

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 54-67.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025102
李瑒琨1,2( ), 本转林1,2, 张筠钰1,2, 杨惠敏1,2(
), 本转林1,2, 张筠钰1,2, 杨惠敏1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-25
修回日期:2025-05-22
出版日期:2026-02-20
发布日期:2025-12-24
通讯作者:
杨惠敏
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: huimyang@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Yang-kun LI1,2( ), Zhuan-lin BEN1,2, Jun-yu ZHANG1,2, Hui-min YANG1,2(
), Zhuan-lin BEN1,2, Jun-yu ZHANG1,2, Hui-min YANG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-03-25
Revised:2025-05-22
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2025-12-24
Contact:
Hui-min YANG
摘要:
足量优质饲草供应是草地畜牧业高质量可持续发展的基础条件,这就要求不断扩大紫花苜蓿等优质饲草种植面积。因此,亟须扩大苜蓿种子生产以满足苜蓿种植的需求,但不同气候土壤条件下施肥对苜蓿种子产量的影响仍没有一致结论。本研究以中国为研究区域,采用整合分析(meta-analysis)方法,研究了不同肥料类型对苜蓿种子产量的影响,并探讨气候和土壤条件对施肥效应的影响。结果表明:1)施肥能显著提高苜蓿种子产量,其中微量元素肥单施增产效果最好,钾肥单施和氮钾肥配施会导致产量降低。2)随年均降水量增加,肥料单施的增产效果减弱而多肥料配施的增产效果增强。较高年均温度导致除微量元素肥单施外其他施肥类型的增产效果均减弱。3)土壤因子对施肥效果的影响因施肥类型而异。较高土壤有机质和全氮含量导致大部分施肥类型的增产效果增强而微量元素肥单施的增产效果减弱。较高土壤碱解氮和速效磷含量降低了氮、钾单施的增产效果而增强了磷单施的增产效果,对多肥料配施的增产效果影响不一致。较高土壤速效钾含量增强各施肥类型的增产效果。本研究可为中国不同气候和土壤下苜蓿种子生产的施肥管理措施优化提供借鉴。
李瑒琨, 本转林, 张筠钰, 杨惠敏. 不同气候和土壤条件下施肥类型影响紫花苜蓿种子产量的整合分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 54-67.
Yang-kun LI, Zhuan-lin BEN, Jun-yu ZHANG, Hui-min YANG. A meta-analysis on the effect of fertilizer type on alfalfa seed yield under various climate and soil conditions[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(2): 54-67.
