

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 53-64.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025039
俞鸿千1,2( ), 马雪鹏1, 曾翰国3, 单晓艳1, 李曼莉3, 王占军1,2(
), 马雪鹏1, 曾翰国3, 单晓艳1, 李曼莉3, 王占军1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-13
修回日期:2025-04-15
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2025-11-13
通讯作者:
王占军
作者简介:E-mail: nxwzhj@163.com基金资助:
Hong-qian YU1,2( ), Xue-peng MA1, Han-guo ZENG3, Xiao-yan SHAN1, Man-li LI3, Zhan-jun WANG1,2(
), Xue-peng MA1, Han-guo ZENG3, Xiao-yan SHAN1, Man-li LI3, Zhan-jun WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-02-13
Revised:2025-04-15
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2025-11-13
Contact:
Zhan-jun WANG
摘要:
灌水是提高紫花苜蓿种子产量的重要管理手段,为了明确滴灌时期和水量对紫花苜蓿种子产量组分和实际产量的影响,探讨水分影响种子产量形成的机制,以‘甘农4号’紫花苜蓿为材料,2021-2022年开展田间精细化灌水试验,设置灌水时期(现蕾期、盛花期、现蕾期+盛花期)和灌水量(225、450 m3·hm-2)两个因素,测定土壤水分含量、种子产量因子和产量,并分析它们之间的相关性。结果表明:1)灌水时期是影响种子产量的主因素,灌水量可影响种子数/小荚;2)现蕾期灌水与花序数/生殖枝呈显著正相关,现蕾期+盛花期灌水与种子产量呈显著正相关;3)20~40 cm土层土壤水分含量、收获期土壤水分含量、花序数/生殖枝、小花数/花序和荚果数/花序对种子产量的影响具有直接效应。因此,适宜宁夏中部干旱半干旱区的地下滴灌方案为现蕾期灌水225 m3·hm-2,盛花期灌水225~450 m3·hm-2,配合冬灌450 m3·hm-2。
俞鸿千, 马雪鹏, 曾翰国, 单晓艳, 李曼莉, 王占军. 地下滴灌时期和水量对紫花苜蓿种子生产的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 53-64.
Hong-qian YU, Xue-peng MA, Han-guo ZENG, Xiao-yan SHAN, Man-li LI, Zhan-jun WANG. Effects of the amount and timing of subsurface drip irrigation on alfalfa seed production[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(1): 53-64.

图2 2021年6月试验小区俯拍T1为现蕾期灌水;T2为盛花期灌水;T3为现蕾期+盛花期灌水。V1为每次灌水225 m3·hm-2;V2为每次灌水450 m3·hm-2。“-1、-2、-3、-4”分别为小区重复数。T1 is irrigation at the budding stage, T2 is irrigation at the full flowering stage, T3 is irrigation at both the budding stage and the full flowering stage, V1 is 225 m3·ha-1 for each irrigation, V2 is 450 m3·ha-1 for each irrigation. “-1, -2, -3, -4” are the number of plot repeats.
Fig.2 Overhead view of the experimental plot in June 2021
年份 Year | 返青期 Regeneration stage | 分枝期 Branching stage | 现蕾期 Budding stage | 初花期 Early flowering stage | 盛花期 Full flowering stage | 结荚期 Podding stage | 收获期 Harvest stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 04-07 | 05-07 | 05-26 | 06-05 | 06-14 | 07-09 | 07-31 |
| 2022 | 04-10 | 05-07 | 05-25 | 06-02 | 06-20 | 07-10 | 08-01 |
表1 2021-2022年紫花苜蓿种子田生育期
Table 1 Alfalfa seed field growth period in 2021-2022 (月-日Month-day)
年份 Year | 返青期 Regeneration stage | 分枝期 Branching stage | 现蕾期 Budding stage | 初花期 Early flowering stage | 盛花期 Full flowering stage | 结荚期 Podding stage | 收获期 Harvest stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 04-07 | 05-07 | 05-26 | 06-05 | 06-14 | 07-09 | 07-31 |
| 2022 | 04-10 | 05-07 | 05-25 | 06-02 | 06-20 | 07-10 | 08-01 |

图3 2021-2022年土壤水分含量方差分析红色、绿色、蓝色分别为现蕾期(T1)、盛花期(T2)、现蕾期+盛花期(T3)灌水;空心为每次灌水225 m3·hm-2 (V1),实心为每次灌水450 m3·hm-2 (V2);下同。不同大写、小写字母分别表示相同生育期内各处理在0.01和0.05水平差异显著。Red is irrigation at the budding stage (T1), green is irrigation at the full flowering stage (T2), and blue is irrigation at both the budding stage and the full flowering stage (T3). The hollow is 225 m3·ha-1 for each irrigation (V1), and the solid is 450 m3·ha-1 for each irrigation (V2). The same below. Different uppercase and lowercase letters indicated significant differences at the levels of 0.01 and 0.05 among different treatments during the same growth period, respectively.
