

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 94-108.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024154
欧翔( ), 连海, 陈荣强, 邱静芸, 吴丽娟, 操贤洪, 张强, 雷小文(
), 连海, 陈荣强, 邱静芸, 吴丽娟, 操贤洪, 张强, 雷小文( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-30
修回日期:2024-06-05
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
雷小文
作者简介:E-mail: 343224896@qq.com基金资助:
Xiang OU( ), Hai LIAN, Rong-qiang CHEN, Jing-yun QIU, Li-juan WU, Xian-hong CAO, Qiang ZHANG, Xiao-wen LEI(
), Hai LIAN, Rong-qiang CHEN, Jing-yun QIU, Li-juan WU, Xian-hong CAO, Qiang ZHANG, Xiao-wen LEI( )
)
Received:2024-04-30
Revised:2024-06-05
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Xiao-wen LEI
摘要:
为探究不同施肥处理对种植王草修复稀土尾矿土壤的改良效果,设置化肥(CK)、沼液(Z)、腐熟牛粪(N)、腐熟牛粪+沼液(N+Z)、蚯蚓粪(Q)、蚯蚓粪+沼液(Q+Z)6个处理进行田间等氮量施肥试验,分析连续3年各处理对稀土尾矿土壤理化性质、酶活性及其相互作用规律的影响。结果表明:1)连续3年各组土壤容重呈下降趋势,最大持水量、毛管持水量、孔隙度、通气度、pH、有机质、氮、磷、钾、碱解氮、速效磷呈上升趋势;在修复第3年Q+Z组对土壤容重、持水量、孔隙度、通气度、pH、速效磷、速效钾的改良效果优于其他处理。2)连续3年N、N+Z、Q、Q+Z组土壤脲酶、酸性磷酸酶、蔗糖酶活性呈上升趋势,第3年均显著高于CK组,土壤脱氢酶活性仅N+Z组第1年显著高于同期CK组,其中Q组对土壤脲酶、酸性磷酸酶、蔗糖酶活性的提升优于其他处理。3)土壤脲酶、酸性磷酸酶、蔗糖酶活性与土壤容重呈极显著负相关,与pH、有机质、速效养分、持水量、孔隙度、通气度呈极显著相关,脱氢酶活性与全磷呈极显著相关,与全钾、碱解氮、速效磷、有机质、毛管持水量、孔隙度、通气度显著相关。通过模糊数学隶属函数法进行综合评价发现,施用蚯蚓粪+沼液处理连续3年综合排序第一,可作为种植王草修复赣南离子型稀土尾矿土壤的最佳施肥处理。
欧翔, 连海, 陈荣强, 邱静芸, 吴丽娟, 操贤洪, 张强, 雷小文. 不同施肥处理种植王草后对稀土尾矿土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 94-108.
Xiang OU, Hai LIAN, Rong-qiang CHEN, Jing-yun QIU, Li-juan WU, Xian-hong CAO, Qiang ZHANG, Xiao-wen LEI. Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activity of rare earth mine tailings after planting king grass[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 94-108.

图1 研究区地理位置基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)3266号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map of GS (2019) 3266 of the standard map service network of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig. 1 Geographical location of study area
| 项目Items | 尾矿土壤Tailing soil | 非尾矿土壤Non-tailing soil |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.20±0.29 | 5.86±0.10 |
| 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 2.30±0.44 | 15.39±3.56 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 0.06±0.01 | 0.63±0.04 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 0.15±0.01 | 1.38±0.60 |
| 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 10.53±0.89 | 19.66±2.55 |
| 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 3.78±0.29 | 94.67±15.53 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus ( mg·kg-1) | 0.92±0.12 | 20.55±7.37 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 56.68±3.95 | 875.50±122.39 |
| 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 1.37±0.24 | 1.14±0.05 |
| 最大持水量 Maximum moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 266.86±28.91 | 510.27±5.76 |
| 毛管持水量 Capillary moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 147.45±16.98 | 382.06±10.17 |
| 田间持水量 Field moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 139.71±17.46 | 229.80±22.97 |
| 土壤孔隙度 Soil porosity (%) | 36.54±2.08 | 58.16±4.55 |
| 土壤通气度 Soil aeration (%) | 19.76±1.39 | 30.16±2.09 |
表1 尾矿与非尾矿土壤理化性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of tailings and non-tailings soil
| 项目Items | 尾矿土壤Tailing soil | 非尾矿土壤Non-tailing soil |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.20±0.29 | 5.86±0.10 |
| 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 2.30±0.44 | 15.39±3.56 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 0.06±0.01 | 0.63±0.04 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 0.15±0.01 | 1.38±0.60 |
| 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 10.53±0.89 | 19.66±2.55 |
| 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 3.78±0.29 | 94.67±15.53 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus ( mg·kg-1) | 0.92±0.12 | 20.55±7.37 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 56.68±3.95 | 875.50±122.39 |
| 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 1.37±0.24 | 1.14±0.05 |
| 最大持水量 Maximum moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 266.86±28.91 | 510.27±5.76 |
| 毛管持水量 Capillary moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 147.45±16.98 | 382.06±10.17 |
| 田间持水量 Field moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 139.71±17.46 | 229.80±22.97 |
| 土壤孔隙度 Soil porosity (%) | 36.54±2.08 | 58.16±4.55 |
| 土壤通气度 Soil aeration (%) | 19.76±1.39 | 30.16±2.09 |
| 项目Items | 沼液Biogas slurry | 腐熟牛粪Decomposed cow dung | 蚯蚓粪Earthworm cast |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水分 Water content | - | 30.93±2.17 | 50.81±2.11 |
| 有机质 Organic matter | 0.79±0.04 | 47.80±4.13 | 42.34±1.10 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.62±0.04 | 1.81±0.12 | 1.87±0.06 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 0.09±0.01 | 1.54±0.30 | 3.15±0.07 |