研究地点 Research site# | 年均降水 Annual average precipitation (mm) | 年均温度 Mean annual temperature (℃) | 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (g·kg-1) | 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 土壤碱解氮 Soil alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 土壤速效磷 Soil available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 土壤速效钾 Soil available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘肃Gansu (14) | 48.4~600.0 | 7.3~8.9 | 1.58~11.30 | 0.24~0.94 | 22.23~59.45 | 6.03~30.70 | 109.00~231.00 |
| 新疆Xinjiang (10) | 150.0~228.0 | 7.5~7.6 | 12.48~19.36 | 1.55~1.56 | 14.20~25.69 | 12.00~37.00 | 230.30~338.80 |
| 宁夏Ningxia (4) | 250.0~430.0 | 7.4~7.7 | 0.51~26.36 | 0.43~2.03 | 19.80~114.60 | 4.44~13.97 | 9.87~209.00 |
| 青海Qinghai (1) | 391.0 | 0.1 | 4.80 | 0.06 | - | 6.00 | 129.50 |
| 内蒙古Inner Mongolia (5) | 225.0~400.0 | 1.6~7.2 | 12.02~13.00 | 0.72 | 1.48~72.70 | 2.05~40.45 | 75.81~98.33 |
| 黑龙江Heilongjiang (6) | 427.4~450.0 | 3.0~4.2 | 2.10~30.70 | - | 89.25 | 2.40~16.12 | 137.35~150.00 |
| 吉林Jilin (2) | 426.8 | - | 2.16 | - | - | - | - |
| 北京Beijing (1) | 628.9 | 12.5 | 1.64 | 0.09 | 72.20 | 23.00 | 101.00 |
| 西藏Tibet (1) | 400.0 | 8.2 | 19.60 | 1.31 | 81.00 | 5.31 | 22.00 |
表1 文献中涉及的研究地点概况
Table 1 Overview of research sites described in the literature
