

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 54-66.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025170
刘畅1,2,3( ), 陈积山2,3, 朱瑞芬2,3, 孙万斌2,3, 姚博2,3, 董世魁1,4(
), 陈积山2,3, 朱瑞芬2,3, 孙万斌2,3, 姚博2,3, 董世魁1,4( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-30
修回日期:2025-07-01
出版日期:2026-04-20
发布日期:2026-02-07
通讯作者:
董世魁
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: dongshikui@bjfu.edu.cn基金资助:
Chang LIU1,2,3( ), Ji-shan CHEN2,3, Rui-fen ZHU2,3, Wan-bin SUN2,3, Bo YAO2,3, Shi-kui DONG1,4(
), Ji-shan CHEN2,3, Rui-fen ZHU2,3, Wan-bin SUN2,3, Bo YAO2,3, Shi-kui DONG1,4( )
)
Received:2025-04-30
Revised:2025-07-01
Online:2026-04-20
Published:2026-02-07
Contact:
Shi-kui DONG
摘要:
为了探究施肥对亚热带人工草地土壤酶活性以及酶化学计量特征的影响,通过施加有机肥和生物炭,探究土壤理化指标的变化以及对土壤酶活性及酶化学计量指标的影响,并通过土壤胞外酶活性计量特征来评估微生物养分限制。结果表明,施加有机肥和生物炭显著增加亚热带人工草地土壤有机碳、全氮含量和pH(P<0.05)。施加有机肥显著增加0~10 cm、10~20 cm、20~30 cm土层β-葡萄糖苷酶活性(βG)36.18%、37.21%、59.30%(P<0.05),增加0~10 cm、10~20 cm、20~30 cm土层β-1,4-N-乙酰葡萄糖苷酶活性(NAG)21.16%、17.25%、30.24%(P<0.05),生物炭显著增加各土层亮氨酸氨基肽酶(LAP)和NAG活性(P<0.05)。亚热带人工草地土壤C∶N∶P获取酶的平均比例为1∶1.31∶1.72,偏离了1∶1∶1,表明微生物受磷限制。施肥后矢量长度、矢量夹角降低,说明施肥可以缓解碳、磷限制。研究结果为亚热带人工草地改良与管理提供理论依据,适当施加有机肥或生物炭,有助于亚热带人工草地的改善与恢复,以缓解碳、磷限制。
刘畅, 陈积山, 朱瑞芬, 孙万斌, 姚博, 董世魁. 有机肥和生物炭添加对亚热带人工草地土壤微生物碳、磷限制的缓解作用[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(4): 54-66.
Chang LIU, Ji-shan CHEN, Rui-fen ZHU, Wan-bin SUN, Bo YAO, Shi-kui DONG. Mitigation of soil microbial carbon and phosphorus limitations through organic fertilizer and biochar inputs in subtropical cultivated grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(4): 54-66.
项目 Item | 0~10 cm | 10~20 cm | 20~30 cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | O | B | CK | O | B | CK | O | B | |
| 土壤含水量Soil moisture content (%) | 34.05±0.35c | 35.52±0.09b | 37.01±0.37a | 28.50±0.30b | 33.07±0.28a | 32.85±0.24a | 26.38±0.07c | 34.77±0.20a | 29.37±0.40b |
| 土壤容重Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 1.46±0.01a | 1.43±0.01b | 1.42±0.02c | 1.51±0.02a | 1.50±0.03b | 1.50±0.02b | 1.52±0.03a | 1.49±0.02c | 1.50±0.03b |
| pH | 4.88±0.01c | 6.01±0.03a | 5.06±0.02b | 5.00±0.01b | 5.74±0.01a | 5.01±0.02b | 4.93±0.06c | 5.70±0.02a | 5.13±0.04b |
| 土壤铵态氮Soil ammonia nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 5.19±0.01c | 6.54±0.02a | 5.50±0.01b | 3.39±0.04a | 3.20±0.05b | 3.33±0.06ab | 3.51±0.11b | 4.70±0.03a | 2.62±0.06c |
| 土壤硝态氮Soil nitric nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 8.77±0.08b | 4.89±0.05c | 11.34±0.06a | 6.44±0.26b | 7.76±0.12a | 8.28±0.05a | 5.54±0.07b | 5.06±0.01c | 5.88±0.01a |
| 全氮Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 1.92±0.02c | 2.11±0.01b | 2.25±0.01a | 1.65±0.02c | 1.78±0.02b | 1.91±0.02a | 1.58±0.03b | 1.61±0.01b | 1.65±0.02a |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 0.63±0.01c | 0.87±0.01a | 0.79±0.01b | 0.50±0.01c | 0.60±0.03b | 0.64±0.03a | 0.48±0.03c | 0.60±0.01a | 0.52±0.01b |
| 全钾Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 14.02±0.06c | 14.78±0.04b | 15.34±0.05a | 14.55±0.01c | 15.73±0.03a | 15.58±0.02b | 14.53±0.02c | 14.98±0.04b | 15.54±0.03a |
| 碳氮比Carbon to nitrogen ratio | 9.05±0.04b | 9.21±0.02b | 11.22±0.17a | 8.48±0.04c | 9.24±0.12a | 8.81±0.05b | 7.95±0.05b | 8.36±0.03a | 8.39±0.08a |
| 碳磷比Carbon to phosphorus ratio | 27.70±0.05b | 22.36±0.01c | 31.86±0.86a | 27.85±0.07a | 27.27±0.12b | 26.17±0.09c | 26.18±0.20a | 22.40±0.22b | 26.71±0.27a |
