

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 195-204.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024506
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
孙守江( ), 刘昊臻, 徐淑涵, 张景鈜, 李淑霞, 张金青, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲
), 刘昊臻, 徐淑涵, 张景鈜, 李淑霞, 张金青, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲
收稿日期:2024-12-25
修回日期:2025-02-19
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-10-09
通讯作者:
孙守江
作者简介:E-mail: shoujiangsun@nxu.edu.cn基金资助:
Shou-jiang SUN( ), Hao-zhen LIU, Shu-han XU, Jing-hong ZHANG, Shu-xia LI, Jin-qing ZHANG, Xue-qin GAO, Bing-zhe FU
), Hao-zhen LIU, Shu-han XU, Jing-hong ZHANG, Shu-xia LI, Jin-qing ZHANG, Xue-qin GAO, Bing-zhe FU
Received:2024-12-25
Revised:2025-02-19
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-10-09
Contact:
Shou-jiang SUN
摘要:
为研究老化苜蓿种子发芽特性、萌发早期抗氧化系统生理变化规律以及探索抗氧化相关基因对种子老化的响应模式,以老化紫花苜蓿种子为材料,研究了老化处理后种子发芽特性、萌发早期种子抗氧化酶活性和抗氧化物含量的变化规律,并分析了抗氧化系统相关基因表达量的变化。结果表明,老化处理不仅抑制了苜蓿种子萌发进程,同时显著影响了种子萌发后幼苗的正常生长,导致萌发后期幼苗较小。老化处理也严重影响了活性氧(ROS)的代谢,导致老化种子萌发早期过氧化氢(H2O2)含量升高,过氧化物酶(POD)和谷胱甘肽还原酶(GR)活性显著(P<0.05)降低,抗坏血酸(AsA)和谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量也极显著(P<0.01)降低。抗氧化酶活性和抗氧化物含量降低使种子抗氧化能力降低。此外,老化处理也显著(P<0.05)抑制了抗氧化系统中MsCAT1、MsPOD12、MsDHAR、MsGR1、MsFe-SOD和MsMn-SOD的表达。基于抗氧化生理和基因表达模式分析,从抗氧化系统中挖掘到一些关键的候选基因,为深入研究种子老化的分子调控机制提供了重要基因资源,也为进一步研究这些候选基因调控种子活力的精确途径奠定了基础。
孙守江, 刘昊臻, 徐淑涵, 张景鈜, 李淑霞, 张金青, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲. 苜蓿种子发芽特性和萌发早期抗氧化系统对老化的生理和分子响应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 195-204.
Shou-jiang SUN, Hao-zhen LIU, Shu-han XU, Jing-hong ZHANG, Shu-xia LI, Jin-qing ZHANG, Xue-qin GAO, Bing-zhe FU. Germination characteristics and antioxidant responses of alfalfa seeds to aging treatment[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(11): 195-204.
