

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 223-234.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025130
张世超1( ), 崔国文2, 张德鹏1, 韩福迎1, 丁叮1, 吕向丽1, 林硕1, 陈乐然1, 李吉儒1, 才华1(
), 崔国文2, 张德鹏1, 韩福迎1, 丁叮1, 吕向丽1, 林硕1, 陈乐然1, 李吉儒1, 才华1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-16
修回日期:2025-06-11
出版日期:2026-03-20
发布日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
才华
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: caihua@neau.edu.cn基金资助:
Shi-chao ZHANG1( ), Guo-wen CUI2, De-peng ZHANG1, Fu-ying HAN1, Ding DING1, Xiang-li LYU1, Shuo LIN1, Le-ran CHEN1, Ji-ru LI1, Hua CAI1(
), Guo-wen CUI2, De-peng ZHANG1, Fu-ying HAN1, Ding DING1, Xiang-li LYU1, Shuo LIN1, Le-ran CHEN1, Ji-ru LI1, Hua CAI1( )
)
Received:2025-04-16
Revised:2025-06-11
Online:2026-03-20
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
Hua CAI
摘要:
针对紫花苜蓿传统遗传转化技术存在的周期长、效率低、基因型依赖性强的技术瓶颈,本研究创新性地建立了基于发根农杆菌介导的高效非组培遗传转化体系。以‘龙牧806’苜蓿枝条为材料,采用优化的节下穿刺浸染法,构建无需组织培养的高效遗传转化体系。该方法可在14 d内获得转基因苜蓿嵌合体,生根率达72%~82%,毛状根遗传转化率达90.24%~94.59%。在应用验证方面,本研究取得两项重要突破:首先,利用该体系快速鉴定了耐盐基因MsRCI2D的功能,获得的转基因苜蓿嵌合体在200 mmol·L-1 NaCl胁迫下抗氧化酶活性显著提高、活性氧的积累显著下降、离子稳态调节能力增强;其次,结合可视化报告基因RUBY,建立了苜蓿基因编辑gRNA快速筛选技术,编辑效率达到23.07%。本研究建立的体系大幅缩短了转基因苜蓿嵌合体的获得周期,提高了转化效率。该技术不仅为紫花苜蓿基因功能研究提供了高效平台,同时为牧草分子设计育种提供了可靠的技术支撑,对其他饲草的遗传改良也具有重要参考价值。
张世超, 崔国文, 张德鹏, 韩福迎, 丁叮, 吕向丽, 林硕, 陈乐然, 李吉儒, 才华. 紫花苜蓿非组培遗传转化体系创建及在耐盐基因功能鉴定与基因编辑中的应用[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(3): 223-234.
Shi-chao ZHANG, Guo-wen CUI, De-peng ZHANG, Fu-ying HAN, Ding DING, Xiang-li LYU, Shuo LIN, Le-ran CHEN, Ji-ru LI, Hua CAI. Establishment of a tissue culture-free genetic transformation system for alfalfa and its applications in salt-tolerance gene functional characterization and gene editing[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(3): 223-234.