| 氮磷比Nitrogen to phosphorus ratio | 3.06±0.01a | 2.43±0.01c | 2.84±0.03b | 3.28±0.01a | 2.95±0.03b | 2.97±0.01b | 3.29±0.01a | 2.68±0.03b | 3.18±0.06a |
| 土壤有机碳Soil organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 17.41±0.05c | 19.38±0.01b | 25.27±0.46a | 14.03±0.04c | 16.42±0.19b | 16.86±0.07a | 12.55±0.08c | 13.45±0.07b | 13.83±0.05a |
表1 施肥对不同土层土壤理化性质的影响
Table 1 Effect of fertilizer application on soil physical and chemical properties of different soil layers
项目 Item | 0~10 cm | 10~20 cm | 20~30 cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | O | B | CK | O | B | CK | O | B | |
| 土壤含水量Soil moisture content (%) | 34.05±0.35c | 35.52±0.09b | 37.01±0.37a | 28.50±0.30b | 33.07±0.28a | 32.85±0.24a | 26.38±0.07c | 34.77±0.20a | 29.37±0.40b |
| 土壤容重Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 1.46±0.01a | 1.43±0.01b | 1.42±0.02c | 1.51±0.02a | 1.50±0.03b | 1.50±0.02b | 1.52±0.03a | 1.49±0.02c | 1.50±0.03b |
| pH | 4.88±0.01c | 6.01±0.03a | 5.06±0.02b | 5.00±0.01b | 5.74±0.01a | 5.01±0.02b | 4.93±0.06c | 5.70±0.02a | 5.13±0.04b |
| 土壤铵态氮Soil ammonia nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 5.19±0.01c | 6.54±0.02a | 5.50±0.01b | 3.39±0.04a | 3.20±0.05b | 3.33±0.06ab | 3.51±0.11b | 4.70±0.03a | 2.62±0.06c |
| 土壤硝态氮Soil nitric nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 8.77±0.08b | 4.89±0.05c | 11.34±0.06a | 6.44±0.26b | 7.76±0.12a | 8.28±0.05a | 5.54±0.07b | 5.06±0.01c | 5.88±0.01a |
| 全氮Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 1.92±0.02c | 2.11±0.01b | 2.25±0.01a | 1.65±0.02c | 1.78±0.02b | 1.91±0.02a | 1.58±0.03b | 1.61±0.01b | 1.65±0.02a |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 0.63±0.01c | 0.87±0.01a | 0.79±0.01b | 0.50±0.01c | 0.60±0.03b | 0.64±0.03a | 0.48±0.03c | 0.60±0.01a | 0.52±0.01b |
| 全钾Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 14.02±0.06c | 14.78±0.04b | 15.34±0.05a | 14.55±0.01c | 15.73±0.03a | 15.58±0.02b | 14.53±0.02c | 14.98±0.04b | 15.54±0.03a |
| 碳氮比Carbon to nitrogen ratio | 9.05±0.04b | 9.21±0.02b | 11.22±0.17a | 8.48±0.04c | 9.24±0.12a | 8.81±0.05b | 7.95±0.05b | 8.36±0.03a | 8.39±0.08a |
| 碳磷比Carbon to phosphorus ratio | 27.70±0.05b | 22.36±0.01c | 31.86±0.86a | 27.85±0.07a | 27.27±0.12b | 26.17±0.09c | 26.18±0.20a | 22.40±0.22b | 26.71±0.27a |
| 氮磷比Nitrogen to phosphorus ratio | 3.06±0.01a | 2.43±0.01c | 2.84±0.03b | 3.28±0.01a | 2.95±0.03b | 2.97±0.01b | 3.29±0.01a | 2.68±0.03b | 3.18±0.06a |
| 土壤有机碳Soil organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 17.41±0.05c | 19.38±0.01b | 25.27±0.46a | 14.03±0.04c | 16.42±0.19b | 16.86±0.07a | 12.55±0.08c | 13.45±0.07b | 13.83±0.05a |

图1 不同施肥处理土壤酶活性变化不同小写字母表示同一土层不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the same soil layer among different treatments (P<0.05). CK: 未施肥No fertilizer; O: 施加有机肥Organic fertilizer; B: 施加生物炭Biochar; 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Changes in soil enzyme activity under different fertilization treatments

图3 酶化学计量特征与土壤碳氮和碳磷获取酶化学计量比的相对比例
Fig.3 Enzyme stoichiometric characteristics and the reative ratio of soil carbon-nitrogen and carbon-phosphorus acquiring enzyme stoichiometries

图4 碳氮磷相关酶活性的标准主轴回归黑色虚线表示斜率为1.0的参考线,黑色实线表示线性拟合方程。The black dotted line represents a reference lines with a slope of 1.0, and the solid black line represent the linear fitting equation.