Fig.3 Analysis of variance of soil water content from 2021 to 2022
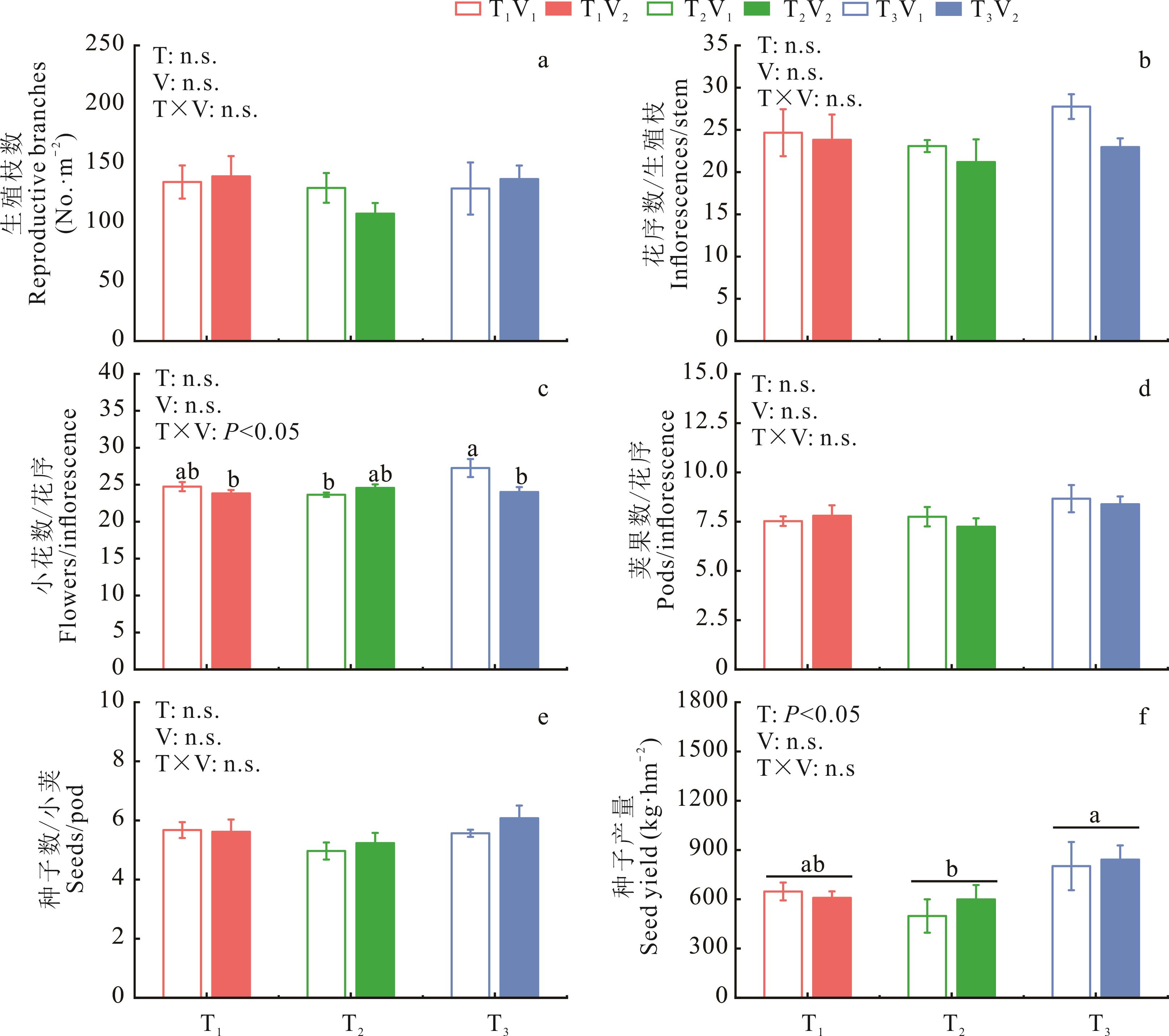
图4 2021年种子产量因子及种子产量的双因素方差分析T表示不同灌水时期;V表示不同灌水量;T×V表示灌水时期和灌水量交互作用。“n.s.”表示无显著差异,不同小写字母表示差异在0.05水平显著。下同。T indicates different irrigation periods; V indicates different irrigation amounts; T×V indicates the interaction between irrigation period and irrigation amount. n.s. indicates no significant difference, and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.4 Two-way ANOVA of seed yield factors and seed yield in 2021

图6 灌水时期与产量因子、产量的相关性分析*和**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平显著相关。* and ** indicate significant correlations at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively.