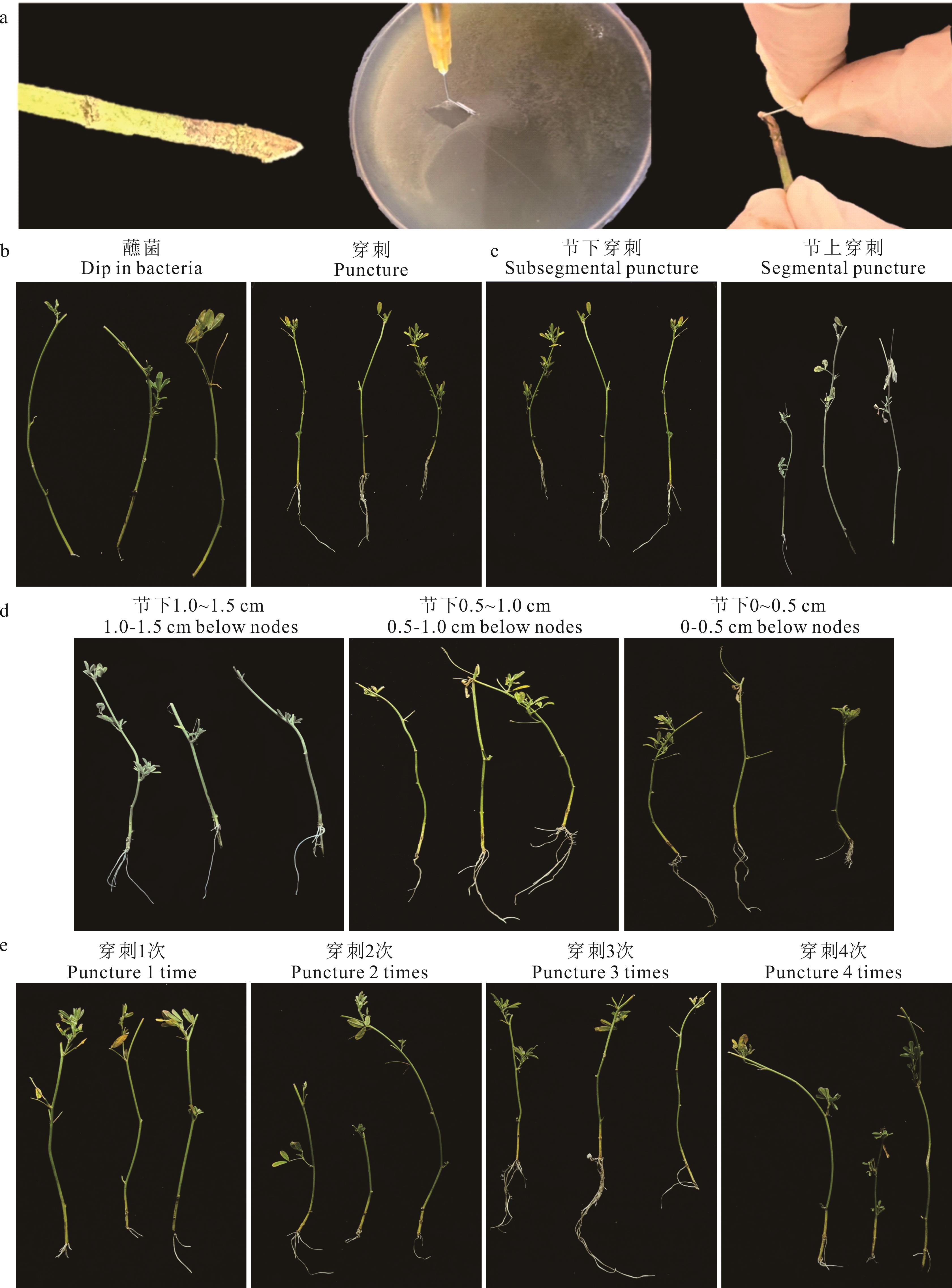
图2 不同穿刺方式毛状根的生长情况(a)穿刺准备及过程Puncture preparation and procedure; (b)蘸菌与穿刺转化毛状根Dip and puncture transformed hairy roots; (c)节上与节下穿刺Subsegmental and segmental punctured hairy roots; (d)节下不同位置穿刺Different locations of below nodes punctured hairy roots; (e)节下0.5~1.0 cm处穿刺不同次数Different times of punctured hairy roots from 0.5-1.0 cm below the node.