编号 No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 产物大小 Product size (bp) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MsCAT1 | F: ACAGGGATGAGGAGGTGAACTAC R: CGCTGGATGAAACGGTCTTGC | 130 | 63.6 63.3 |
| 2 | MsPOD12 | F: CCCAAGGCAGAGTCCATCGTG R: CCGTCCAGGAGCACTGAAGC | 102 | 60.0 59.8 |
| 3 | MsAPX | F: AAGGACTATGCTGAATCACACAAG R: CAACTGCTACGCCGACTGC | 111 | 56.9 58.5 |
| 4 | MsDHAR | F: AAGACCAAGCCAGCCAAGGAG R: AAGGACAGGACAGAACACAGACG | 96 | 60.2 60.9 |
| 5 | MsCu/Zn-SOD | F: ACCGCCGTGACAGGAAGC R: GCAACACCATCCGCTCCAG | 85 | 60.7 60.5 |
| 6 | MsFe-SOD | F: AGAAGCACCACGCCACCTAC R: CGCCGCCGTTGAACTTGATG | 112 | 59.1 59.8 |
| 7 | MsMn-SOD | F: GCTGATGTGCTTGAATCCTTGAAC R: GTGCTTGTGCTGGTGAACTCC | 147 | 59.7 59.0 |
| 8 | MsGR1 | F: AGAACAGCATATCCAAACGACAG R: CAGCCTTGAGTGCGACAGC | 133 | 60.0 59.7 |
| 9 | MsAOX1c | F: GCTGGAGGAGGCGGAGAAC R: TCGGTGTAGGAGTGGATGGC | 96 | 58.4 56.5 |
| 10 | MsNAC67 | F: TGCCAAGCCTGCCCTGATATG R: ATTATTGTTGCCCACCTCGTTTCC | 142 | 58.8 59.7 |
| 11 | MsNAC74 | F: CCGCCTTGCCGACACCTC R: TCTTCTCCCATTCGTTCTTCTTGC | 101 | 58.6 59.9 |
| 12 | MsNAC83 | F: CGGAAGGCTGGGTGCTCTG R: TCGTGGACGGGATCTTCTTGG | 124 | 60.3 60.1 |
| 13 | MsACTIN | F: CAAAAGATGGCAGATGCTGAGGAT R: CATGACACCAGTATGACGAGGTCG | 88 | 59.4 59.5 |
表1 qRT-PCR分析引物信息
Table 1 Primers for qRT-PCR analysis
编号 No. | 基因名称 Gene name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 产物大小 Product size (bp) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MsCAT1 | F: ACAGGGATGAGGAGGTGAACTAC R: CGCTGGATGAAACGGTCTTGC | 130 | 63.6 63.3 |
| 2 | MsPOD12 | F: CCCAAGGCAGAGTCCATCGTG R: CCGTCCAGGAGCACTGAAGC | 102 | 60.0 59.8 |
| 3 | MsAPX | F: AAGGACTATGCTGAATCACACAAG R: CAACTGCTACGCCGACTGC | 111 | 56.9 58.5 |
| 4 | MsDHAR | F: AAGACCAAGCCAGCCAAGGAG R: AAGGACAGGACAGAACACAGACG | 96 | 60.2 60.9 |
| 5 | MsCu/Zn-SOD | F: ACCGCCGTGACAGGAAGC R: GCAACACCATCCGCTCCAG | 85 | 60.7 60.5 |
| 6 | MsFe-SOD | F: AGAAGCACCACGCCACCTAC R: CGCCGCCGTTGAACTTGATG | 112 | 59.1 59.8 |
| 7 | MsMn-SOD | F: GCTGATGTGCTTGAATCCTTGAAC R: GTGCTTGTGCTGGTGAACTCC | 147 | 59.7 59.0 |
| 8 | MsGR1 | F: AGAACAGCATATCCAAACGACAG R: CAGCCTTGAGTGCGACAGC | 133 | 60.0 59.7 |