| 全钾 Total potassium | 0.08±0.00 | 2.21±0.27 | 2.26±0.22 |
表2 沼液、腐熟牛粪、蚯蚓粪养分含量
Table 2 Nutrient content of biogas slurry, decomposed cow dung and earthworm cast (%)
| 项目Items | 沼液Biogas slurry | 腐熟牛粪Decomposed cow dung | 蚯蚓粪Earthworm cast |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水分 Water content | - | 30.93±2.17 | 50.81±2.11 |
| 有机质 Organic matter | 0.79±0.04 | 47.80±4.13 | 42.34±1.10 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.62±0.04 | 1.81±0.12 | 1.87±0.06 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 0.09±0.01 | 1.54±0.30 | 3.15±0.07 |
| 全钾 Total potassium | 0.08±0.00 | 2.21±0.27 | 2.26±0.22 |
| 施肥用量Fertilization amount | 施肥种类Fertilization type | CK | Z | N | N+Z | Q | Q+Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
基肥用量 Ground fertilizer amounts | 沼液 Biogas slurry (t·hm-2) | 0 | 161.40 | 0 | 80.70 | 0 | 80.00 |
| 腐熟牛粪 Decomposed cow dung (t·hm-2) | 0 | 0 | 80.00 | 40.00 | 0 | 0 | |
| 蚯蚓粪 Earthworm cast (t·hm-2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 108.80 | 55.00 | |
| 氮总量 Total nitrogen (kg·hm-2) | 1000.00 | 1000.68 | 1000.13 | 1000.14 | 1000.80 | 1001.92 | |
| 磷总量Total phosphorus (kg·hm-2) | 1142.86 | 145.26 | 1232.00 | 688.63 | 3427.20 | 1804.50 | |
| 钾总量 Total potassium (kg·hm-2) | 1071.43 | 129.12 | 1768.00 | 948.56 | 2458.88 | 1307.00 | |
单次追肥用量 Single additional fertilizer amounts | 沼液 Biogas slurry (t·hm-2) | 0 | 80.70 | 0 | 40.30 | 0 | 40.00 |
| 腐熟牛粪 Decomposed cow dung (t·hm-2) | 0 | 0 | 40.00 | 20.00 | 0 | 0 | |
| 蚯蚓粪 Earthworm cast (t·hm-2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 54.40 | 27.50 | |
| 氮总量 Total nitrogen (kg·hm-2) | 500.00 | 500.34 | 500.07 | 499.89 | 500.40 | 500.96 | |
| 磷总量Total phosphorus (kg·hm-2) | 571.43 | 72.63 | 616.00 | 344.32 | 1713.60 | 902.25 | |
| 钾总量 Total potassium (kg·hm-2) | 535.71 | 64.56 | 884.00 | 474.28 | 1229.44 | 653.50 |
表3 各处理施肥用量
Table 3 Fertilization amount of each treatment
| 施肥用量Fertilization amount | 施肥种类Fertilization type | CK | Z | N | N+Z | Q | Q+Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
基肥用量 Ground fertilizer amounts | 沼液 Biogas slurry (t·hm-2) | 0 | 161.40 | 0 | 80.70 | 0 | 80.00 |
| 腐熟牛粪 Decomposed cow dung (t·hm-2) | 0 | 0 | 80.00 | 40.00 | 0 | 0 | |
| 蚯蚓粪 Earthworm cast (t·hm-2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 108.80 | 55.00 | |
| 氮总量 Total nitrogen (kg·hm-2) | 1000.00 | 1000.68 | 1000.13 | 1000.14 | 1000.80 | 1001.92 | |
| 磷总量Total phosphorus (kg·hm-2) | 1142.86 | 145.26 | 1232.00 | 688.63 | 3427.20 | 1804.50 | |
| 钾总量 Total potassium (kg·hm-2) | 1071.43 | 129.12 | 1768.00 | 948.56 | 2458.88 | 1307.00 | |
单次追肥用量 Single additional fertilizer amounts | 沼液 Biogas slurry (t·hm-2) | 0 | 80.70 | 0 | 40.30 | 0 | 40.00 |
| 腐熟牛粪 Decomposed cow dung (t·hm-2) | 0 | 0 | 40.00 | 20.00 | 0 | 0 | |
| 蚯蚓粪 Earthworm cast (t·hm-2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 54.40 | 27.50 | |
| 氮总量 Total nitrogen (kg·hm-2) | 500.00 | 500.34 | 500.07 | 499.89 | 500.40 | 500.96 | |
| 磷总量Total phosphorus (kg·hm-2) | 571.43 | 72.63 | 616.00 | 344.32 | 1713.60 | 902.25 | |
| 钾总量 Total potassium (kg·hm-2) | 535.71 | 64.56 | 884.00 | 474.28 | 1229.44 | 653.50 |
土壤理化性质 Soil physical and chemical properties | 组Group | 年份Year | 组×年份Group×year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| pH | 64.07*** | <0.001 | 45.04*** | <0.001 | 6.04*** | <0.001 |
| 有机质 Organic matter | 1.93 | 0.114 | 82.23*** | <0.001 | 1.55 | 0.163 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 7.28*** | <0.001 | 36.18*** | <0.001 | 2.54* | 0.020 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 6.55*** | <0.001 | 7.54** | 0.002 | 0.49 | 0.886 |
| 全钾 Total potassium | 13.96*** | <0.001 | 101.49*** | <0.001 | 2.34* | 0.030 |
| 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen | 47.32*** | <0.001 | 93.26*** | <0.001 | 9.91*** | <0.001 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 113.87*** | <0.001 | 4.55* | 0.017 | 1.85 | 0.087 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium | 54.93*** | <0.001 | 45.79*** | <0.001 | 1.56 | 0.160 |
| 容重 Bulk density | 113.02*** | <0.001 | 62.85*** | <0.001 | 3.29** | 0.004 |
| 最大持水量 Maximum moisture capacity | 153.58*** | <0.001 | 104.89*** | <0.001 | 3.24** | 0.004 |
| 毛管持水量 Capillary moisture capacity | 183.22*** | <0.001 | 89.43*** | <0.001 | 2.52* | 0.020 |
| 田间持水量 Field moisture capacity | 62.01*** | <0.001 | 7.47** | 0.002 | 2.97** | 0.008 |
| 土壤孔隙度 Soil porosity | 101.75*** | <0.001 | 70.65*** | <0.001 | 1.72 | 0.113 |
| 土壤通气度 Soil aeration | 31.78*** | <0.001 | 57.60*** | <0.001 | 3.44** | 0.003 |
表4 不同施肥处理对稀土尾矿土壤理化性质的双因素方差分析结果
Table 4 Two-way analysis of variance results of different fertilization treatments on soil physical and chemical properties of rare earth tailings