Fig.6 Point-Biserial correlation analysis between irrigation period with yield factor and yield
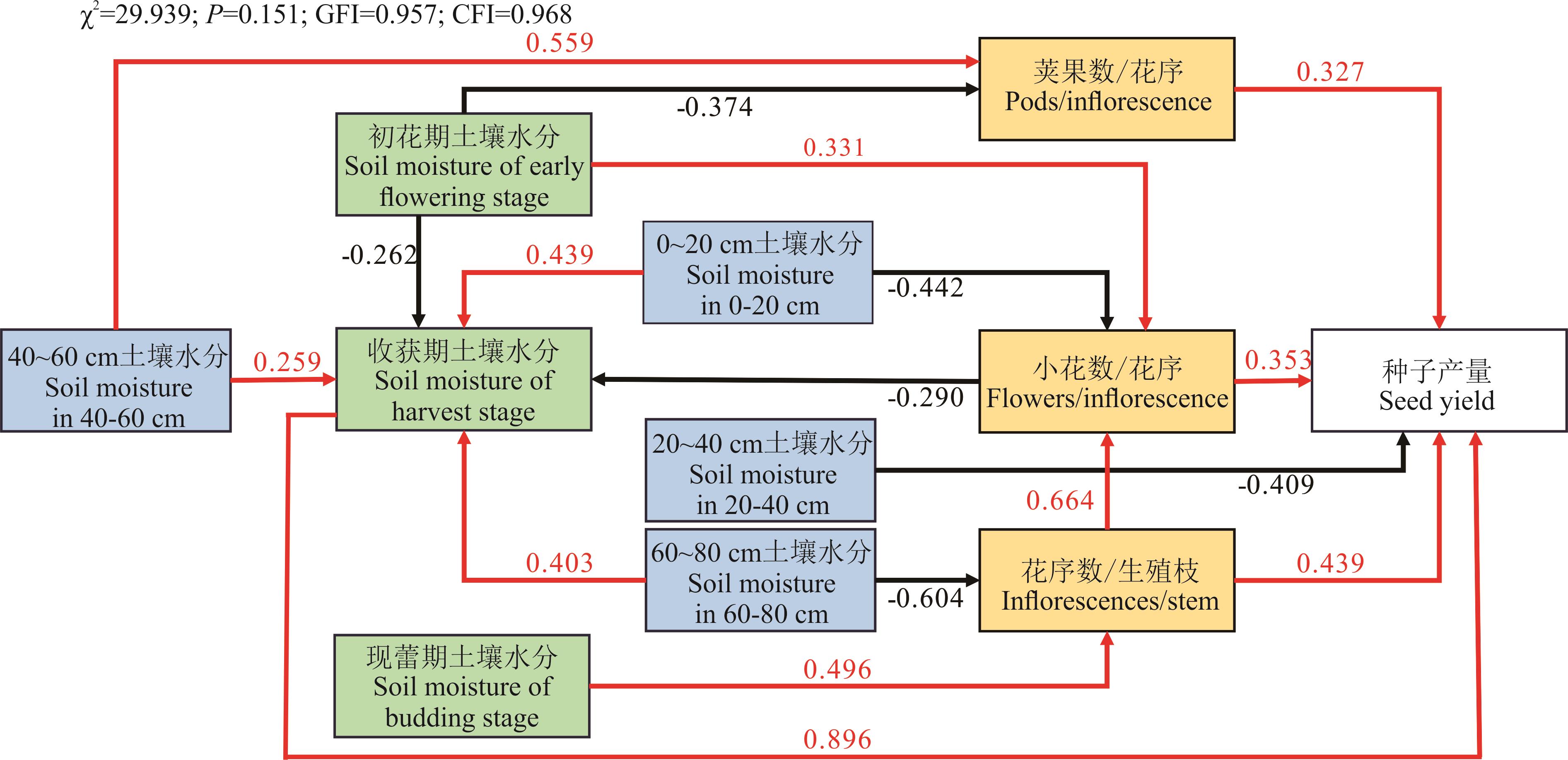
图7 土壤水分、产量因子与种子产量的结构方程模型图中因子均为测量变量,蓝色为不同土层土壤水分含量,绿色为不同生育期土壤水分含量,黄色为种子产量因子。红色和黑色实线分别表示在0.01水平有显著正向和负向影响,线条上的数字表示标准化路径系数,图中仅展示显著相关的路径。The factors in the figure are all measured variables, blue is the soil moisture content of different soil layers, green is the soil moisture content of different growth stages, and yellow is the seed yield factor. The solid red and black lines indicate significant positive or negative effects at the 0.01 level, respectively, and the value on the lines represent the standardized path coefficients, and only the significantly correlated paths are shown in the graph. GFI: 拟合指数Goodness of fit index; CFI: 相对拟合指数Comparative fit index.
Fig.7 Structural equation model of soil moisture, yield factors and seed yield
| [1] | Mao P S, Ou C M, Jia Z C, et al. Research progress for seed production technology of herbage and turfgrass in China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(1): 1-11. |
| 毛培胜, 欧成明, 贾志程, 等. 我国牧草与草坪草种子生产技术的研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(1): 1-11. | |
| [2] | Mao P S, Wang M Y, Ou C M. Analysis for the developing status and trend in the forage seed industry in China. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2018(6): 1-6. |
| 毛培胜, 王明亚, 欧成明. 中国草种业的发展现状与趋势分析. 草学, 2018(6): 1-6. | |
| [3] | Mao P S, Hou L Y, Wang M Y. Limited factors and key technologies of forage seed production in the northern of China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(2): 250-260. |
| 毛培胜, 侯龙鱼, 王明亚. 中国北方牧草种子生产的限制因素和关键技术. 科学通报, 2016, 61(2): 250-260. | |
| [4] | Xiao C, Ji Q, Zhang F, et al. Effects of various soil water potential thresholds for drip irrigation on soil salinity, seed cotton yield and water productivity of cotton in northwest China. Agricultural Water Management, 2023, 279: 108172. |
| [5] | Yavuz D, Yavuz N. How does lateral spacing affect seed yield and net income in trickle-irrigated sunflower under different irrigation regimes? Gesunde Pflanzen, 2023, 75(2): 415-429. |
| [6] | Thomas, Robertson M J, Fukai S, et al. The effect of timing and severity of water deficit on growth, development, yield accumulation and nitrogen fixation of mungbean. Field Crops Research, 2004, 86(1): 67-80. |
| [7] | Lu Y, Zhuang C N, Wang L H, et al. Comprehensive technology study on improving alfalfa seed yield. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2015, 36(2): 338-340. |
| 鲁英, 庄长楠, 王丽红, 等. 提高苜蓿种子产量综合配套技术研究. 中国农机化学报, 2015, 36(2): 338-340. | |