Fig.4 Standard major axial regression of enzyme activities related to carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus
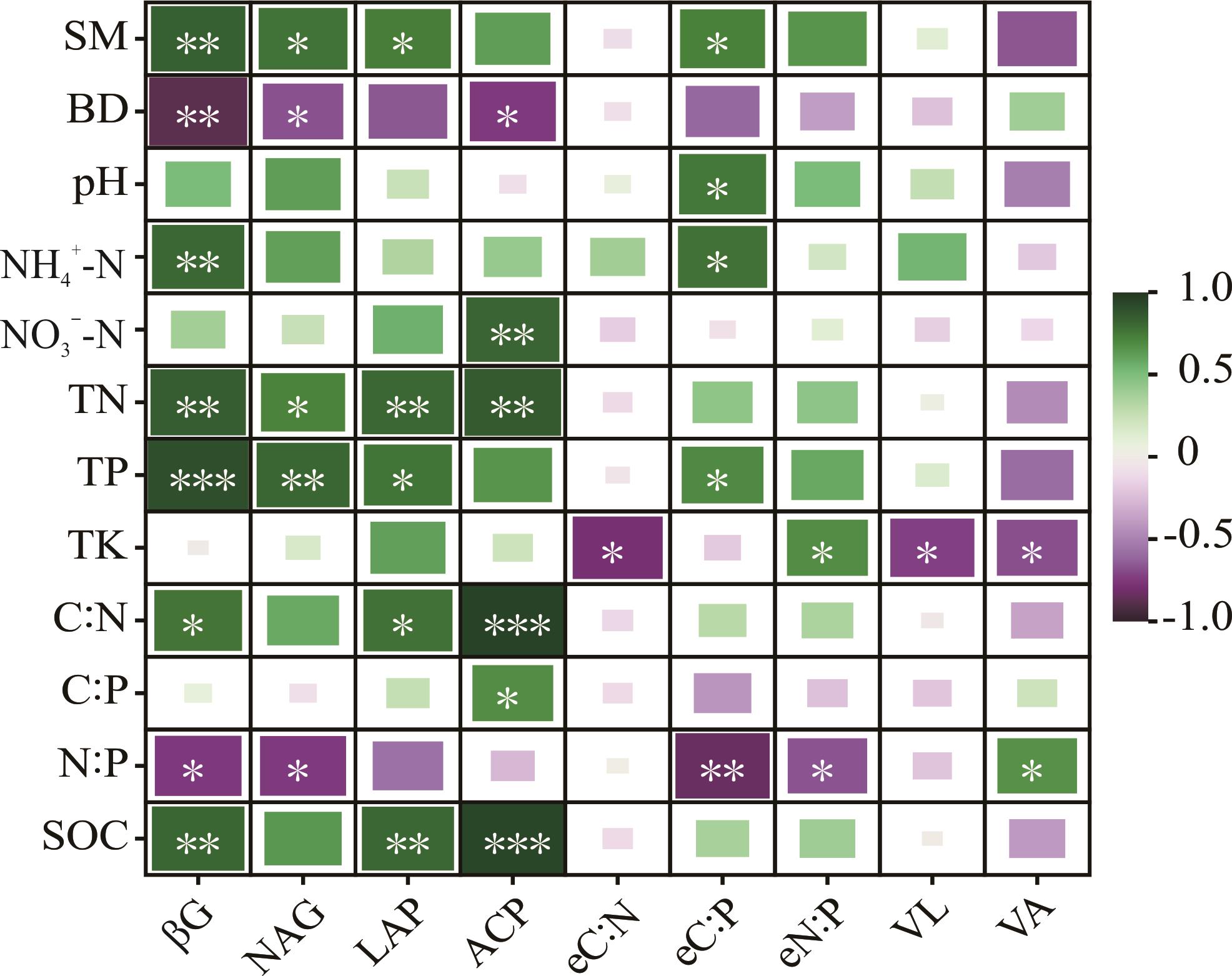
图5 土壤酶活性及其化学计量特征与土壤理化性质的相关性SM: 土壤含水量Soil moisture; BD: 土壤容重Soil bulk density; pH: 土壤pH; NH4+-N: 土壤铵态氮Soil ammonia nitrogen; NO3--N: 土壤硝态氮Soil nitric nitrogen; TN: 土壤全氮Soil total nitrogen; TP: 土壤全磷Soil total phosphorus; TK: 土壤全钾Soil total potassium; C∶N: 土壤碳氮比Soil carbon nitrogen ratio; C∶P: 土壤碳磷比Soil carbon phosphorus ratio; N∶P: 土壤氮磷比Soil nitrogen phosphorus ratio; SOC: 土壤有机碳Soil organic carbon; βG: β-葡萄糖苷酶活性β- glucosidase activity; NAG: β-1,4-N-乙酰葡萄糖苷酶β-1,4-N-acetyl glucosidase; LAP: 亮氨酸氨基肽酶Leucine aminopeptidase; ACP: 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase activity; eC∶N: 酶碳氮比Enzyme C∶N; eC∶P: 酶碳磷比Enzyme C∶P; eN∶P: 酶氮磷比Enzyme N∶P; VL: 矢量长度Vector length; VA: 矢量角度Vector angle; 下同The same below; 方框中的绿色和紫色分别代表两个变量之间的正相关和负相关Green and violet in the square represent positive and negative correlations between the two variables, respectively。颜色越深,关系越强The deeper the color, the stronger the relationship. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001.
Fig.5 Correlation of soil enzyme activities and their stoichiometric characteristics with soil physicochemical properties
| [1] | Bengtsson J, Bullock J M, Egoh B, et al. Grasslands-more important for ecosystem services than you might think. Ecosphere, 2019, 10(2): 1-20. |
| [2] | Fang J Y, Yu G R, Liu L L, et al. Climate change, human impacts, and carbon sequestration in China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States, 2018, 115(16): 4015-4020. |
| [3] | Cao X, Shi Z, Chen J, et al. Extracellular enzyme characteristics and microbial metabolic limitation in soil of subalpine forest ecosystems on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plant and Soil, 2022, 479(2): 337-353. |
| [4] | Kallenbach C, Frey S, Grandy A. Direct evidence for microbial-derived soil organic matter formation and its ecophysiological controls. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(9): 13630. |
| [5] | Kuzyakov Y, Xu X. Competition between roots and microorganisms for nitrogen: Mechanisms and ecological relevance. New Phytologist, 2013, 198(3): 656-669. |
| [6] | Cenini V, Fornara D, Mcmullan G, et al. Linkages between extracellular enzyme activities and the carbon and nitrogen content of grassland soils. Soil Biology Biochemistry, 2016, 96(1): 198-206. |
| [7] | Yang Y, Liang C, Wang Y Q. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects the shift from P- to N-limitation of microorganisms with grassland restoration. Soil Biology Biochemistry, 2020, 149(1): 107928. |
| [8] | Lei J C, Liu X W, Deng J, et al. Characteristics of changes in soil enzyme activities and stoichiometric under different abandoned years in the dry area of northern Weihe River Basin. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2024, 31(1): 44-52. |
| 雷跻初, 刘小伟, 邓军, 等. 渭北旱塬不同年限撂荒地土壤酶活性及其化学计量变化特征. 水土保持研究, 2024, 31(1): 44-52. | |
| [9] | Mmoorhead D, Sinsabaugh R, Hill B, et al. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C, N and P dynamics. Soil Biology Biochemistry, 2016, 93(1): 1-7. |
| [10] | Sinsabaugh R L, Lauber C L, Weintraub M N, et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecology Letters, 2008, 11(11): 1252-1264. |
| [11] | Doi H, Cherif M, Iwabuchi T, et al. Integrating elements and energy through the metabolic dependencies of gross growth efficiency and the threshold elemental ratio. Oikos, 2010, 119(5): 752-765. |
| [12] | Zhen Z, Sibo W, Shuwen L, et al. Significant impacts of both total amount and availability of heavy metals on the functions and assembly of soil microbial communities in different land use patterns. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10(1): 2293. |