土壤理化性质 Soil physical and chemical properties | 组Group | 年份Year | 组×年份Group×year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| pH | 64.07*** | <0.001 | 45.04*** | <0.001 | 6.04*** | <0.001 |
| 有机质 Organic matter | 1.93 | 0.114 | 82.23*** | <0.001 | 1.55 | 0.163 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 7.28*** | <0.001 | 36.18*** | <0.001 | 2.54* | 0.020 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 6.55*** | <0.001 | 7.54** | 0.002 | 0.49 | 0.886 |
| 全钾 Total potassium | 13.96*** | <0.001 | 101.49*** | <0.001 | 2.34* | 0.030 |
| 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen | 47.32*** | <0.001 | 93.26*** | <0.001 | 9.91*** | <0.001 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 113.87*** | <0.001 | 4.55* | 0.017 | 1.85 | 0.087 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium | 54.93*** | <0.001 | 45.79*** | <0.001 | 1.56 | 0.160 |
| 容重 Bulk density | 113.02*** | <0.001 | 62.85*** | <0.001 | 3.29** | 0.004 |
| 最大持水量 Maximum moisture capacity | 153.58*** | <0.001 | 104.89*** | <0.001 | 3.24** | 0.004 |
| 毛管持水量 Capillary moisture capacity | 183.22*** | <0.001 | 89.43*** | <0.001 | 2.52* | 0.020 |
| 田间持水量 Field moisture capacity | 62.01*** | <0.001 | 7.47** | 0.002 | 2.97** | 0.008 |
| 土壤孔隙度 Soil porosity | 101.75*** | <0.001 | 70.65*** | <0.001 | 1.72 | 0.113 |
| 土壤通气度 Soil aeration | 31.78*** | <0.001 | 57.60*** | <0.001 | 3.44** | 0.003 |
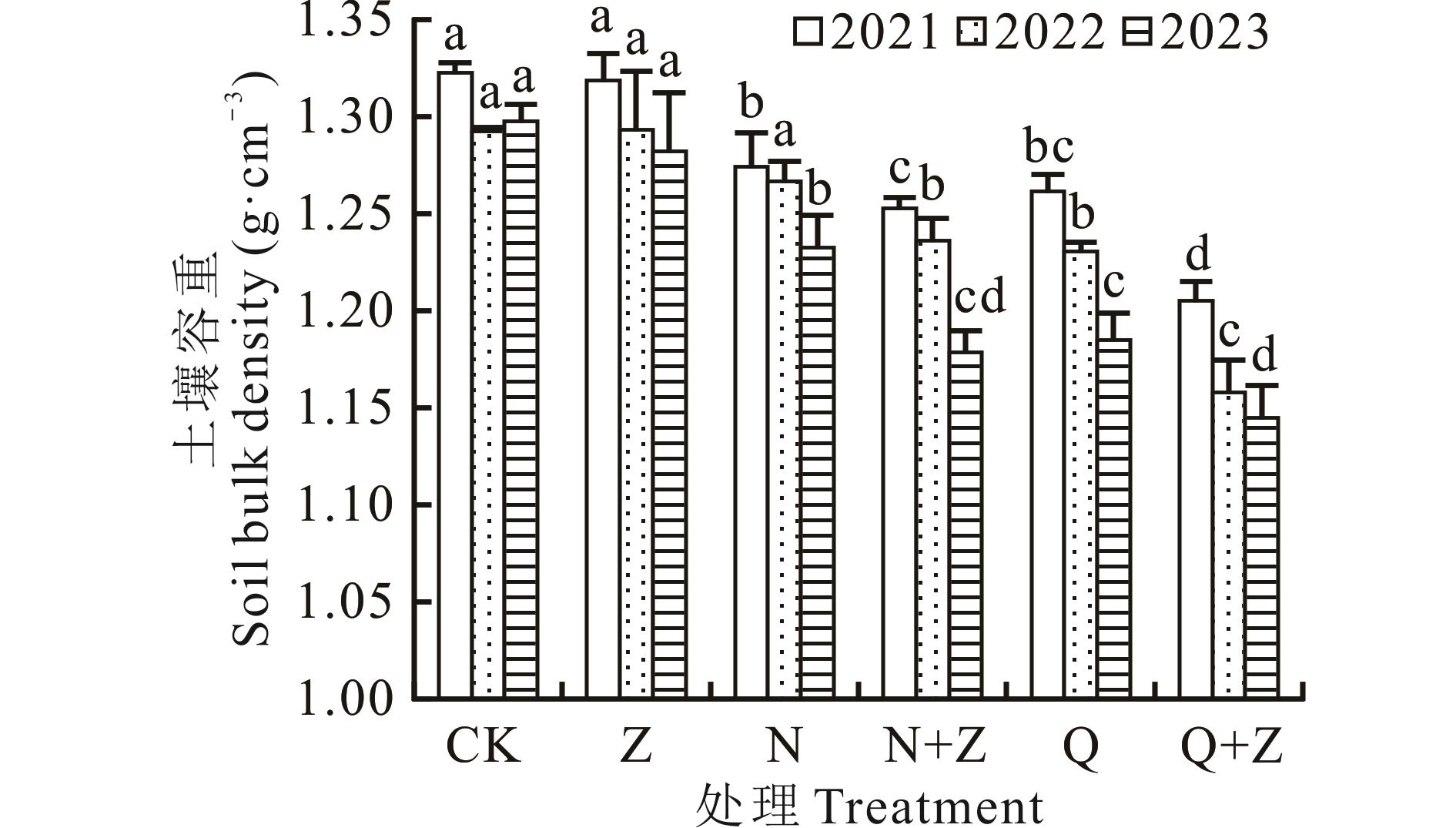
图2 不同施肥处理对土壤容重的影响CK:化肥Chemical fertilizer;Z:沼液Biogas slurry;N:腐熟牛粪Decomposed cow dung;N+Z:腐熟牛粪+沼液Decomposed cow dung +biogas slurry;Q:蚯蚓粪Earthworm cast;Q+Z:蚯蚓粪+沼液Earthworm cast+biogas slurry。不同小写字母表示同一年份不同施肥处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicated that there were significant differences among different fertilization treatments in the same year (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.2 Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil bulk density
处理 Treatment | 年份 Year | 最大持水量 Maximum moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 毛管持水量 Capillary moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 田间持水量 Field moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 土壤孔隙度 Soil porosity (%) | 土壤通气度 Soil aeration (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2021 | 293.58±11.16c | 173.74±6.83c | 151.69±10.16e | 38.83±1.44c | 18.77±2.39bc |
| 2022 | 314.73±12.06e | 201.90±5.58e | 180.76±9.45c | 40.68±1.61d | 17.32±2.79d | |
| 2023 | 350.71±9.44d | 233.70±11.90d | 176.50±6.92d | 45.50±0.92c | 22.60±1.03c | |
| Z | 2021 | 303.31±30.89c | 182.72±16.34c | 167.32±3.93d | 39.96±3.63c | 17.90±3.71c |
| 2022 | 329.55±4.12e | 214.54±3.80e | 194.74±8.44bc | 42.62±1.13d | 17.42±0.68d | |
| 2023 | 350.85±19.29d | 230.88±23.06d | 171.88±3.97d | 44.94±1.72c | 22.90±2.58c | |
| N | 2021 | 368.19±11.08b | 261.60±15.29b | 190.50±7.09c | 46.90±0.80b | 22.63±0.62ab |
| 2022 | 380.04±17.59d | 268.13±12.50d | 211.61±21.50ab | 48.14±2.29c | 21.35±3.80c | |
| 2023 | 425.40±3.33c | 317.82±4.01c | 192.91±10.90c | 52.37±1.16b | 28.63±1.99b | |
| N+Z | 2021 | 389.53±9.65b | 276.43±12.53b | 209.69±4.22b | 48.80±1.23ab | 22.53±0.69ab |
| 2022 | 407.21±7.77c | 286.51±8.68c | 207.24±6.99ab | 50.33±1.08c | 24.72±0.60bc | |
| 2023 | 486.18±4.01ab | 365.48±6.58b | 214.64±11.30b | 57.05±0.56a | 31.86±1.54a | |
| Q | 2021 | 377.05±15.09b | 290.08±15.00b | 219.54±7.44b | 47.55±1.81b | 19.87±2.15abc |
| 2022 | 432.03±7.21b | 334.38±13.11b | 226.80±7.39a | 53.15±0.73b | 25.25±0.28b | |
| 2023 | 483.30±9.24b | 386.12±10.46ab | 224.50±4.32b | 57.02±0.63a | 30.53±0.65ab | |
| Q+Z | 2021 | 435.20±27.82a | 342.42±37.15a | 234.60±7.62a | 52.42±2.99a | 24.16±2.56a |
| 2022 | 495.12±14.27a | 393.28±7.88a | 225.10±12.31a | 57.32±1.26a | 31.27±1.13a | |
| 2023 | 510.45±22.76a | 411.37±28.06a | 239.74±11.70a | 58.43±2.36a | 30.99±1.37ab |
表5 不同施肥处理对土壤持水量、孔隙度和通气度的影响
Table 5 Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil water holding capacity, porosity and aeration
处理 Treatment | 年份 Year | 最大持水量 Maximum moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 毛管持水量 Capillary moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 田间持水量 Field moisture capacity (g·kg-1) | 土壤孔隙度 Soil porosity (%) | 土壤通气度 Soil aeration (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2021 | 293.58±11.16c | 173.74±6.83c | 151.69±10.16e | 38.83±1.44c | 18.77±2.39bc |
| 2022 | 314.73±12.06e | 201.90±5.58e | 180.76±9.45c | 40.68±1.61d | 17.32±2.79d | |
| 2023 | 350.71±9.44d | 233.70±11.90d | 176.50±6.92d | 45.50±0.92c | 22.60±1.03c | |
| Z | 2021 | 303.31±30.89c | 182.72±16.34c | 167.32±3.93d | 39.96±3.63c | 17.90±3.71c |
| 2022 | 329.55±4.12e | 214.54±3.80e | 194.74±8.44bc | 42.62±1.13d | 17.42±0.68d | |