| 9 | MsAOX1c | F: GCTGGAGGAGGCGGAGAAC R: TCGGTGTAGGAGTGGATGGC | 96 | 58.4 56.5 |
| 10 | MsNAC67 | F: TGCCAAGCCTGCCCTGATATG R: ATTATTGTTGCCCACCTCGTTTCC | 142 | 58.8 59.7 |
| 11 | MsNAC74 | F: CCGCCTTGCCGACACCTC R: TCTTCTCCCATTCGTTCTTCTTGC | 101 | 58.6 59.9 |
| 12 | MsNAC83 | F: CGGAAGGCTGGGTGCTCTG R: TCGTGGACGGGATCTTCTTGG | 124 | 60.3 60.1 |
| 13 | MsACTIN | F: CAAAAGATGGCAGATGCTGAGGAT R: CATGACACCAGTATGACGAGGTCG | 88 | 59.4 59.5 |
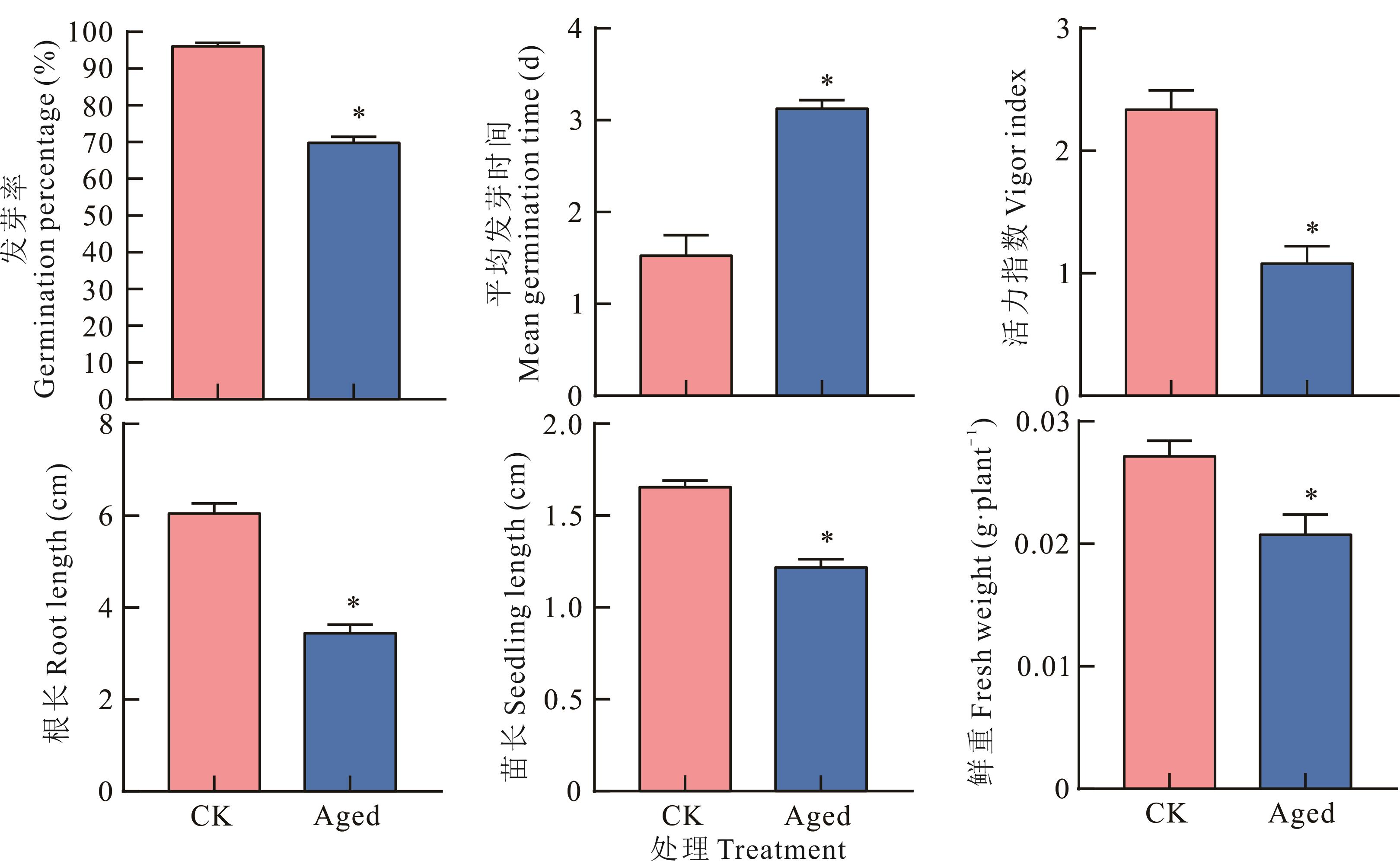
图1 老化苜蓿种子萌发特性的变化*表示在0.05水平下差异显著* indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level. CK: 未老化Unaged; Aged: 老化10 d Aged 10 days. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Changes in germination related indicators of aged alfalfa seeds

图2 老化苜蓿种子萌发早期抗氧化酶活性的变化**: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001. 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Changes in antioxidant enzyme activities during the early germination stage of aged alfalfa seeds
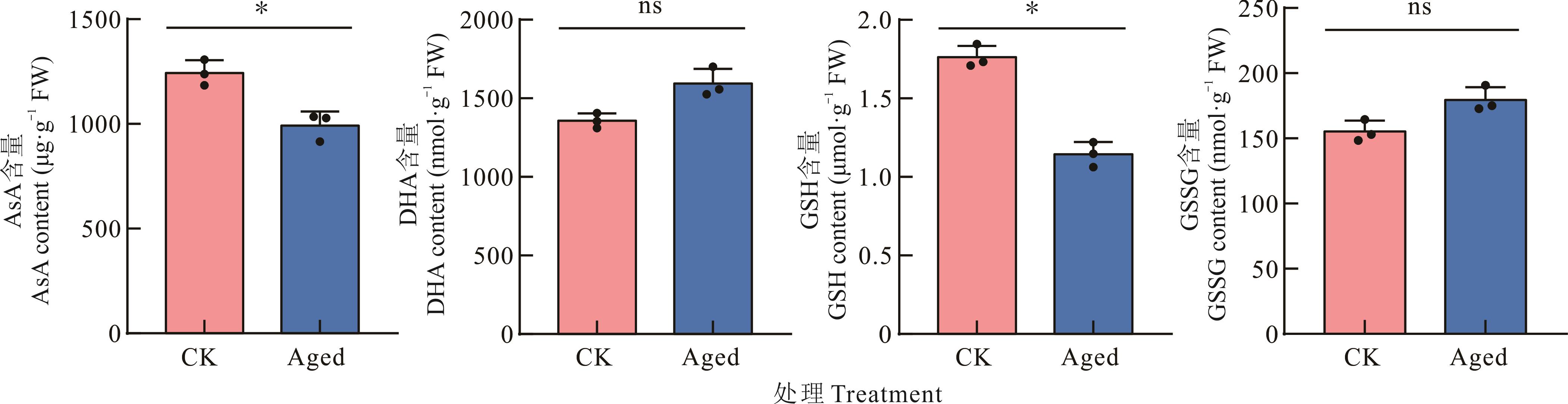
图3 老化苜蓿种子萌发早期抗氧化物含量的变化ns表示无显著差异。ns indicate no significant differences.
Fig.3 Changes in antioxidant content during the early germination stage of aged alfalfa seeds

图4 老化苜蓿种子抗氧化系统和ROS代谢相关基因表达量的变化
Fig.4 Changes in the expression levels of genes related to the antioxidant system and ROS metabolism of aged alfalfa seeds
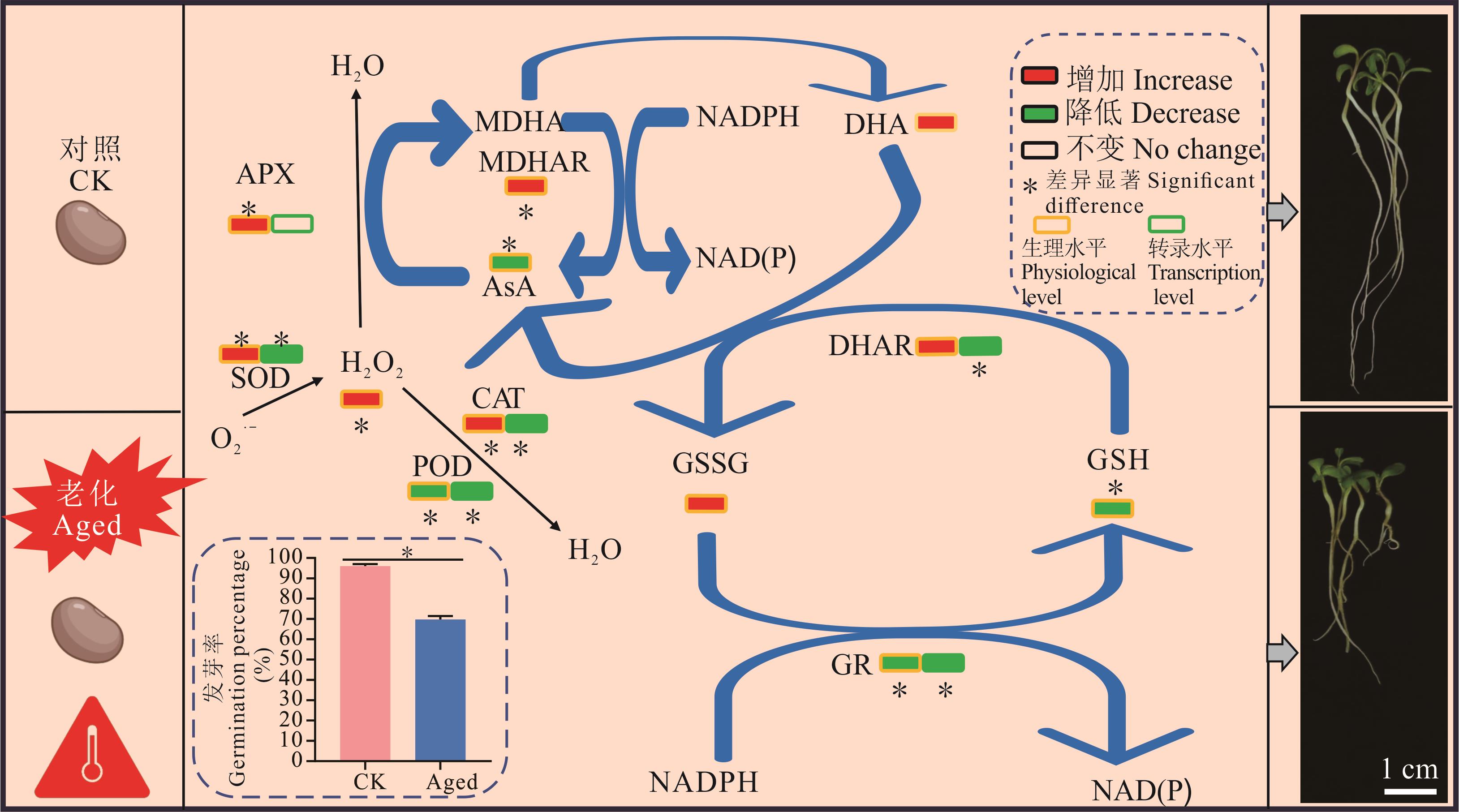
图5 苜蓿种子抗氧化系统对老化处理的响应示意图H2O2: 过氧化氢Hydrogen peroxide; O2?-: 超氧阴离子Superoxide anion; SOD: 超氧化物歧化酶Superoxide dismutase; CAT: 过氧化氢酶Catalase; POD: 过氧化物酶Peroxidase; APX: 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶Ascorbate peroxidase; GR: 谷胱甘肽还原酶Glutathione reductase; DHAR: 去氢抗坏血酸还原酶Dehydroascorbate reductase; MDHAR: 单脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶Monodehydroascorbate reductase; AsA: 抗坏血酸Ascorbic acid; DHA: 去氢抗坏血酸Dehydroascorbic acid; GSH: 谷胱甘肽Glutathione; GSSG: 氧化型谷胱甘肽Glutathione oxidized; NADPH: 还原型辅酶Ⅱ Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; MDHA: 单脱氢抗坏血酸Monodehydroascorbic acid; NADPH: 还原型烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of the response of the antioxidant system in alfalfa seeds to ageing treatments