Fig.2 Growth of hairy roots in different puncture methods
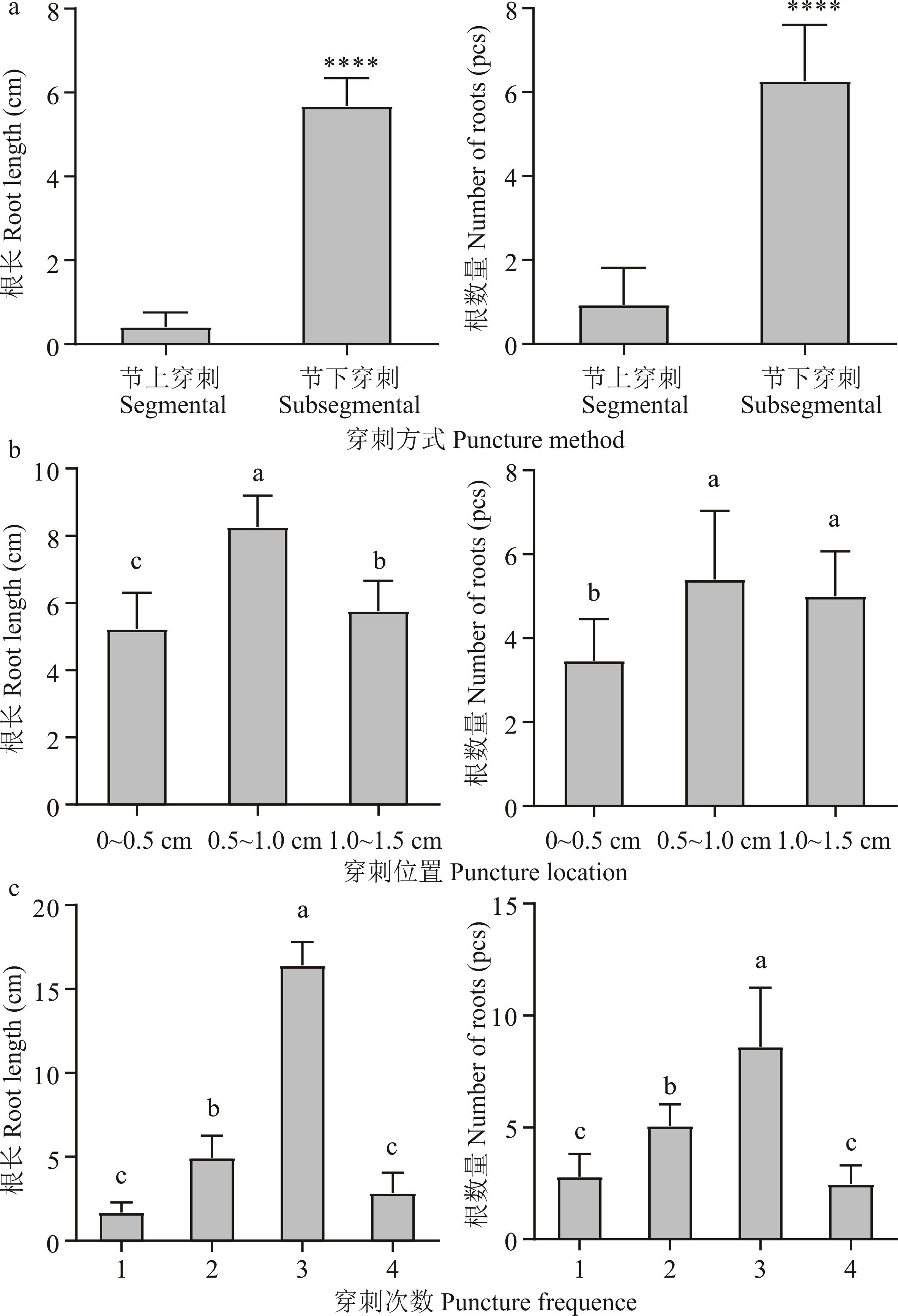
图3 不同转化方式处理14 d后毛状根生长情况(a)节上与节下穿刺Statistics on hairy root growth of subsegmental and segmental punctured branches; (b)不同位置节下穿刺Below nodes punctured branches at different locations; (c)节下0.5~1.0 cm处穿刺不同次数 Punctured branches with different number of times from 0.5-1.0 cm below the node. ****: 差异极显著Extremely significant difference (P<0.0001). 不同小写字母表示不同穿刺位置或不同穿刺次数间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among different puncture locations or frequencies.