| 2023 | 350.85±19.29d | 230.88±23.06d | 171.88±3.97d | 44.94±1.72c | 22.90±2.58c | |
| N | 2021 | 368.19±11.08b | 261.60±15.29b | 190.50±7.09c | 46.90±0.80b | 22.63±0.62ab |
| 2022 | 380.04±17.59d | 268.13±12.50d | 211.61±21.50ab | 48.14±2.29c | 21.35±3.80c | |
| 2023 | 425.40±3.33c | 317.82±4.01c | 192.91±10.90c | 52.37±1.16b | 28.63±1.99b | |
| N+Z | 2021 | 389.53±9.65b | 276.43±12.53b | 209.69±4.22b | 48.80±1.23ab | 22.53±0.69ab |
| 2022 | 407.21±7.77c | 286.51±8.68c | 207.24±6.99ab | 50.33±1.08c | 24.72±0.60bc | |
| 2023 | 486.18±4.01ab | 365.48±6.58b | 214.64±11.30b | 57.05±0.56a | 31.86±1.54a | |
| Q | 2021 | 377.05±15.09b | 290.08±15.00b | 219.54±7.44b | 47.55±1.81b | 19.87±2.15abc |
| 2022 | 432.03±7.21b | 334.38±13.11b | 226.80±7.39a | 53.15±0.73b | 25.25±0.28b | |
| 2023 | 483.30±9.24b | 386.12±10.46ab | 224.50±4.32b | 57.02±0.63a | 30.53±0.65ab | |
| Q+Z | 2021 | 435.20±27.82a | 342.42±37.15a | 234.60±7.62a | 52.42±2.99a | 24.16±2.56a |
| 2022 | 495.12±14.27a | 393.28±7.88a | 225.10±12.31a | 57.32±1.26a | 31.27±1.13a | |
| 2023 | 510.45±22.76a | 411.37±28.06a | 239.74±11.70a | 58.43±2.36a | 30.99±1.37ab |
处理 Treatment | 年份 Year | 有机质 Organic matter(g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2021 | 2.31±0.33b | 0.27±0.09a | 0.15±0.03c | 10.91±0.99ab | 7.34±1.39b | 4.28±1.90a | 60.84±3.60c |
| 2022 | 7.35±1.16b | 0.53±0.03b | 0.17±0.01a | 12.88±0.93ab | 15.60±4.82b | 4.93±1.42d | 75.40±9.10b | |
| 2023 | 6.17±1.76b | 0.47±0.11a | 0.25±0.07c | 13.81±2.14ab | 25.78±2.32c | 5.00±2.00d | 72.67±8.62c | |
| Z | 2021 | 3.00±1.75b | 0.15±0.06b | 0.16±0.02c | 9.45±1.20b | 9.67±0.83ab | 5.37±1.92a | 83.40±11.13c |
| 2022 | 9.65±2.91b | 0.49±0.04b | 0.19±0.04a | 9.35±3.46b | 38.51±9.98ab | 6.51±1.78cd | 85.54±14.82b | |
| 2023 | 8.35±1.93b | 0.43±0.18a | 0.22±0.08c | 10.49±2.49b | 46.72±14.01b | 8.50±1.82cd | 76.33±10.69c | |
| N | 2021 | 13.19±1.20a | 0.12±0.03b | 0.19±0.04bc | 11.48±2.37ab | 13.01±3.07ab | 7.23±1.60a | 189.56±23.57b |
| 2022 | 16.07±2.38a | 0.51±0.12b | 0.23±0.12a | 13.67±3.16ab | 56.72±19.37a | 12.69±2.46abc | 227.37±39.49a | |
| 2023 | 21.10±3.04a | 0.64±0.19a | 0.35±0.06bc | 15.72±1.99a | 66.32±10.53a | 14.58±1.92bc | 194.67±27.59b | |
| N+Z | 2021 | 11.92±1.57a | 0.12±0.03b | 0.23±0.07ab | 12.01±1.07a | 13.91±3.73ab | 6.07±1.87a | 242.68±23.71a |
| 2022 | 19.43±3.00a | 0.58±0.09b | 0.21±0.07a | 15.09±1.98a | 54.09±18.84a | 13.92±2.40ab | 272.84±37.78a | |
| 2023 | 19.48±4.07a | 0.63±0.15a | 0.34±0.07bc | 15.10±1.97a | 69.69±10.76a | 21.57±4.31ab | 191.67±30.75b | |
| Q | 2021 | 13.72±1.37a | 0.12±0.05b | 0.27±0.03a | 13.06±1.17a | 14.54±4.92a | 9.16±1.76a | 276.51±56.17a |
| 2022 | 18.13±3.15a | 0.51±0.04b | 0.25±0.04a | 14.85±1.52a | 51.12±12.07a | 19.24±2.87a | 262.30±35.82a | |
| 2023 | 22.89±2.13a | 0.54±0.19a | 0.52±0.09a | 14.81±1.74a | 65.52±4.41a | 24.70±2.29a | 275.67±9.07a | |
| Q+Z | 2021 | 12.15±2.54a | 0.14±0.04b | 0.19±0.01bc | 12.95±1.53a | 14.35±4.66a | 8.40±2.28a | 269.25±8.68a |
| 2022 | 21.23±2.45a | 0.71±0.05a | 0.17±0.07a | 14.31±2.20a | 62.74±12.01a | 12.26±1.88bc | 339.90±43.62a | |
| 2023 | 21.70±3.50a | 0.68±0.17a | 0.50±0.12ab | 14.78±1.82a | 61.45±5.59ab | 27.17±2.15a | 305.33±27.79a |
表6 不同施肥处理对土壤养分的影响
Table 6 Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil nutrients
处理 Treatment | 年份 Year | 有机质 Organic matter(g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2021 | 2.31±0.33b | 0.27±0.09a | 0.15±0.03c | 10.91±0.99ab | 7.34±1.39b | 4.28±1.90a | 60.84±3.60c |
| 2022 | 7.35±1.16b | 0.53±0.03b | 0.17±0.01a | 12.88±0.93ab | 15.60±4.82b | 4.93±1.42d | 75.40±9.10b | |
| 2023 | 6.17±1.76b | 0.47±0.11a | 0.25±0.07c | 13.81±2.14ab | 25.78±2.32c | 5.00±2.00d | 72.67±8.62c | |
| Z | 2021 | 3.00±1.75b | 0.15±0.06b | 0.16±0.02c | 9.45±1.20b | 9.67±0.83ab | 5.37±1.92a | 83.40±11.13c |
| 2022 | 9.65±2.91b | 0.49±0.04b | 0.19±0.04a | 9.35±3.46b | 38.51±9.98ab | 6.51±1.78cd | 85.54±14.82b | |
| 2023 | 8.35±1.93b | 0.43±0.18a | 0.22±0.08c | 10.49±2.49b | 46.72±14.01b | 8.50±1.82cd | 76.33±10.69c | |
| N | 2021 | 13.19±1.20a | 0.12±0.03b | 0.19±0.04bc | 11.48±2.37ab | 13.01±3.07ab | 7.23±1.60a | 189.56±23.57b |
| 2022 | 16.07±2.38a | 0.51±0.12b | 0.23±0.12a | 13.67±3.16ab | 56.72±19.37a | 12.69±2.46abc | 227.37±39.49a | |
| 2023 | 21.10±3.04a | 0.64±0.19a | 0.35±0.06bc | 15.72±1.99a | 66.32±10.53a | 14.58±1.92bc | 194.67±27.59b | |
| N+Z | 2021 | 11.92±1.57a | 0.12±0.03b | 0.23±0.07ab | 12.01±1.07a | 13.91±3.73ab | 6.07±1.87a | 242.68±23.71a |
| 2022 | 19.43±3.00a | 0.58±0.09b | 0.21±0.07a | 15.09±1.98a | 54.09±18.84a | 13.92±2.40ab | 272.84±37.78a | |
| 2023 | 19.48±4.07a | 0.63±0.15a | 0.34±0.07bc | 15.10±1.97a | 69.69±10.76a | 21.57±4.31ab | 191.67±30.75b | |
| Q | 2021 | 13.72±1.37a | 0.12±0.05b | 0.27±0.03a | 13.06±1.17a | 14.54±4.92a | 9.16±1.76a | 276.51±56.17a |
