. 种植密度与施氮对玉米/秣食豆间作系统饲草产量、品质和氮肥利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 157-171. |
| [5] | 张晴, 邢静, 姚佳明, 殷庭超, 黄心如, 何悦, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草细胞分裂素信号通路B类ARR转录因子LpARR10的耐镉功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| [6] | 陈文瑞, 蒋朝, 周齐新, 王云琴, 李春鸣, 郭鹏辉, 刘慧霞. 不同盐分条件下硅对两个高羊茅品种生物量分配和营养元素氮、磷、钾吸收利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 51-60. |
| [7] | 杨德智, 王晨, 侯明杰, 王虎成. 饲用甜高粱和全株玉米青贮对肉羊前胃微生态的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 145-154. |
| [8] | 魏畅, 焦秋娟, 柳海涛, 张静静, 申凤敏, 姜瑛, 张雪海, 孙娈姿, 杨芳, 刘振. 镉暴露条件下玉米生长及根系构型分级特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 101-113. |
| [9] | 吴玉环, 王自奎, 刘亚男, 马千虎. 带幅设计对玉米/苜蓿间作群体光环境特征及光能利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 144-155. |
| [10] | 吴欣明, 方志红, 池惠武, 贾会丽, 刘建宁, 石永红, 王学敏. 30个青贮玉米在雁门关地区品种评比试验[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 205-216. |
| [11] | 温媛媛, 张美琦, 刘桃桃, 沈宜钊, 高艳霞, 李秋凤, 曹玉凤, 李建国. 体外产气法评价生薯条加工副产品-稻草混贮与全株玉米青贮组合效应的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 154-163. |
| [12] | 吴慧丽, 田薇, 纪燕玲, 娄来清, 蔡庆生. 促进镉吸收积累的植物根际促生菌的筛选及其对一年生黑麦草的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 53-61. |
| [13] | 张丹丹, 张元庆, 程景, 靳光, 李博, 王栋才, 徐芳, 孙锐锋. 不同粗饲料组合对晋南牛瘤胃体外发酵特性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 93-100. |
| [14] | 黄丽琴, 李松桥, 袁振中, 唐晶, 闫景彩, 唐启源. 全株水稻与平菇菌糠共发酵料对浏阳黑山羊屠宰性能、肉品质和器官指数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 133-140. |
| [15] | 祁鹤兴, 芦光新, 李宗仁, 徐成体, 德科加, 周孝娟, 王英成, 马桂花. 青海省青贮玉米链格孢叶枯病病原菌鉴定及其致病力分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 94-105. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||