Fig.3 Statistical comparison of hairy root growth after 14 days of treatment by different transformation methods
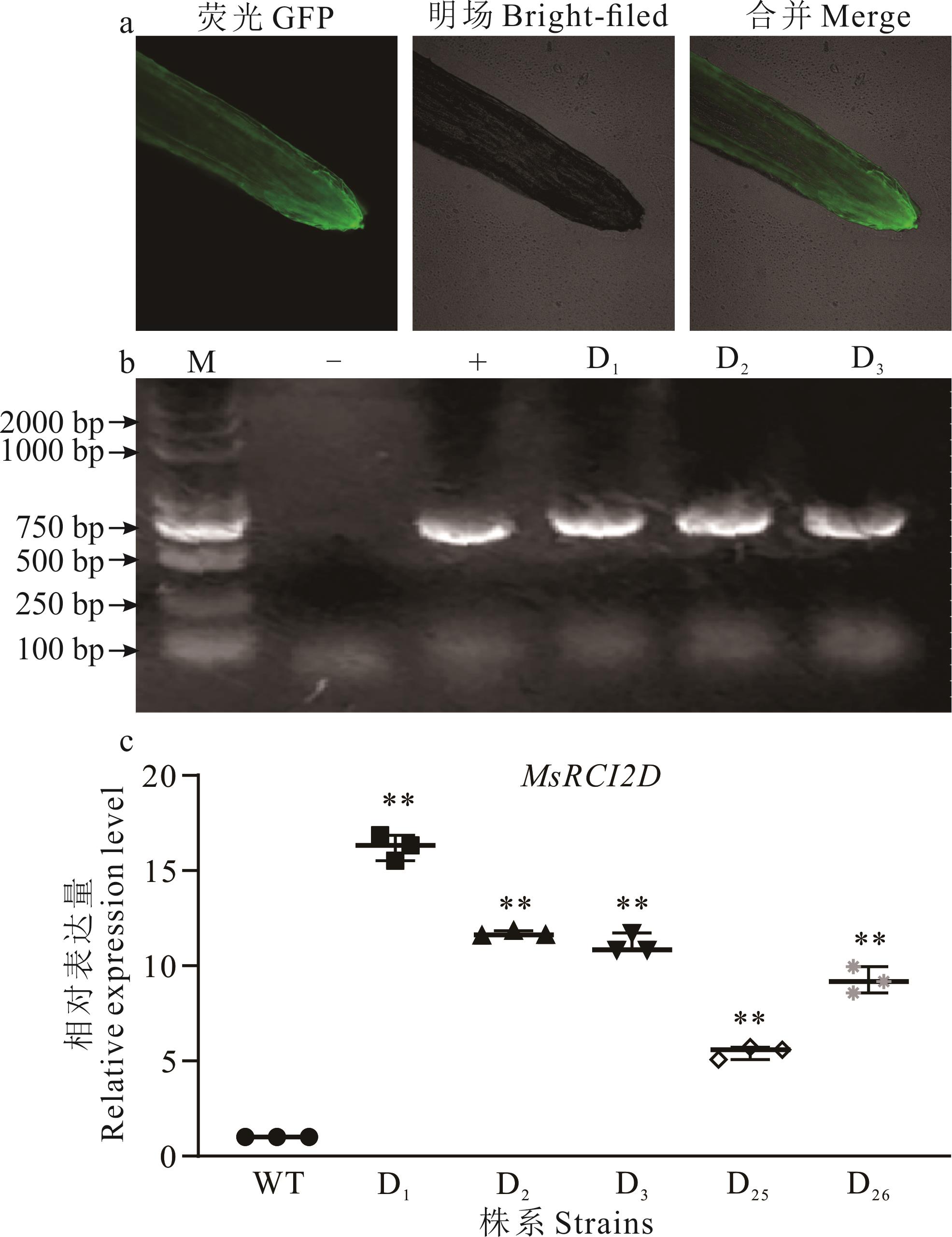
图4 毛状根阳性苗鉴定(a)MsRCI2D基因的毛状根荧光Fluorescence observation of hairy roots of MsRCI2D gene; (b)毛状根阳性苗PCR鉴定PCR identification of hairy root positive seedlings; (c)阳性苗实时荧光定量PCR Real-time quantitative PCR of positive seedlings; M: 分子量标记Trans 2K DNA Marker; -: 阴性对照Negative control; +: 阳性对照Positive control; WT: 野生型植株Wild-type plant; D1~D3, D25, D26: MsRCI2D基因不同转化株系Plants transformed with MsSCI2D.**: 差异极显著Extremely significant difference (P<0.01).