研究地点 Research site# | 年均降水 Annual average precipitation (mm) | 年均温度 Mean annual temperature (℃) | 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (g·kg-1) | 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 土壤碱解氮 Soil alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 土壤速效磷 Soil available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 土壤速效钾 Soil available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘肃Gansu (14) | 48.4~600.0 | 7.3~8.9 | 1.58~11.30 | 0.24~0.94 | 22.23~59.45 | 6.03~30.70 | 109.00~231.00 |
| 新疆Xinjiang (10) | 150.0~228.0 | 7.5~7.6 | 12.48~19.36 | 1.55~1.56 | 14.20~25.69 | 12.00~37.00 | 230.30~338.80 |
| 宁夏Ningxia (4) | 250.0~430.0 | 7.4~7.7 | 0.51~26.36 | 0.43~2.03 | 19.80~114.60 | 4.44~13.97 | 9.87~209.00 |
| 青海Qinghai (1) | 391.0 | 0.1 | 4.80 | 0.06 | - | 6.00 | 129.50 |
| 内蒙古Inner Mongolia (5) | 225.0~400.0 | 1.6~7.2 | 12.02~13.00 | 0.72 | 1.48~72.70 | 2.05~40.45 | 75.81~98.33 |
| 黑龙江Heilongjiang (6) | 427.4~450.0 | 3.0~4.2 | 2.10~30.70 | - | 89.25 | 2.40~16.12 | 137.35~150.00 |
| 吉林Jilin (2) | 426.8 | - | 2.16 | - | - | - | - |
| 北京Beijing (1) | 628.9 | 12.5 | 1.64 | 0.09 | 72.20 | 23.00 | 101.00 |
| 西藏Tibet (1) | 400.0 | 8.2 | 19.60 | 1.31 | 81.00 | 5.31 | 22.00 |
平均效应值 Mean effect size | 95%置信区间95%CI | 效应量检验Effect size test | 异质性检验Heterogeneity test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上限Upper limit | 下限Lower limit | Z | P | Q | P | |
| 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 9.52 | <0.01 | 7249.13 | <0.01 |