| 2022 | 18.13±3.15a | 0.51±0.04b | 0.25±0.04a | 14.85±1.52a | 51.12±12.07a | 19.24±2.87a | 262.30±35.82a | |
| 2023 | 22.89±2.13a | 0.54±0.19a | 0.52±0.09a | 14.81±1.74a | 65.52±4.41a | 24.70±2.29a | 275.67±9.07a | |
| Q+Z | 2021 | 12.15±2.54a | 0.14±0.04b | 0.19±0.01bc | 12.95±1.53a | 14.35±4.66a | 8.40±2.28a | 269.25±8.68a |
| 2022 | 21.23±2.45a | 0.71±0.05a | 0.17±0.07a | 14.31±2.20a | 62.74±12.01a | 12.26±1.88bc | 339.90±43.62a | |
| 2023 | 21.70±3.50a | 0.68±0.17a | 0.50±0.12ab | 14.78±1.82a | 61.45±5.59ab | 27.17±2.15a | 305.33±27.79a |
酶种类 Kinds of enzyme | 组Group | 年份Year | 组×年份Group×year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 脲酶活性Urease activity | 30.76*** | <0.001 | 48.17*** | <0.001 | 4.57*** | <0.001 |
| 酸性磷酸酶活性Acid phosphatase activity | 110.03*** | <0.001 | 80.63*** | <0.001 | 7.28*** | <0.001 |
| 蔗糖酶活性Sucrase activity | 39.40*** | <0.001 | 13.25*** | <0.001 | 3.29** | 0.004 |
| 脱氢酶活性Dehydrogenase activity | 1.08 | 0.39 | 3.55* | 0.039 | 0.78 | 0.648 |
表7 不同施肥处理对稀土尾矿土壤酶活性的双因素方差分析
Table 7 Two-way analysis of variance of soil enzyme activity of rare earth tailings under different fertilization treatments
酶种类 Kinds of enzyme | 组Group | 年份Year | 组×年份Group×year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 脲酶活性Urease activity | 30.76*** | <0.001 | 48.17*** | <0.001 | 4.57*** | <0.001 |
| 酸性磷酸酶活性Acid phosphatase activity | 110.03*** | <0.001 | 80.63*** | <0.001 | 7.28*** | <0.001 |
| 蔗糖酶活性Sucrase activity | 39.40*** | <0.001 | 13.25*** | <0.001 | 3.29** | 0.004 |
| 脱氢酶活性Dehydrogenase activity | 1.08 | 0.39 | 3.55* | 0.039 | 0.78 | 0.648 |

图4 不同施肥处理对稀土尾矿土壤脲酶、酸性磷酸酶、蔗糖酶、脱氢酶活性的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of different fertilization treatments on the activities of urease, acid phosphatase, sucrase and dehydrogenase in rare earth tailings soil
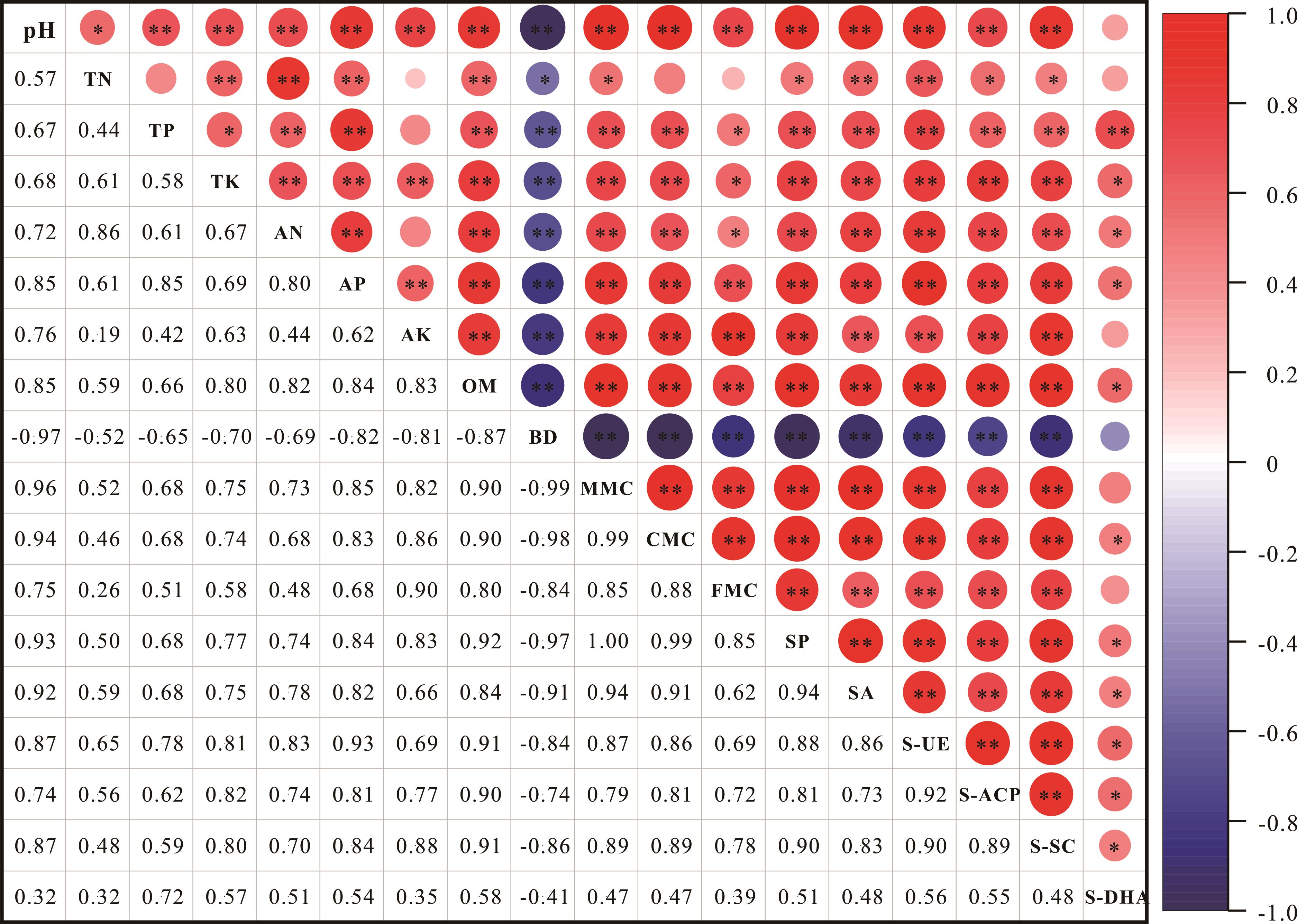
图5 土壤酶活性与土壤理化性质的相关性TN:全氮Total nitrogen;TP:全磷Total phosphorus;TK:全钾Total potassium;AN:碱解氮Alkaline nitrogen;AP:速效磷Available phosphorus;AK:速效钾Available potassium;OM:有机质Organic matter;BD:容重Bulk density;MMC:最大持水量Maximum moisture capacity;CMC:毛管持水量Capillary moisture capacity;FMC:田间持水量Field moisture capacity;SP:土壤孔隙度Soil porosity;SA:土壤通气度Soil aeration;S-UE:土壤脲酶活性Soil urease activity;S-ACP:土壤酸性磷酸酶活性Soil acid phosphatase activity;S-SC:土壤蔗糖酶活性Soil sucrase activity;S-DHA:土壤脱氢酶活性Soil dehydrogenase activity. “**”, “*”分别表示在 0.01、0.05 水平上显著相关。圆形颜色深浅反映相关系数大小,数字为正代表正相关,数字为负代表负相关。“**”, “*”indicate significant correlation at 0.01,0.05 levels. The depth of the circular color reflects the size of the correlation coefficient. A positive number represents a positive correlation, and a negative number represents a negative correlation.
Fig. 5 Correlation between soil enzyme activity and soil physical and chemical properties
| 年份Year | CK | Z | N | N+Z | Q | Q+Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 0.1188 | 0.0899 | 0.5466 | 0.6075 | 0.7546 | 0.8897 |
| 2022 | 0.0722 | 0.1134 | 0.5238 | 0.6428 | 0.7455 | 0.8379 |
| 2023 | 0.0841 | 0.1065 | 0.6265 | 0.6898 | 0.8710 | 0.8976 |
| 平均值Average | 0.0917 | 0.1033 | 0.5656 | 0.6467 | 0.7904 | 0.8751 |
| 排序Rank | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
表8 不同施肥处理下稀土尾矿土壤修复效果的隶属函数值
Table 8 Subordinate function values of soil remediation effect of rare earth tailings under different fertilization treatments
| 年份Year | CK | Z | N | N+Z | Q | Q+Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 0.1188 | 0.0899 | 0.5466 | 0.6075 | 0.7546 | 0.8897 |
| 2022 | 0.0722 | 0.1134 | 0.5238 | 0.6428 | 0.7455 | 0.8379 |
| 2023 | 0.0841 | 0.1065 | 0.6265 | 0.6898 | 0.8710 | 0.8976 |
| 平均值Average | 0.0917 | 0.1033 | 0.5656 | 0.6467 | 0.7904 | 0.8751 |
| 排序Rank | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | Yu W, Feng P, Qiong W, et al. The effect of different remediation treatments on soil fungal communities in rare earth tailings soil. Forests, 2022, 13(12): 1987-1987. |
| 2 | Zheng X K, Feng X J, Chen Z, et al. Research progress on environmental problems of ionic rare earth mining and restoration of abandoned land. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(3): 681-684. |
| 郑先坤, 冯秀娟, 陈哲, 等. 离子型稀土矿开采环境问题及废弃地修复治理研究进展. 应用化工, 2019, 48(3): 681-684. | |
| 3 | Yang J, Xu X L, Liu M X, et al. Effects of Napier grass management on soil hydrologic functions in a karst landscape, Southwestern China. Soil & Tillage Research, 2016, 157: 83-92. |
| 4 | Lei X W, Qiu J Y, Li J J, et al. Effects of earthworm cast and biogas slurry treatment on planting Pennisetum hydridum and soil improvement in rare earth tailings in Gannan. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(11): 191-196. |
| 雷小文, 邱静芸, 李建军, 等. 蚯蚓粪及沼液处理对赣南稀土尾矿种植皇竹草及改良土壤的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(11): 191-196. | |