Fig.4 Identification of hairy root positive seedlings

图5 盐胁迫下转MsRCI2D基因苜蓿嵌合体的表型分析D1, D2: 不同转MsRCI2D植株Different trans-MsRCI2D plants; *: 差异显著Significant difference (P<0.05); **: 差异极显著Extremely significant difference (P<0.01).
Fig.5 Phenotypic analysis of alfalfa chimeras transgenic for the MsRCI2D gene under salt stress
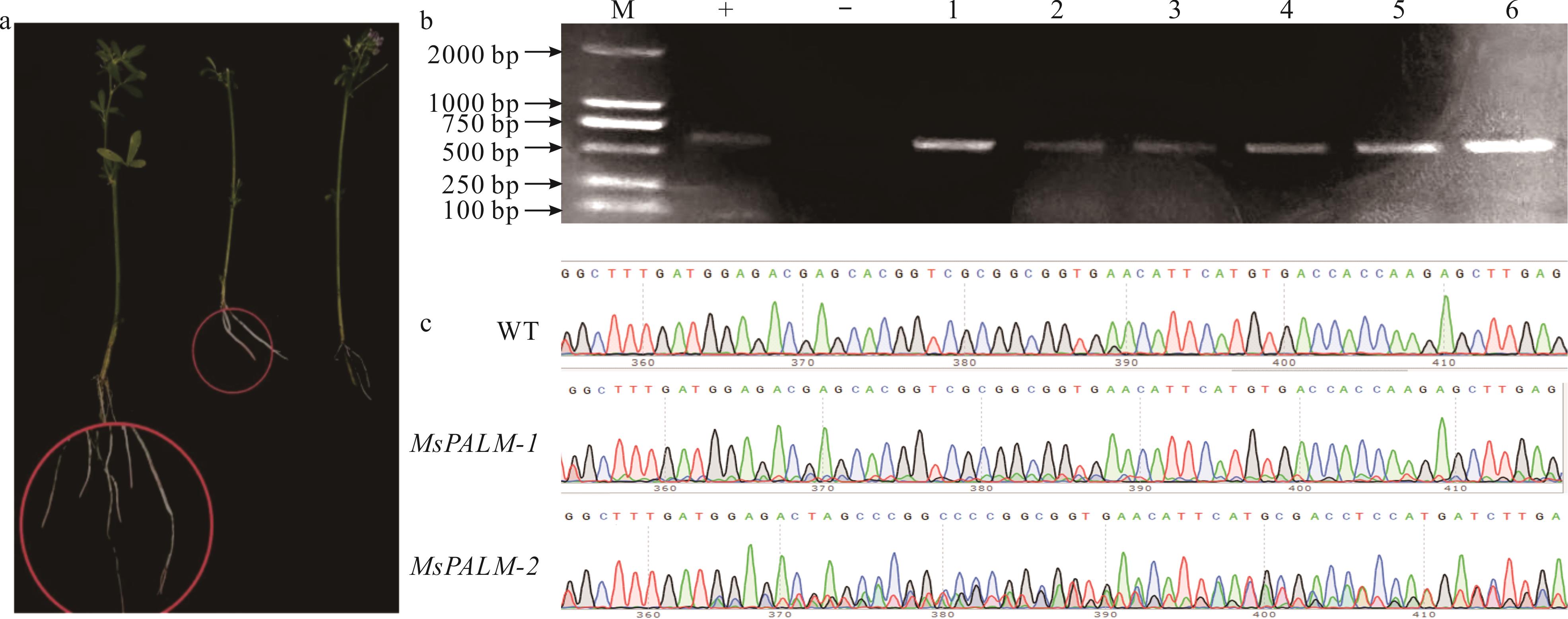
图6 毛状根阳性苗鉴定及Sanger测序(a)红色毛状根表型Red hairy root phenotype; (b)毛状根阳性鉴定Hairy root positive identification; (c)Sanger测序结果Sanger sequencing results; M: DL2000 Marker; -: 阴性对照Negative control; WT: 野生型Wild type; +: 阳性对照Positive control; 1~6: 阳性苗鉴定Positive seedling identification; WT: 野生型Wild type; MsPALM-1/2: 阳性毛状根部分测序结果Positive trichome root sequencing results.