| [13] | Xu H, Qu Q, Chen Y, et al. Responses of soil enzyme activity and soil organic carbon stability over time after cropland abandonment in different vegetation zones of the Loess Plateau of China. Catena, 2021, 196(2): 104812. |
| [14] | Turner B. Variation in pH optima of hydrolytic enzyme activities in tropical rain forest soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(19): 6485-6493. |
| [15] | Ou X, Lian H, Chen R Q, et al. Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activity of rare earth mine tailings after planting king grass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 94-108. |
| 欧翔, 连海, 陈荣强, 等. 不同施肥处理种植王草后对稀土尾矿土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 94-108. | |
| [16] | Men X, Bao Y, Wu M, et al. Soil enzyme activities responded differently to short-term litter input manipulation under coniferous and broad-leaved forests in the subalpine area of Southwest China. Forest Ecology and Management, 2023, 12(2): 546-557. |
| [17] | Tang S, Ma Q, Marsden K A, et al. Microbial community succession in soil is mainly driven by carbon and nitrogen contents rather than phosphorus and sulphur contents. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2023, 180(2): 109019. |
| [18] | Ling J, Dungait J A J, Delgado-Baquerizo M, et al. Soil organic carbon thresholds control fertilizer effects on carbon accrual in croplands worldwide. Nature Communications, 2025, 16(1): 3009-3018. |
| [19] | He B H, Hao Y Q, Li X G, et al. Community characteristics in Hongchiba area of Wuxi County during ecological restoration after controlled burning. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(6): 1105-1108. |
| 何丙辉, 郝云庆, 李旭光, 等. 红池坝炼山后生态恢复过程中群落特征研究. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(6): 1105-1108. | |
| [20] | Zhou J H, Yang S M. Ecological suitability assessment of landscape planning on Hongchiba Scenic Zone in Chongqing. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2012, 28(12): 74-78. |
| 周建华, 杨淑梅. 重庆红池坝景区景观规划中的生态适宜性分析. 中国园林, 2012, 28(12): 74-78. | |
| [21] | Liu G M, Zhang X C, Wang X P, et al. Soil enzymes as indicators of saline soil fertility under various soil amendments. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2017, 237(2): 274-279. |
| [22] | Duan C W, Li X L, Chai Y, et al. Effects of different rehabilitation measures on plant community and soil nutrient of degraded alpine meadow in the Yellow River Source. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(18): 7652-7662. |
| 段成伟, 李希来, 柴瑜, 等. 不同修复措施对黄河源退化高寒草甸植物群落与土壤养分的影响. 生态学报, 2022, 42(18): 7652-7662. | |
| [23] | Jia R, Zhou J, Yang L, et al. Trade-off between soil enzyme activities and hotspots area depends on long-term fertilization: In situ field zymography. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 954(1): 176386. |
| [24] | Wu Z, Han X, Chen X, et al. Application of organic manure as a potential strategy to alleviate the limitation of microbial resources in soybean rhizospheric and bulk soils. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2024, 23(6): 2065-2082. |
| [25] | Chen Z, Jin P, Wang H, et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals stronger microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in biochar amendment soils: A Meta-analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 838: 156532. |
| [26] | Li Q, Zhang D, Song Z, et al. Organic fertilizer activates soil beneficial microorganisms to promote strawberry growth and soil health after fumigation. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 295(2): 118653. |
| [27] | Tian S Y, Zhu B J, Yin Y, et al. Organic fertilization promotes crop productivity through changes in soil aggregation. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2021, 165(5): 108533-108539. |