| 5 | Wang J Q, Gu D Y, Yu X D, et al. Application effects of biogas slurry partly substituting for chemical fertilizer on autumn tomato production in winter-solar greenhouse. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(1): 243-250. |
| 王靖荃, 谷端银, 于晓东, 等. 沼液部分替代化肥在日光温室秋番茄上的应用效果. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(1): 243-250. | |
| 6 | Wang F, Li W, Liu X, et al. Bacteria communities of Medicago sativa rhizosphere soil in response to composted cow manure. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(3): 603-611. |
| 王芳, 李伟, 刘鑫, 等. 紫花苜蓿根际土壤细菌群落对腐熟牛粪响应. 草地学报, 2022, 30(3): 603-611. | |
| 7 | Shang L R, Tong Z Y, Liu G Q, et al. Effects of organic fertilizer on plant species diversity and biomass of common species of Leymus chinensis steppe. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(2): 344-349. |
| 商丽荣, 仝宗永, 刘国庆, 等. 有机肥对羊草草原植物群落物种多样性和生物量的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(2): 344-349. | |
| 8 | Wu J C, Pan X Y, Yang Y H, et al. Effects of long-term application of biogas slurry on soil nutrient content and enzyme activity. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 50(7): 76-86. |
| 武继承, 潘晓莹, 杨永辉, 等. 长期施用沼液对土壤养分含量和酶活性的影响. 河南农业科学, 2021, 50(7): 76-86. | |
| 9 | Zewide I, Singh S, Wogi L, et al. Soil physico-chemical properties as affected by integrated use of blended fertilizer, cattle manure, vermicompost and mineral nitrogen and phosphorus in potato (Solanum tubersoum) in acidic soil of south-western Ethiopia. Indian Journal of Agronomy, 2021, 66(4): 474-482. |
| 10 | Zhao F, Zhang Y, Li Z, et al. Vermicompost improves microbial functions of soil with continuous tomato cropping in a greenhouse. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(1): 380-391. |
| 11 | Li G Q, Zhao P P, Shao W S, et al. Studies on the soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activities of two fenced plant communities in desert steppe grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(7): 49-59. |
| 李国旗, 赵盼盼, 邵文山, 等. 围封条件下荒漠草原两种植物群落土壤理化性状与酶活性的研究. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 49-59. | |
| 12 | Zhang D, Hou C, Ma W M, et al. Study on soil enzyme activities under shrub encroachment gradients in alpine grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| 张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 等. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. | |
| 13 | Banerjee S, Bora S, Thrall P H, et al. Soil C and N as causal factors of spatial variation in extracellular enzyme activity across grassland-woodland ecotones. Applied Soil Ecology, 2016, 105: 1-8. |
| 14 | Song D C, Wu H, Wang L D, et al. Distribution of heavy metals and their effects on enzymatic activity in soil of artificial Hippophae rhamnoides forests of different ages near abandoned mines in Shuanglonggou. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(8): 61-70. |
| 宋达成, 吴昊, 王理德, 等. 双龙沟废弃矿区不同造林年限人工沙棘林土壤重金属分布特征及其对酶活性的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 61-70. | |
| 15 | Quan G L, Xie K Y, Tong Z Y, et al. The effect of compound bio-fertilizers on soil physical and chemical properties and soil enzyme activity in Leymus chinensis steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 27-36. |
| 权国玲, 谢开云, 仝宗永, 等. 复合微生物肥料对羊草草原土壤理化性质及酶活性的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 27-36. | |
| 16 | Zhang T, Liu Y F, Sui X, et al. Land use patterns effects on soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activities in the Western Heilongjiang. Journal of Agriculture, 2021, 11(5): 33-41. |
| 张童, 刘宇飞, 隋心, 等. 土地利用方式对黑龙江西部地区土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响. 农学学报, 2021, 11(5): 33-41. | |
| 17 | He Y Z, Tian Z Y, Ma R, et al. Response of super-absorbent polymers to dry-wet cycle and effect on soil moisture in rare earth tailing area. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2023, 45(1): 210-219. |
| 贺燕子, 田芷源, 马瑞, 等. 保水剂对干湿循环的响应及对稀土尾砂土壤水分状况的影响. 江西农业大学学报, 2023, 45(1): 210-219. | |
| 18 | Shen F X, Zheng T H, Duan J, et al. Feasibility on artificial cultivation of bryophytes in rare earth tailings in Southern Jiangxi. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 20(4): 136-144. |
| 沈发兴, 郑太辉, 段剑, 等. 赣南稀土尾矿人工培育苔藓植物的可行性. 中国水土保持科学, 2022, 20(4): 136-144. | |
| 19 | Dai W J, Liu R L, Yang F, et al. Denitrifying bacteria agent together with composite materials enhanced soil chemical properties and denitrifying functions in rare earth tailings: A field study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 448: 130913-130913. |
| 20 | Zhang W R, Yang G Y, Tu X N, et al. Determination of forest soil water-physical properties, LY/T 1215-1999. |
| 张万儒, 杨光滢, 屠星南, 等. 森林土壤水分-物理性质的测定, LY/T 1215-1999. | |