| [8] | Meng J M, Li W J. Effects of subsurface drip irrigation on alfalfa growth and seed production. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(1): 291-295. |
| 孟季蒙, 李卫军. 地下滴灌对苜蓿的生长发育与种子产量的影响. 草业学报, 2012, 21(1): 291-295. | |
| [9] | Li G L, Liu X P, Du G M, et al. Influence of different irrigation treatments on alfalfa seed yield and components. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2011, 42(12): 130-134. |
| 李国良, 刘香萍, 杜广明, 等. 不同时期滴灌对紫花苜蓿种子产量及其构成因子的影响. 东北农业大学学报, 2011, 42(12): 130-134. | |
| [10] | Chen J W, Li W J, Shi D. Effect of different water volume of subsurface drip irrigation on the yield and components of alfalfa seeds. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 48(1): 177-181. |
| 陈金炜, 李卫军, 师东. 地下滴灌不同灌水量对苜蓿种子产量构成因子的影响. 新疆农业科学, 2011, 48(1): 177-181. | |
| [11] | Wang X, Huang W, Yu S Y, et al. Effect of water and fertilizer coupling on seed yield and composition of alfalfa grown with underground drip irrigation in Ningxia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 76-85. |
| 王星, 黄薇, 余淑艳, 等. 宁夏地区地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿种子产量及构成因素的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 76-85. | |
| [12] | Wang X M, Zhang H, Song R, et al. Comparison of forage seed production between China and U.S.A. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(10): 2115-2125. |
| 王雪萌, 张涵, 宋瑞, 等. 中美牧草种子生产比较. 草地学报, 2021, 29(10): 2115-2125. | |
| [13] | Graham M, Ates S, Melathopoulos A P, et al. Partial shading by solar panels delays bloom, increases floral abundance during the late-season for pollinators in a dryland, agrivoltaic ecosystem. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 7452. |
| [14] | Zhang J, Ma P F, Wu S L, et al. Study on characteristics of soil water change and law of crop water consumption under shallow buried drip irrigation. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 37(6): 111-118. |
| 张洁, 马鹏飞, 吴素利, 等. 浅埋滴灌土壤水分变化特征及作物耗水规律. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(6): 111-118. | |
| [15] | Bai W M, Zuo Q, Huang Y F, et al. Effect of water supply on root growth and water uptake of alfalfa in Wulanbuhe sandy region. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2001, 25(1): 35-41. |
| 白文明, 左强, 黄元仿, 等. 乌兰布和沙区紫花苜蓿根系生长及吸水规律的研究. 植物生态学报, 2001, 25(1): 35-41. | |
| [16] | Sun T J, Nie M H, Teng W J, et al. Effects of different grasses for ecological restoration on soil evapotranspiration. Northern Horticulture, 2024(3): 71-78. |
| 孙铁军, 聂明鹤, 滕文军, 等. 不同生态修复草种对土壤水分蒸散的影响. 北方园艺, 2024(3): 71-78. | |