| [28] | Wang J, Sun L J, Sun Y F, et al. Long-term biochar-based fertilizer substitution promotes carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus acquisition enzymes in dryland soils by affecting soil properties and regulating bacterial community. Applied Soil Ecology, 2025, 206(3): 105801-105810. |
| [29] | Wan H Y, Chen L, Pang D B, et al. Soil enzyme activities and their stoichiometry at different altitudes in Helan Mountains, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(9): 3045-3052. |
| 万红云, 陈林, 庞丹波, 等. 贺兰山不同海拔土壤酶活性及其化学计量特征. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(9): 3045-3052. | |
| [30] | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2000: 200-495. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 200-495. | |
| [31] | Wu C W, Xia J X, Duan Z R. Review on detection methods of soil organic matter (SOM). Soil, 2015, 47(3): 453-460. |
| 吴才武, 夏建新, 段峥嵘. 土壤有机质测定方法述评与展望. 土壤, 2015, 47(3): 453-460. | |
| [32] | Steinweg J M, Dukes J S, Paul E A, et al. Microbial responses to multi-factor climate change: Effects on soil enzymes. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2013, 4(5): 146-158. |
| [33] | Verchot L V, Borelli T. Application of para-nitrophenol (pNP) enzyme assays in degraded tropical soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2004, 37(4): 625-633. |
| [34] | Wallenius K, Rita H, Mikkonen A, et al. Effects of land use on the level, variation and spatial structure of soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2011, 43(7): 1464-1473. |
| [35] | Sinsabaugh R L, Hill B H, Shah J F. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature, 2010, 462(7320): 795-798. |
| [36] | He M, Wang Y C, Wang L G, et al. Effects of subsoiling combined with fertilization on the fractions of soil active organic carbon and soil active nitrogen, and enzyme activities in black soil in Northeast China. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(2): 446-456. |
| 贺美, 王迎春, 王立刚, 等. 深松施肥对黑土活性有机碳氮组分及酶活性的影响. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(2): 446-456. | |
| [37] | Wang X B, Luo Y M, Li Z G, et al. Effect of long-term stationary fertilization on upland red soil quality in subtropical hilly regions acidity. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2011, 48(1): 98-102. |
| 王小兵, 骆永明, 李振高, 等. 长期定位施肥对亚热带丘陵地区红壤旱地质量的影响酸度. 土壤学报, 2011, 48(1): 98-102. | |
| [38] | Ma F, Ma H L, Qiu H, et al. Effects of water levels and the additions of different nitrogen forms on soil net nitrogen transformation rate and N2O emission in subtropical forest soils. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(2): 379-387. |
| 马芬, 马红亮, 邱泓, 等. 水分状况与不同形态氮添加对亚热带森林土壤氮素净转化速率及N2O排放的影响. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(2): 379-387. | |
| [39] | Wei Z, Well R, Ma X, et al. Organic fertilizer amendment decreased N2O/(N2O+N2) ratio by enhancing the mutualism between bacterial and fungal denitrifiers in high nitrogen loading arable soils. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2024, 198(9): 109550. |
| [40] | Farrell M, Macdonald L M, Butler G, et al. Biochar and fertiliser applications influence phosphorus fractionation and wheat yield. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2014, 50(1): 169-178. |
| [41] | Qambrani N A, Rahman M M, Won S, et al. Biochar properties and eco-friendly applications for climate change mitigation, waste management, and wastewater treatment: A review. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 79(11): 255-273. |
| [42] | Wang H Y, Gai X P, Zhai L M, et al. Effect of biochar on soil nitrogen cycling: A review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(19): 5998-6011. |
| 王洪媛, 盖霞普, 翟丽梅, 等. 生物炭对土壤氮循环的影响研究进展. 生态学报, 2016, 36(19): 5998-6011. | |
| [43] | Li J S, Shao X, Huang D, et al. Short-term biochar effect on soil physicochemical and microbiological properties of a degraded alpine grassland. Pedosphere, 2022, 32(3): 426-437. |