| [1] | TeKrony D M, Egli D B. Relationship of seed vigor to crop yield: A review. Crop Science, 1991, 31(3): 816-822. |
| [2] | Finch-Savage W E, Bassel G W. Seed vigour and crop establishment: Extending performance beyond adaptation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(3): 567-591. |
| [3] | Zhou W G, Chen F F, Luo X F, et al. A matter of life and death: Molecular, physiological, and environmental regulation of seed longevity. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2020, 43(2): 293-302. |
| [4] | Aken O V. Mitochondrial redox systems as central hubs in plant metabolism and signalling. Plant Physiology, 2021, 186(1): 36-52. |
| [5] | Bailly C. Active oxygen species and antioxidants in seed biology. Seed Science Research, 2007, 14(2): 93-107. |
| [6] | Mignolet-Spruyt L, Xu E, Idanheimo N, et al. Spreading the news: Subcellular and organellar reactive oxygen species production and signalling. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(13): 3831-3844. |
| [7] | Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan M, Anee T I, et al. Regulation of ascorbate-glutathione pathway in mitigating oxidative damage in plants under abiotic stress. Antioxidants, 2019, 8(9): 384. |
| [8] | Brand K A, Hermfisse U. Aerobic glycolysis by proliferating cells: A protective strategy against reactive oxygen species. FASEB Journal, 1997, 11(5): 388-395. |
| [9] | Nietzel T, Mostertz J, Ruberti C, et al. Redox-mediated kick-start of mitochondrial energy metabolism drives resource-efficient seed germination. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 117(1): 741-751. |
| [10] | Renard J, Ninoles R, Martinez-Almonacid I, et al. Identification of novel seed longevity genes related to oxidative stress and seed coat by genome-wide association studies and reverse genetics. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2020, 43(10): 2523-2539. |
| [11] | Lee Y P, Baek K H, Lee H S, et al. Tobacco seeds simultaneously over-expressing Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase display enhanced seed longevity and germination rates under stress conditions. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(9): 2499-2506. |