| [17] | Zhang Z Y, Qin B T, Xiong S P, et al. Effects of irrigation at flowering stage on soil nutrient and root distribution in wheat field. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(12): 3328-3336. |
| 张志勇, 秦步坛, 熊淑萍, 等. 小麦开花期灌水对土壤养分及根系分布的影响. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(12): 3328-3336. | |
| [18] | Han D W, He J N, Li H R, et al. Effects of irrigation period on individual structure, population structure and canopy photosynthesis of winter wheat. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 38(3): 577-586. |
| 韩东伟, 何建宁, 李浩然, 等. 灌水时期对冬小麦个体、群体结构和冠层光合作用的影响. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(3): 577-586. | |
| [19] | Yang S, Zhang X Q, Xu J R, et al. Effects of irrigation period on growth and water consumption characteristics of winter wheat. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2021, 40(6): 36-44. |
| 杨思, 张晓琪, 徐家瑞, 等. 灌水时期对冬小麦生长发育及耗水特性的影响. 灌溉排水学报, 2021, 40(6): 36-44. | |
| [20] | Mansoor R, Hassan H. Wick irrigation improves seed yield and water use efficiency in mung bean. Irrigation and Drainage, 2024, 73(3): 813-828. |
| [21] | Gao R, Chen Z Q, Hong M, et al. Effects of soil moisture threshold on growth, water consumption and yield of cotton under mulched drip irrigation in northern Xinjiang. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 2023, 34(6): 200-209. |
| 高瑞, 陈志卿, 洪明, 等. 土壤水分阈值对北疆膜下滴灌棉花生长、耗水规律及产量的影响. 水资源与水工程学报, 2023, 34(6): 200-209. | |
| [22] | Li Y J, Min J C, Xia T G, et al. Path-coefficient analysis on seed yield of single alfalfa plant and correlative traits. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 1996, 4(2): 141-147. |
| 李拥军, 闵继淳, 夏天刚, 等. 留种苜蓿单株粒重与相关性状的通径分析. 草地学报, 1996, 4(2): 141-147. | |
| [23] | Hou Z Z, Zhang A Q, Zhu J Z. The quantitative characteristics of seed yield components and floral traits under different irrigation patterns of alfalfa. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 50(9): 1668-1674. |
| 侯真珍, 张爱勤, 朱进忠. 不同灌溉模式下苜蓿种子产量构成因素及花部特征对水分亏缺的响应. 新疆农业科学, 2013, 50(9): 1668-1674. | |
| [24] | Gu Z, Qi Z, Burghate R, et al. Irrigation scheduling approaches and applications: A review. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 2020, 146(6): 4020007. |
| [25] | Meng J M, Li W J. Water distribution pattern and influence on alfalfa seed yield using subsurface drip irrigation. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(6): 907-910. |
| 孟季蒙, 李卫军. 苜蓿种子生产田地下滴灌水分分布格局及其对苜蓿种子产量的影响. 草地学报, 2010, 18(6): 907-910. | |
| [26] | Li X F, Yu X G, Li W J, et al. Study on water requiring regulation and prediction model of alfalfa seed production. Pratacultural Science, 2007, 24(3): 30-34. |