| [44] | Hu W, Zhang Y P, Rong X M, et al. Biochar and organic fertilizer applications enhance soil functional microbial abundance and agroecosystem multifunctionality. Biochar, 2024, 6(1): 3-15. |
| [45] | Lehmann J, Rillig M C, Thies J, et al. Biochar effects on soil biota-A review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2011, 43(9): 1812-1836. |
| [46] | Wang Z H, Tang C S, Wang H, et al. Effect of different amounts of biochar on meadow soil characteristics and maize yields over three years. Bioresources, 2019, 14(2): 4194-4209. |
| [47] | Tian F F, Ji H F, Wang L Y, et al. Effects of various combinations of fertilizer, soil moisture, and temperature on nitrogen mineralization and soluble organic nitrogen in agricultural soil. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(10): 4717-4726. |
| 田飞飞, 纪鸿飞, 王乐云, 等. 施肥类型和水热变化对农田土壤氮素矿化及可溶性有机氮动态变化的影响. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10): 4717-4726. | |
| [48] | Dong L, Yang X, Shi L L, et al. Biochar and nitrogen fertilizer co-application changed SOC content and fraction composition in Huang-Huai-Hai plain, China. Chemosphere, 2022, 291(1): 132925. |
| [49] | Zhang D, Hou C, Ma W M, et al. Study on soil enzyme activities under shrub encroachment gradients in alpine grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| 张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 等. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. | |
| [50] | Dick W A. Influence of long-term tillage and crop rotation combinations on soil enzyme activities. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1984, 48(3): 569-574. |
| [51] | Dominchin M F, Verdenelli R A, Berger M G, et al. Impact of N-fertilization and peanut shell biochar on soil microbial community structure and enzyme activities in a typic haplustoll under different management practices. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2021, 104(7): 103298. |
| [52] | Zhou G, Gao S, Lu Y, et al. Co-incorporation of green manure and rice straw improves rice production, soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a typical paddy field in Southern China. Soil Tillage Research, 2020, 197(9): 104499. |
| [53] | He C C, Li G C, Yin C B, et al. Effect of manure N input ratios on the utilization of different soil microbial carbon sources. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2018, 24(2): 383-393. |
| 何翠翠, 李贵春, 尹昌斌, 等. 有机肥氮投入比例对土壤微生物碳源利用特征的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(2): 383-393. | |
| [54] | Zhang H J, Yu H Y, Ding W X. The influence of the long-term application of organic manure and mineral fertilizer on microbial community in calcareous fluvo-aquic soil.Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(12): 3308-3314. |
| 张焕军, 郁红艳, 丁维新. 长期施用有机无机肥对潮土微生物群落的影响. 生态学报, 2011, 31(12): 3308-3314. | |
| [55] | Ren C, Zhou Z, Delgado-Baquerizo M, et al. Thermal sensitivity of soil microbial carbon use efficiency across forest biomes. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 6269-6279. |
| [56] | Hu P L, Zhang W, Kuzyakov Y, et al. Linking bacterial life strategies with soil organic matter accrual by Karst vegetation restoration. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2023, 177(17): 12-20. |
| [57] | Shao J, Zhou W J, Song Y, et al. Effects of biochar from different raw materials on microbial activity in heavy metal contaminated soil. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2022, 39(3): 644-652. |
| 邵佳, 周文晶, 宋瑶, 等. 不同原料生物质炭对重金属污染土壤微生物活性的影响. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(3): 644-652. | |
| [58] | Wang Q, Geng Z C, Xu C Y, et al. Effects of biochar application on soil microbial nutrient limitations and carbon use efficiency in Lou soil. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(5): 2425-2433. |