| [12] | Nigam M, Mishra A P, Salehi B, et al. Accelerated aging induces physiological and biochemical changes in tomato seeds involving MAPK pathways. Scientia Horticulturae, 2019, 248: 20-28. |
| [13] | Xue F, Gao B, Qiao G H, et al. Analysis of the differences in green farming behavior of operating agents in grassland pastoral areas. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2023, 11: 1109430. |
| [14] | Song X Q, Yang Z R, Zhang D, et al. Proteomic analysis of the effect of accelerated ageing on Allium mongolicum seeds. Horticulturae, 2023, 9(10): 9101155. |
| [15] | Xia F S, Cheng H, Chen L L, et al. Influence of exogenous ascorbic acid and glutathione priming on mitochondrial structural and functional systems to alleviate aging damage in oat seeds. BMC Plant Biology, 2020, 20: 1-11. |
| [16] | Milivojević M, Ripka Z, Petrović T. ISTA rules changes in seed germination testing at the beginning of the 21st century. Journal on Processing and Energy in Agriculture, 2018, 22(1): 40-45. |
| [17] | Lu J Y, Tian H, Zhang H S, et al. Effects of H2O2 immersion on seed germination and seedling growth of alfalfa under salt stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 141-152. |
| 陆姣云, 田宏, 张鹤山, 等. H2O2浸种对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 141-152. | |
| [18] | Luo Y J, Zhang Y X, Le J Y,et al. Full-length transcriptome sequencing reveals the molecular mechanism of Metasequoia glyptostroboides seed responding to aging. Antioxidants, 2023, 12(7): 1353. |
| [19] | Kurek K, Plitta-Michalak B, Ratajczak E. Reactive oxygen species as potential drivers of the seed aging process. Plants, 2019, 8(6): 174. |
| [20] | Sun M, Sun S J, Mao C L, et al. Dynamic responses of antioxidant and glyoxalase systems to seed aging based on full-length transcriptome in oat (Avena sativa L.). Antioxidants, 2022, 11(2): 395. |
| [21] | Gu J W, Hou D L, Li Y H, et al. Integration of proteomic and genomic approaches to dissect seed germination vigor in Brassica napus seeds differing in oil content. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19: 1-20. |