Fig.6 Identification of hairy root positive seedlings and sanger sequencing results
| [1] | Ma J L, Cheng W Y. The feeding value and high-yield cultivation technology of alfalfa. Tillage and Cultivation, 2023, 43(3): 104-107. |
| 马娇丽, 程婉莹. 紫花苜蓿饲喂价值及高产栽培技术. 耕作与栽培, 2023, 43(3): 104-107. | |
| [2] | Guo C Y, Fang Y Y, Yi F Y, et al. Current status of protection and utilization of pasture germplasm resources in China. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2024, 45(6): 81-86. |
| 郭呈宇, 房永雨, 伊风艳, 等. 我国牧草种质资源保护与利用现状. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2024, 45(6): 81-86. | |
| [3] | Cong L L, Danzhencuo, Zhang W Y, et al. Research progress of CRISPR/Cas gene editing technology in grasses. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(9): 107-120. |
| 丛丽丽, 旦真措, 张文玉, 等. CRISPR/Cas基因编辑技术在草类植物中的研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(9): 107-120. | |
| [4] | Yi D X, Tong Z Y. Optimization of genetic transformation system in alfalfa. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(2): 504-511. |
| 仪登霞, 仝宗永. 紫花苜蓿遗传转化体系的优化. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(2): 504-511. | |
| [5] | Jiang L. Establishment of plant regeneration system of alfalfa. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 姜柳. 紫花苜蓿植株再生体系的建立. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2017. | |
| [6] | Yue W N, Xu T Y, Miao J M, et al. Screening of reference genes in different tissues and hormone treatments of alfalfa. Grassland and Turf, (2024-05-22)[2025-06-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1156.S.20240521.1243.002.html. |
| 岳炜楠, 胥通玉, 苗佳敏, 等. 紫花苜蓿不同组织及不同激素处理下内参基因的筛选. 草原与草坪, (2024-05-22)[2025-06-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1156.S.20240521.1243.002.html. | |
| [7] | Tao Y H, Fang L S, Yue J F, et al. Effects of exogenous ABA application on dormancy of terminal buds and its physiological and biochemical characteristics in paulownia. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, (2024-08-28)[2025-06-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1908.s.20240828.0929.002.html. |
| 陶昱含, 房丽莎, 岳继飞, 等. 外源ABA施用对泡桐顶芽休眠及其生理生化特征的影响. 林业科学, (2024-08-28)[2025-06-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1908.s.20240828.0929.002.html. | |
| [8] | Luo X W. Establishment of plant genetic transformation selection system based on biuret and its metabolic enzyme. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University, 2023. |
| 罗晓伟. 基于缩二脲及其代谢酶的植物遗传转化筛选系统的建立. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2023. | |
| [9] | Ye Q Y, Zhou C E, Lin H, et al. Medicago2035: Genomes, functional genomics, and molecular breeding. Molecular Plant, 2025, 18(2): 219-244. |
| [10] | Wang Z J, Li M X, Zhang W J. Optimization of Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation system of alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(6): 1665-1671. |
| 王之杰, 李明序, 张万军. 根癌农杆菌介导的紫花苜蓿遗传转化体系的优化. 草地学报, 2024, 32(6): 1665-1671. | |
| [11] | Zhao H X, Zhao S Y, Cao Y P, et al. Development of a single transcript CRISPR/Cas9 toolkit for efficient genome editing in autotetraploid alfalfa. The Crop Journal, 2024, 12(3): 788-795. |
| [12] | Luo Y Q, Wang X S, Zhang D P, et al. Overexpression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase kinase gene MsPPCK1 from Medicago sativa L. increased alkali tolerance of alfalfa by enhancing photosynthetic efficiency and promoting nodule development. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2024, 214: 108764. |
| [13] | Huo X Y, Schnabel E, Hughes K, et al. RNAi phenotypes and the localization of a protein:: GUS fusion imply a role for Medicago truncatula PIN genes in nodulation. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2006, 25: 156-165. |