| 李雪锋, 余晓光, 李卫军, 等. 苜蓿种子生产需水规律及其需水量预测预报模型的研究. 草业科学, 2007, 24(3): 30-34. | |
| [27] | Han J G, Wang Y W, Gao H W. The seed production of purple alfalfa//Proceedings of the first China alfalfa development conference. Beijing: China Grassland Society, Beijing Rural Committee, 2001: 21-25. |
| 韩建国, 王赟文, 高洪文. 紫花苜蓿的种子生产//首届中国苜蓿发展大会论文集. 北京: 中国草原学会, 北京市农村委员会, 2001: 21-25. | |
| [28] | Liu M G, Wang Z K, Mu L, et al. Effect of regulated deficit irrigation on alfalfa performance under two irrigation systems in the inland arid area of midwestern China. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 248: 106764. |
| [1] | 张颖, 贺善睦, 何傲蕾, 李昌宁, 姚拓. 微生物菌剂与有机钙蛋白配施对紫花苜蓿生长和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 25-39. |
| [2] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [3] | 鲜燃, 邓雨, 付秋月, 蒋晶霞, 陶佳丽, 许涛, 朱慧森, 岑慧芳. 紫花苜蓿MsMYB86基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 162-172. |
| [4] | 刘沂欣, 隋晓青, 王鑫尧, 郎梦卿, 孙凌子寅, 吉尔尔格. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿的缓解作用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 206-214. |
| [5] | 张译尹, 王斌, 王腾飞, 兰剑, 胡海英. 苜蓿种子田间作小黑麦对饲草产量、水分利用及苜蓿种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 43-53. |
| [6] | 樊文娟, 宋建超, 张小娟, 盛宇航, 史金涛, 张龙骥, 鱼小军. 氮磷配施对甘肃省武威灌区扁蓿豆种子产量和质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 54-65. |
| [7] | 李文秀, 姚拓, 李昌宁, 贾倩民, 何傲蕾, 周杨. “凹凸棒-有机基质”菌肥载体最佳配比的筛选及对紫花苜蓿的促生效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 88-98. |
| [8] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [9] | 温小月, 赵颖, 王宝强, 王贤, 朱晓林, 王义真, 魏小红. 外源NO调控干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿AP2/ERFs基因的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 154-167. |
| [10] | 张英豪, 刘楚波, 周坤, 郭家存, 刘世鹏, 孙娈姿. 果草系统中枣树对不同方位紫花苜蓿和鸭茅生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 203-212. |
| [11] | 崔灿, 王梦琦, 赵琬璐, 刘新颖, 鉴晶晶, 严俊鑫. 胺鲜酯浸种对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 46-58. |
| [12] | 曾燕霞, 陈志龙, 尚继红, 沙晓弟, 吴娟, 陈彩锦. 太空诱变对PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿材料苗期生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 59-69. |
| [13] | 刘耀博, 裴渌, 刘琛琢, 李晓霞, 邹博坤. 基于Meta分析中国老芒麦种子产量和产量组分对施肥的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 85-98. |
| [14] | 魏孔钦, 张盈盈, 回金峰, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷配施对紫花苜蓿根系非结构碳水化合物及碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 40-50. |
| [15] | 周昕越, 王丽萍, 蒋庆雪, 马晓冉, 仪登霞, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿低温诱导蛋白MsLTI65的分离及其对不同逆境的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 89-104. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||