| 21 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2005. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2005. | |
| 22 | Guan S Y. Soil enzymes and their research methods. Beijing: Agricultural Press, 1986. |
| 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究方法. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986. | |
| 23 | Chen M, Zhang D C, Zhu Q J, et al. Ionic rare earth mine of abandoned land of ecological restoration of research progress. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2017, 35(4): 461-468. |
| 陈敏, 张大超, 朱清江, 等. 离子型稀土矿山废弃地生态修复研究进展. 中国稀土学报, 2017, 35(4): 461-468. | |
| 24 | Luo J, Zhang Q, Luo M M, et al. Degradation characteristics of soil in different functional areas of an ion-type rare earth mine. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2022, 40(2): 329-338. |
| 罗杰, 张嵚, 罗密密, 等. 某离子型稀土矿不同功能区土壤退化特征. 中国稀土学报, 2022, 40(2): 329-338. | |
| 25 | Shan D, Guo J Y, Rong H, et al. Effect and evaluation of fertilization on soil quality in metal tailing pond in arid and semi-arid steppe regions. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(3): 208-217. |
| 珊丹, 郭建英, 荣浩, 等. 施肥对干旱半干旱草原区金属矿山尾矿库土壤质量的影响及其评价. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(3): 208-217. | |
| 26 | Huang X R, Li H, Li S, et al. Role of cationic polarization in humus-increased soil aggregate stability. European Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 67(3): 341-350. |
| 27 | Zhou C Y, Zhang Q, Zhao X M, et al. Soil quality changes of rare earth tailings before and after reclamation in South Jiangxi Province, China. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2019, 36(1): 89-95. |
| 周彩云, 张嵚, 赵小敏, 等. 赣南某原地浸析稀土尾矿复垦前后土壤质量变化. 农业资源与环境学报, 2019, 36(1): 89-95. | |
| 28 | Yang Q, Zhao L, Hou H, et al. Effect of soil ameliorants on abandoned rare mine tailing in Jiangxi province. Applied Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(2): 211-214. |
| 杨侨, 赵龙, 侯红, 等. 土壤改良剂对赣南废弃稀土尾矿的改良效应. 应用化工, 2018, 47(2): 211-214. | |
| 29 | Chen L M, Chen S S, Zhang Y, et al. Co-occurrence network of microbial communities affected by application of anaerobic fermentation residues during phytoremediation of ionic rare earth tailings area. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 856(2): 159223-159223. |
| 30 | Wang F L, Wang X X, Song N N. Biochar and vermicompost improve the soil properties and the yield and quality of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) grown in plastic shed soil continuously cropped for different years. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2021, 315: 107425. |
| 31 | Kurovsky A, Kornievskaya E, Gummer Y, et al. The balance of nitrogen forms and number of microorganisms of the nitrogen cycle in vermicomposts based on leaf litter and cow manure. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 935(1): 012002. |
| 32 | Qiu J Y, Lei X W, Lian H, et al. Response of imperatoria yield and root growth to fertilizations in rare earth tailings. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1-12[2024-04-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.q.20240108.1127.002.html. |
| 邱静芸, 雷小文, 连海, 等. 稀土尾矿王草产量和根系生长对施肥的响应.生态学杂志, 1-12[2024-04-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.q.20240108.1127.002.html. | |
| 33 | Ou X, Lei X W, Chen R Q, et al. Effects of fertilization treatments on agronomic traits, yield and quality of king grass in rare earth tailings. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(10): 3185-3193. |
| 欧翔, 雷小文, 陈荣强, 等. 施肥处理对稀土尾矿王草农艺性状、产量及品质的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(10): 3185-3193. | |
| 34 | Guo X, Gao Y, Zhang C, et al. Effects of different vegetation restoration types on soil physical and chemical properties of abandoned land in coal logistics park. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 42(2): 67-73. |
| 郭鑫, 高永, 张超, 等. 不同植被恢复类型对煤炭物流园区废弃地土壤理化性质的影响. 水土保持通报, 2022, 42(2): 67-73. | |
| 35 | Chen T, Qu N, Wang J, et al. Effects of different ecological restoration methods on the soil physicochemical properties and vegetation community characteristics of the Baotou light rare earth tailings pond in Inner Mongolia, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2024, 31(13): 19725-19737. |
| 36 | Wu J F, Wei X J, Lu Z H, et al. A study of the effects of soil conditioner and Pennisetum alopecuroides on repair on tailings soil in abandoned rare earth mining area. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2019, 41(6): 1222-1226. |
| 吴建富, 魏雪娇, 卢志红, 等. 土壤调理剂与狼尾草联合修复废弃稀土矿区尾砂土壤研究. 江西农业大学学报, 2019, 41(6): 1222-1226. | |
| 37 | Zhu W T. Study on the stability and hydraulie charaeteristies of ionie rare earth tailings aggregates under the action of vegetation roots. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2022. |