| [22] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [23] | Bailly C, Benamar A, Corbineau F, et al. Changes in malondialdehyde content and in superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione reductase activities in sunflower seeds as related to deterioration during accelerated aging. Plant Physiology, 1996, 97(1): 104-110. |
| [24] | Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A. Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants: Protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Science, 2000, 151(1): 59-66. |
| [25] | Ratajczak E, Małecka A, Ciereszko I, et al. Mitochondria are important determinants of the aging of seeds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(7): 1568. |
| [26] | Nigam M, Singh N, Ranjan V, et al. Centchroman mediated apoptosis involves crosstalk between extrinsic/intrinsic pathways and oxidative regulation. Life Sciences, 2010, 87(23): 750-758. |
| [27] | Ratajczak E, Małecka A, Bagniewska-Zadworna A, et al. The production, localization and spreading of reactive oxygen species contributes to the low vitality of long-term stored common beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) seeds. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2015, 174: 147-156. |
| [28] | Li J, Lei B, Zhai M H, et al. Study on the response mechanism of the AsA-GSH cycle in cotton seedling under low temperature stress. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 35(1): 221-228. |
| [29] | Sercel A J, Sturm G, Gallagher D, et al. Hypermetabolism and energetic constraints in mitochondrial disorders. Nature Metabolism, 2024, 6(2): 192-195. |
| [30] | Ding S H, Wang L, Yang Z P, et al. Decreased glutathione reductase 2 leads to early leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2016, 58(1): 29-47. |
| [31] | Manna M, Rengasamy B, Sinha A K. Revisiting the role of MAPK signalling pathway in plants and its manipulation for crop improvement. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2023, 46(8): 2277-2295. |