| 王强, 耿增超, 许晨阳, 等. 施用生物炭对塿土土壤微生物代谢养分限制和碳利用效率的影响. 环境科学, 2020, 41(5): 2425-2433. | |
| [59] | Chen M, Liu Y F, Pan J C, et al. Low-cost Ca/Mg co-modified biochar for effective phosphorus recovery: Adsorption mechanisms, resourceful utilization, and life cycle assessment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 502(15): 157993. |
| [60] | Huang Y B, Luo F, Gong X J, et al. Effects of organic fertilizers on soil microbial community characteristics: research progress. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(3): 88-96. |
| 黄颖博, 罗凡, 龚雪蛟, 等. 有机肥对土壤微生物群落特征影响的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(3): 88-96. | |
| [61] | Zhang D, Wang L, Qin S, et al. Microbial nitrogen and phosphorus co-limitation across permafrost region. Global Change Biology, 29(14): 3910-3923. |
| [62] | Hill B H, Elonen C M, Jicha T M, et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and microbial processing of organic matter in northern bogs and fens reveals a common P-limitation between peatland types. Biogeochemistry, 120(3): 203-224. |
| [63] | Abay P, Gong L, Luo Y, et al. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reveals the nutrient limitations in soil microbial metabolism under different carbon input manipulations. The Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 913(21): 169-193. |
| [64] | Zhao C, Zhang H, Song C, et al. Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Innovation, 2020, 1(1): 100017. |
| [65] | Schimel J P, Weintraub M N. The implications of exoenzyme activity on microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in soil: A theoretical model. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2003, 35(4): 549-563. |
| [66] | Cui J W, Zhang S, Wang X Y, et al. Enzymatic stoichiometry reveals phosphorus limitation-induced changes in the soil bacterial communities and element cycling: Evidence from a long-term field experiment. Geoderma, 2022, 426(9): 116-124. |
| [67] | Yang W N, Yu L, Luo D H, et al. Effect of combined application of biochar with chemical fertilizer and organic fertilizer on soil phosphatase activity and microbial community. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 540-549. |
| 杨文娜, 余泺, 罗东海, 等. 化肥和有机肥配施生物炭对土壤磷酸酶活性和微生物群落的影响. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 540-549. | |
| [68] | Liu Y L, Li Y, Zhang M, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on phosphorus adsorption and desorption characters in yellow soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(3): 450-459. |
| 刘彦伶, 李渝, 张萌, 等. 长期不同施肥对黄壤磷素吸附-解吸特性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(3): 450-459. | |
| [69] | Zhao K Q, Wang N, Jiang S L, et al. Potential implications of biochar and compost on the stoichiometry-based assessments of soil enzyme activity in heavy metal-polluted soils. Carbon Research, 2022, 13(1): 29-39. |
| [70] | Fang J, Jin L, Meng Q, et al. Interactions of extracellular DNA with aromatized biochar and protection against degradation by DNase I. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 101(21): 205-216. |
| [71] | Lehmann J, Joseph S. Biochar for environmental management. Science, Technology and Implementation, 2015, 20(3): 976-985. |
| [72] | Yan C, Yang G, Li D, et al. Effect of biochar addition on soil respiration of oasis farmland in arid areas. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2018, 39(9): 575-584. |
| [73] | Li S Y, Sun Z J, Yu B J, et al. Effect of grazing exclusion on soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus contents and enzyme activity and stoichiometry in Seriphidium transiliense desert grasslands. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(7): 25-40. |