| [14] | Kavitha T K, Sergey I, Bruna B, et al. Knockdown of CELL DIVISION CYCLE16 reveals an inverse relationship between lateral root and nodule numbers and a link to auxin in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiology, 2009, 151(3): 1155-1166. |
| [15] | Zhang H L, Cao Y P, Zhang H, et al. Efficient generation of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homozygous/biallelic Medicago truncatula mutants using a hairy root system. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 294. |
| [16] | Danzhencuo, Guo Y H, Li C, et al. Developing a hairy root transformation system for alfalfa. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2024, 46(6): 95-102. |
| 旦真措, 郭雨寒, 李聪, 等. 紫花苜蓿毛状根高效转化体系的建立. 中国草地学报, 2024, 46(6): 95-102. | |
| [17] | Chen J X, Mei H, Huang C X, et al. A highly efficient method to generate chimeric soybean plant with transgenic hairy roots. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 89-98. |
| 陈佳欣, 梅浩, 黄彩翔, 等. 利用转基因毛状根高效培育大豆嵌合植株的方法. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 89-98. | |
| [18] | Cao X S, Xie H T, Song M L, et al. Cut-dip-budding delivery system enables genetic modifications in plants without tissue culture. The Innovation, 2023, 4(1): 100345. |
| [19] | Xie K B, Minkenberg B, Yang Y N. Boosting CRISPR/Cas9 multiplex editing capability with the endogenous tRNA-processing system. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(11): 3570-3575. |
| [20] | Zhu F G, Ye Q Y, Chen H, et al. Multigene editing reveals that MtCEP1/2/12 redundantly control lateral root and nodule number in Medicago truncatula. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 72(10): 3661-3676. |
| [21] | Meng Y Y, Hou Y L, Wang H, et al. Targeted mutagenesis by CRISPR/Cas9 system in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell Reports, 2017, 36(2): 371-374. |
| [22] | Luciano P, Philippe B, Sabrina D, et al. QTL analysis for grazing tolerance, autumn dormancy and growth habit offers prospects for marker-assisted selection in lucerne. Euphytica, 2021, 217(8): 171. |
| [23] | Zhao L J. Development and optimization of highly efficient genetic transformation and genome editing system for alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2022. |
| 赵丽娟. 紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa L.)高效遗传转化与基因组编辑体系的建立与优化. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2022. | |
| [24] | Crane C, Wright E, Dixon R A, et al. Transgenic Medicago truncatula plants obtained from Agrobacterium tumefaciens- transformed roots and Agrobacterium rhizogenes-transformed hairy roots. Planta, 2006, 223(6): 1344-1354. |
| [25] | Lin C R, Zhang D M, Zhang W J, et al. Induction of hairy roots of tea plant by three kinds of Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2021, 41(3): 509-516. |
| 林彩容, 张冬敏, 张文静, 等. 3种农杆菌对茶树发状根诱导的影响. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(3): 509-516. | |
| [26] | Bian H H, Zhao W C, Wei J W. Effects of Agrobacterium rhizogenes strains on induction rate and positive rate of hairy roots. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(24): 8237-8244. |
| 边慧慧, 赵文超, 魏婧薇, 等. 不同发根农杆菌菌株对番茄毛状根诱导率及阳性率的影响. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(24): 8237-8244. | |
| [27] | Tao N, Li M X, Guo H C. Optimization of sweet potato genetic transformation system mediated by Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2023, 39(10): 175-183. |
| 陶娜, 李茂兴, 郭华春. 发根农杆菌介导的甘薯遗传转化体系优化. 生物技术通报, 2023, 39(10): 175-183. | |
| [28] | Liu F, Wang Y X, Chen A P, et al. Callus induction and differentiation of Xinjiang Medicago falcata L. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2012, 20(4): 741-746. |
| 刘芳, 王玉祥, 陈爱萍, 等. 新疆野生黄花苜蓿愈伤诱导及分化的研究. 草地学报, 2012, 20(4): 741-746. | |
| [29] | Ren Z M, Liu C, Li S S, et al. Effects calli differentiation of alfalfa and endogenous hormones levels under endogenous hormones and 60Co-γ radiation. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(7): 2162-2169. |