| [32] | Morgan M J, Lehmann M, Schwarzlander M, et al. Decrease in manganese superoxide dismutase leads to reduced root growth and affects tricarboxylic acid cycle flux and mitochondrial redox homeostasis. Plant Physiology, 2008, 147(1): 101-114. |
| [1] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [2] | 鲜燃, 邓雨, 付秋月, 蒋晶霞, 陶佳丽, 许涛, 朱慧森, 岑慧芳. 紫花苜蓿MsMYB86基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 162-172. |
| [3] | 刘沂欣, 隋晓青, 王鑫尧, 郎梦卿, 孙凌子寅, 吉尔尔格. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿的缓解作用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 206-214. |
| [4] | 赵聪, 吴文慧, 王娟玲, 梁改梅, 李娜娜, 黄学芳. 结球甘蓝叶对3种作物芽期与苗期生长的化感效应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 65-77. |
| [5] | 卢天一, 艾艳梅, 汪洋, 那萌, 徐尚起, 周际海. 镉污染土壤中水稻的镉富集特征和生长响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 66-78. |
| [6] | 李文秀, 姚拓, 李昌宁, 贾倩民, 何傲蕾, 周杨. “凹凸棒-有机基质”菌肥载体最佳配比的筛选及对紫花苜蓿的促生效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 88-98. |
| [7] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [8] | 温小月, 赵颖, 王宝强, 王贤, 朱晓林, 王义真, 魏小红. 外源NO调控干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿AP2/ERFs基因的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 154-167. |
| [9] | 张晴晴, 马兴羽, 鲁艳, 赵广兴, 曾凡江, 黄彩变. 沙化盐渍土地不同生长时期油莎豆的耐盐性差异研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 168-180. |
| [10] | 张英豪, 刘楚波, 周坤, 郭家存, 刘世鹏, 孙娈姿. 果草系统中枣树对不同方位紫花苜蓿和鸭茅生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 203-212. |
| [11] | 崔灿, 王梦琦, 赵琬璐, 刘新颖, 鉴晶晶, 严俊鑫. 胺鲜酯浸种对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 46-58. |
| [12] | 曾燕霞, 陈志龙, 尚继红, 沙晓弟, 吴娟, 陈彩锦. 太空诱变对PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿材料苗期生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 59-69. |
| [13] | 魏孔钦, 张盈盈, 回金峰, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷配施对紫花苜蓿根系非结构碳水化合物及碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 40-50. |
| [14] | 周昕越, 王丽萍, 蒋庆雪, 马晓冉, 仪登霞, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿低温诱导蛋白MsLTI65的分离及其对不同逆境的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 89-104. |
| [15] | 罗天蓉, 马健芝, 杜明阳, 多杰措, 熊辉岩, 段瑞君. 紫花苜蓿LACS基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 124-136. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||