| 李思媛, 孙宗玖, 于冰洁, 等. 封育对伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地土壤碳氮磷、酶活性及其化学计量特征的影响. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 25-40. | |
| [74] | Kardol P, Cregger M A, Campany C E, et al. Soil ecosystem functioning under climate change: Plant species and community effects. Ecology, 2010, 91(3): 767-781. |
| [75] | Engelhardt I C, Welty A, Blazewicz S J, et al. Depth matters: effects of precipitation regime on soil microbial activity upon rewetting of a plant-soil system. ISME Journal, 2018, 12(4): 1061-1071. |
| [76] | Jiang J, Wang Y P, Yang Y H, et al. Interactive effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on β-glucosidase activity in paddy soils. Plant and Soil, 2019, 8(440): 523-537. |
| [77] | Knight T R, Dick R P. Differentiating microbial and stabilized β-glucosidase activity relative to soil quality. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2004, 36(12): 2089-2096. |
| [78] | Singh A K, Jiang X J, Yang B, et al. Biological indicators affected by land use change, soil resource availability and seasonality in dry tropics. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 115(20): 106-119. |
| [79] | Huang H L, Zong N, He N P, et al. Characteristics of soil enzyme stoichiometry along an altitude gradient on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau alpine meadow, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(11): 3689-3696. |
| 黄海莉, 宗宁, 何念鹏, 等. 青藏高原高寒草甸不同海拔土壤酶化学计量特征. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(11): 3689-3696. | |
| [80] | Lu J Y, Tan Y, Tian S H, et al. Effect of carbon source on carbon and nitrogen metabolism of common heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification pathway. Chemosphere, 2024, 361(11): 142525. |
| [1] | 臧家艺, 徐明杰, 谢济骋, 沈禹颖, 来兴发. 有机肥等氮替代化肥对旱作区青贮玉米/饲用大豆间作系统饲草产量和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(3): 83-95. |
| [2] | 张颖, 贺善睦, 何傲蕾, 李昌宁, 姚拓. 微生物菌剂与有机钙蛋白配施对紫花苜蓿生长和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 25-39. |
| [3] | 罗叙, 马慧, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 赵莹, 谢应忠, 李建平. 地上净初级生产力对植物物种丰富度的响应及影响因子分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 26-37. |
| [4] | 汤珊珊, 胡敏. 禾本科植物根际土壤酶活性和细菌群落结构差异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 99-108. |
| [5] | 贾蕴欢, 胡雯颖, 邓健, 赵雪, 陈子玥, 王亚楠, 李江文, 张晓曦. 氮添加对黄土丘陵区草地土壤微生物养分限制特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 221-232. |
| [6] | 欧翔, 连海, 陈荣强, 邱静芸, 吴丽娟, 操贤洪, 张强, 雷小文. 不同施肥处理种植王草后对稀土尾矿土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 94-108. |
| [7] | 赵文军, 梁婷, 王剑松, 刘魁, 冯瑜, 王正旭, 徐梓荷, 朱云聪, 孙蒙猛, 李湘伟, 付利波, 尹梅, 周国朋, 陈华, 曹卫东. 种植翻压光叶紫花苕配合氮肥减施提高烤烟产量和土壤质量[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 74-84. |
| [8] | 姚佳妮, 刘爽, 张钧杰, 胡明珠, 代金霞. 宁夏荒漠草原典型灌丛根际土壤酶活性及微生物代谢多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 1-14. |
| [9] | 李思媛, 孙宗玖, 于冰洁, 周晨烨, 周磊, 郑丽, 刘慧霞, 冶华薇. 封育对伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地土壤碳氮磷、酶活性及其化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 25-40. |
| [10] | 黄琳曦, 陈倩, 张先言, 闫顺, 杨云, 辛培尧, 汪琼. 两种乔木凋落叶浸提液处理对地毯草土壤酶活性及其化学计量比的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 35-46. |
| [11] | 李俊瑶, 蒋星驰, 胡晋瑜, 魏栋光, 赵学勇, 王少昆. 生物有机肥施加对荒漠草原植被-土壤-微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 34-45. |
| [12] | 赵文军, 刘蕊, 王正旭, 冯瑜, 薛开政, 刘魁, 徐梓荷, 曹卫东, 付利波, 尹梅, 陈华. 烤烟-绿肥轮作对云南烟田土壤质量与微生物养分限制的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 147-158. |
| [13] | 张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| [14] | 马嵩科, 霍克, 张冬霞, 张静, 张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 王贺正. 玉米秸秆还田配施氮肥对豫西旱地小麦土壤酶活性和氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 120-133. |
| [15] | 王志婷, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 李东方, 刘小勇. 半干旱草甸草地不同处理下植被特征与土壤酶活性的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 41-55. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||