| 朱文韬. 植被根系作用下离子型稀土尾矿团聚体稳定性及水力特性研究. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2022. | |
| 38 | Wang Z H, Shen D K, Shen F, et al. Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies on biosorption of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution by earthworm manure derived biochar. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 120: 104-114. |
| 39 | Wang X, Li J C, Yue J Y, et al. Comparison of soil fertility among open-pit mine reclaimed lands in Antaibao regenerated with different vegetation types. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(9): 3601-3606. |
| 王翔, 李晋川, 岳建英, 等. 安太堡露天矿复垦地不同人工植被恢复下的土壤酶活性和肥力比较. 环境科学, 2013, 34(9): 3601-3606. | |
| 40 | Zhang Y, Wu S X, Lei Q L, et al. Effects of different manures on soil enzyme activity and microbial community. Soils, 2022, 54(6): 1175-1184. |
| 张英, 武淑霞, 雷秋良, 等. 不同类型粪肥还田对土壤酶活性及微生物群落的影响.土壤, 2022, 54(6): 1175-1184. | |
| 41 | Qi L, Li Y L, Zhao W, et al. Effect of Avena sativa L.on soil enzyme activity and microbe functional diversity under strontium pollution. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(13): 4888-4896. |
| 亓琳, 李艳玲, 赵威, 等. 锶污染下燕麦对土壤酶活性和微生物群落功能多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(13): 4888-4896. | |
| 42 | Chen X J, Shen P F, Chen B Y, et al. Effects of different vermicompost additions on microorganisms and enzyme activities in red soil. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(11): 443-445. |
| 陈小锦, 沈鹏飞, 陈博阳, 等. 不同蚓粪添加量对红壤微生物及酶活性的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(11): 443-445. | |
| 43 | Kumar R P, Denish B, Kumar K M, et al. Juxtaposing the quality of compost and vermicompost produced from organic waste amended with cow dung. Environmental Research, 2022, 214(4): 114119-114119. |
| 44 | Hoang T D, Razavi S B, Kuzyakov Y, et al. Earthworm burrows: kinetics and spatial distribution of enzymes of C-, N- and P- cycles. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2016, 99: 94-103. |
| 45 | Subhani A, Liao M, Huang C Y, et al. Effects of some management practices on electron transport system (ETS) activity in paddy soil. Pedosphere, 2000, 10(3): 257-264. |
| 46 | Zhou D X, Li X, Ning Y C, et al. Effect of chemical fertilizer combined with vermicompost on soil characters and enzyme activity in paddy fields. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2021, 52(2): 25-35. |
| 周东兴, 李欣, 宁玉翠, 等. 蚯蚓粪配施化肥对稻田土壤性状和酶活的影响. 东北农业大学学报, 2021, 52(2): 25-35. | |
| 47 | Pathan S I, Ceccherini M T, Pietramellara G, et al. Enzyme activity and microbial community structure in the rhizosphere of two maize lines differing in N use efficiency. Plant and Soil, 2015, 387(1/2): 413-424. |
| [1] | 姚佳妮, 刘爽, 张钧杰, 胡明珠, 代金霞. 宁夏荒漠草原典型灌丛根际土壤酶活性及微生物代谢多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 1-14. |
| [2] | 马远飞, 宋彦涛, 乌云娜, 方乘风. 施肥和刈割5年对呼伦贝尔草甸草原土壤微生物特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 242-251. |
| [3] | 杜文盼, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 杨莉, 张建贵, 史怡超, 张官禄. 根系分隔方式对燕麦/豌豆间作地上生物量、土壤养分及根系性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 25-36. |
| [4] | 李思媛, 孙宗玖, 于冰洁, 周晨烨, 周磊, 郑丽, 刘慧霞, 冶华薇. 封育对伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地土壤碳氮磷、酶活性及其化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 25-40. |
| [5] | 秦瑞敏, 程思佳, 马丽, 张中华, 魏晶晶, 苏洪烨, 史正晨, 常涛, 胡雪, 阿的哈则, 袁访, 李珊, 周华坤. 围封和施肥对高寒草甸群落特征和植被碳氮库的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 1-11. |
| [6] | 黄琳曦, 陈倩, 张先言, 闫顺, 杨云, 辛培尧, 汪琼. 两种乔木凋落叶浸提液处理对地毯草土壤酶活性及其化学计量比的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 35-46. |
| [7] | 鲍平安, 季波, 孙果, 张娜, 吴旭东, 何建龙, 王占军, 田英. 光伏电站建设对植物群落与土壤特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 23-33. |
| [8] | 刘芳, 王佩佩, 曹玉莹, 刘俊娥, 周正朝. 黄土高原典型草本植物根系分布特征及其对土壤理化性质的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 1-13. |
| [9] | 石正海, 刘文辉, 张永超, 秦燕, 米文博, 罗峰, 刘曼, 起惠芳. 季节性氮磷配施提升环湖寒生羊茅生产性能[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 149-158. |
| [10] | 韩其飞, 尹龙, 李超凡, 张润钢, 王文彪, 崔正南. 天山北坡典型草地施肥阈值及不确定性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 19-32. |
| [11] | 张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| [12] | 马嵩科, 霍克, 张冬霞, 张静, 张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 王贺正. 玉米秸秆还田配施氮肥对豫西旱地小麦土壤酶活性和氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 120-133. |
| [13] | 王志婷, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 李东方, 刘小勇. 半干旱草甸草地不同处理下植被特征与土壤酶活性的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 41-55. |
| [14] | 韦文敬, 石兆勇, 张梦歌, 杨爽, 杨文雅. 基于数据库的菌根与施肥对草地植物叶片性状影响的分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 104-114. |
| [15] | 周娟娟, 魏巍. 施肥和刈割协同对藏北高原禾草混播群落动态和超产的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 28-39. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||