| 任忠敏, 刘畅, 李珊珊, 等. 外源激素和60Co-γ辐射对苜蓿愈伤组织分化及内源激素水平的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(7): 2162-2169. | |
| [30] | Ding Y L, Kalo P, Yendrek C R, et al. Abscisic acid coordinates nod factor and cytokinin signaling during the regulation of nodulation in Medicago truncatula. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(10): 2681-2695. |
| [31] | Zhao E H, Xie J P, Zhang Y J, et al. Establishment and application of hairy root transformation system of alfalfa. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(1): 1-9. |
| 赵恩华, 谢建平, 张钰靖, 等. 紫花苜蓿毛状根转化体系的建立及应用. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(1): 1-9. | |
| [32] | Polturak G, Breitel D, Grossman N, et al. Elucidation of the first committed step in betalain biosynthesis enables the heterologous engineering of betalain pigments in plants. New Phytologist, 2016, 210(1): 269-283. |
| [33] | Chen H T, Zeng Y, Yang Y Z, et al. Allele-aware chromosome-level genome assembly and efficient transgene-free genome editing for the autotetraploid cultivated alfalfa. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2494. |
| [34] | Yi X F, Wang C C, Yuan X Q, et al. Exploring an economic and highly efficient genetic transformation and genome-editing system for radish through developmental regulators and visible reporter. The Plant Journal: For Cell and Molecular Biology, 2024, 120(4): 1682-1692. |
| [35] | Ye Q Y, Meng X Z, Chen H, et al. Construction of genic male sterility system by CRISPR/Cas9 editing from model legume to alfalfa. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(4): 613-615. |
| [36] | Wolabu T W, Mahmood K, Jerez I T, et al. Multiplex CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis of alfalfa FLOWERING LOCUS Ta1 (MsFTa1) leads to delayed flowering time with improved forage biomass yield and quality. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2023, 21(7): 1383-1392. |
| [1] | 陈丽娟, 高荣, 王建喜, 马晖玲. 紫花苜蓿与红豆草在不同生长时期缩合单宁合成差异的比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 221-236. |
| [2] | 李瑒琨, 本转林, 张筠钰, 杨惠敏. 不同气候和土壤条件下施肥类型影响紫花苜蓿种子产量的整合分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 54-67. |
| [3] | 张继元, 安海全, 潘靖一, 刘畅, 龙思思, 赵丽丽. 7个紫花苜蓿品种种子萌发及幼苗生长的抗旱性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 68-82. |
| [4] | 张颖, 贺善睦, 何傲蕾, 李昌宁, 姚拓. 微生物菌剂与有机钙蛋白配施对紫花苜蓿生长和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 25-39. |
| [5] | 俞鸿千, 马雪鹏, 曾翰国, 单晓艳, 李曼莉, 王占军. 地下滴灌时期和水量对紫花苜蓿种子生产的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 53-64. |
| [6] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [7] | 鲜燃, 邓雨, 付秋月, 蒋晶霞, 陶佳丽, 许涛, 朱慧森, 岑慧芳. 紫花苜蓿MsMYB86基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 162-172. |
| [8] | 刘沂欣, 隋晓青, 王鑫尧, 郎梦卿, 孙凌子寅, 吉尔尔格. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿的缓解作用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 206-214. |
| [9] | 李文秀, 姚拓, 李昌宁, 贾倩民, 何傲蕾, 周杨. “凹凸棒-有机基质”菌肥载体最佳配比的筛选及对紫花苜蓿的促生效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 88-98. |
| [10] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [11] | 温小月, 赵颖, 王宝强, 王贤, 朱晓林, 王义真, 魏小红. 外源NO调控干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿AP2/ERFs基因的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 154-167. |
| [12] | 张英豪, 刘楚波, 周坤, 郭家存, 刘世鹏, 孙娈姿. 果草系统中枣树对不同方位紫花苜蓿和鸭茅生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 203-212. |
| [13] | 崔灿, 王梦琦, 赵琬璐, 刘新颖, 鉴晶晶, 严俊鑫. 胺鲜酯浸种对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 46-58. |
| [14] | 曾燕霞, 陈志龙, 尚继红, 沙晓弟, 吴娟, 陈彩锦. 太空诱变对PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿材料苗期生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 59-69. |
| [15] | 魏孔钦, 张盈盈, 回金峰, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷配施对紫花苜蓿根系非结构碳水化合物及碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 40-50. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||