表2 施肥对苜蓿种子产量的综合效应量
Table 2 Effect sizes of fertilization on alfalfa seed yield
平均效应值 Mean effect size | 95%置信区间95%CI | 效应量检验Effect size test | 异质性检验Heterogeneity test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上限Upper limit | 下限Lower limit | Z | P | Q | P | |
| 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 9.52 | <0.01 | 7249.13 | <0.01 |
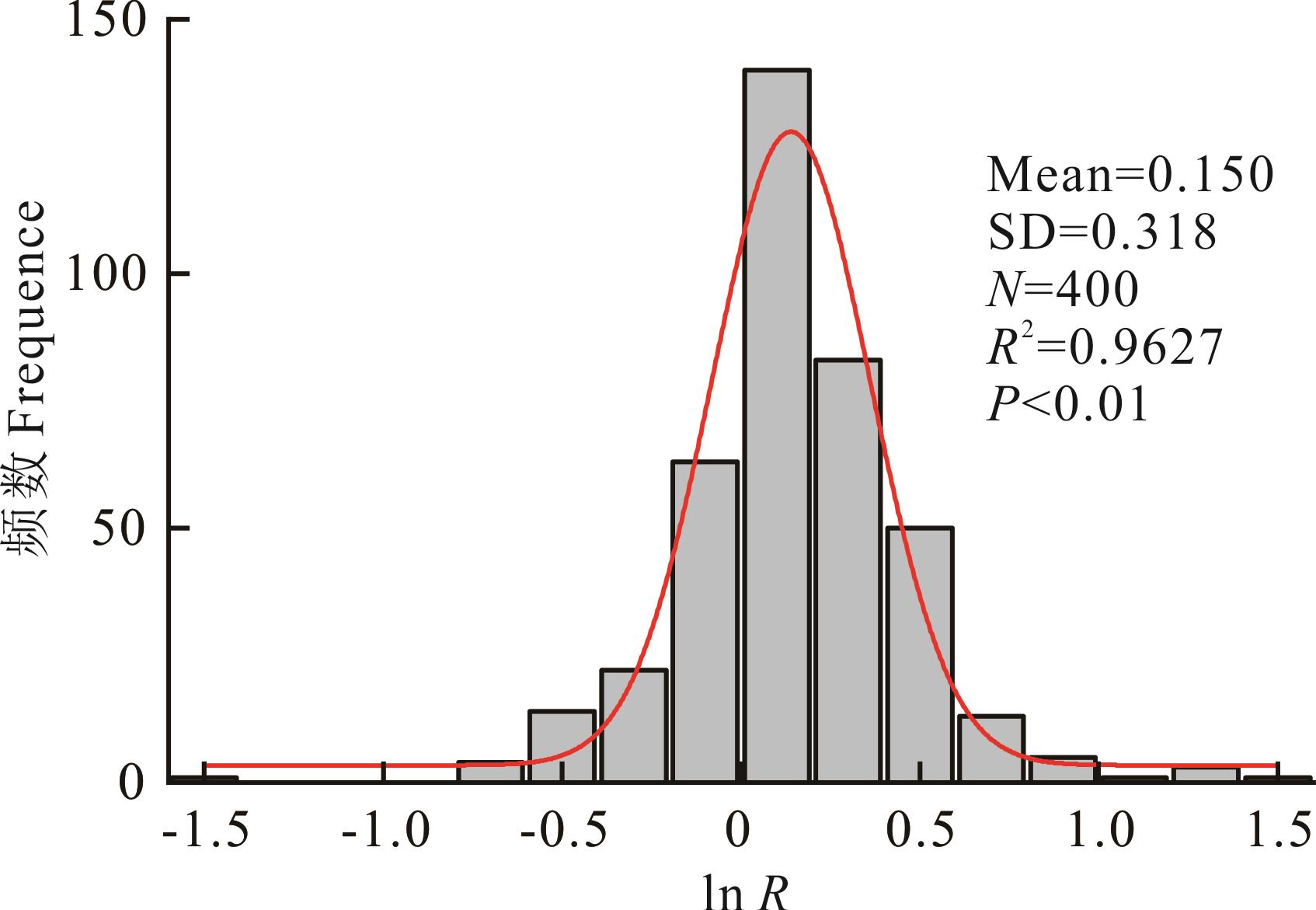
图1 苜蓿种子产量效应值的频率分布Mean、SD、N、R2、P分别代表数据平均值、标准差、组数、高斯拟合曲线的回归系数和K-S(Kolmogorov-Smirnov)检验的P值。Mean, the average value; SD, standard deviation; N, number of groups; R2, R-Squared of a Gaussian distribution function; P, P-value of Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
Fig.1 Frequency distribution of effect size of alfalfa seed yield
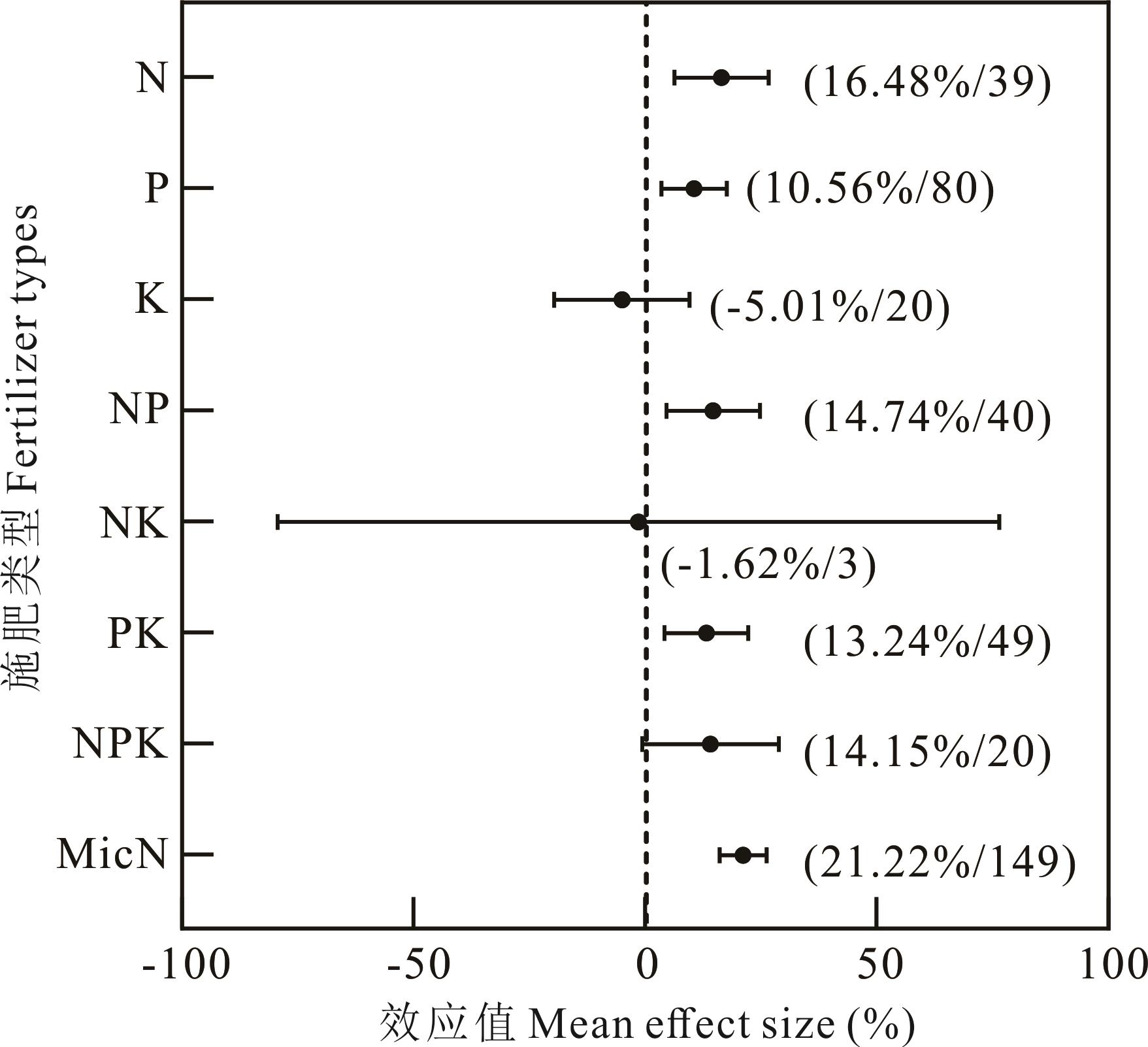
图2 不同施肥类型对苜蓿种子产量的影响N:氮、P:磷、K:钾、MicN:微量元素肥单独施用;NP:氮磷、PK:磷钾、NK:氮钾、NPK:氮磷钾肥料配合施用;括号中左侧的百分数代表效应值;右侧的数字代表该施肥类型的文献中所取得的样本量。下同。N: nitrogen, P: phosphorus, K: potassium, MicN: micronutrient fertilizer alone; NP: nitrogen-phosphorus, PK: phosphorus-potassium, NK: nitrogen-potassium, NPK: nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizers applied in combination; Percentages on the left in parentheses represent the ln R; The numbers on the right represent the sample sizes obtained in the literature for that type of fertilizer application. The same below.
Fig.2 Effect of different types of fertilization on alfalfa seed yield
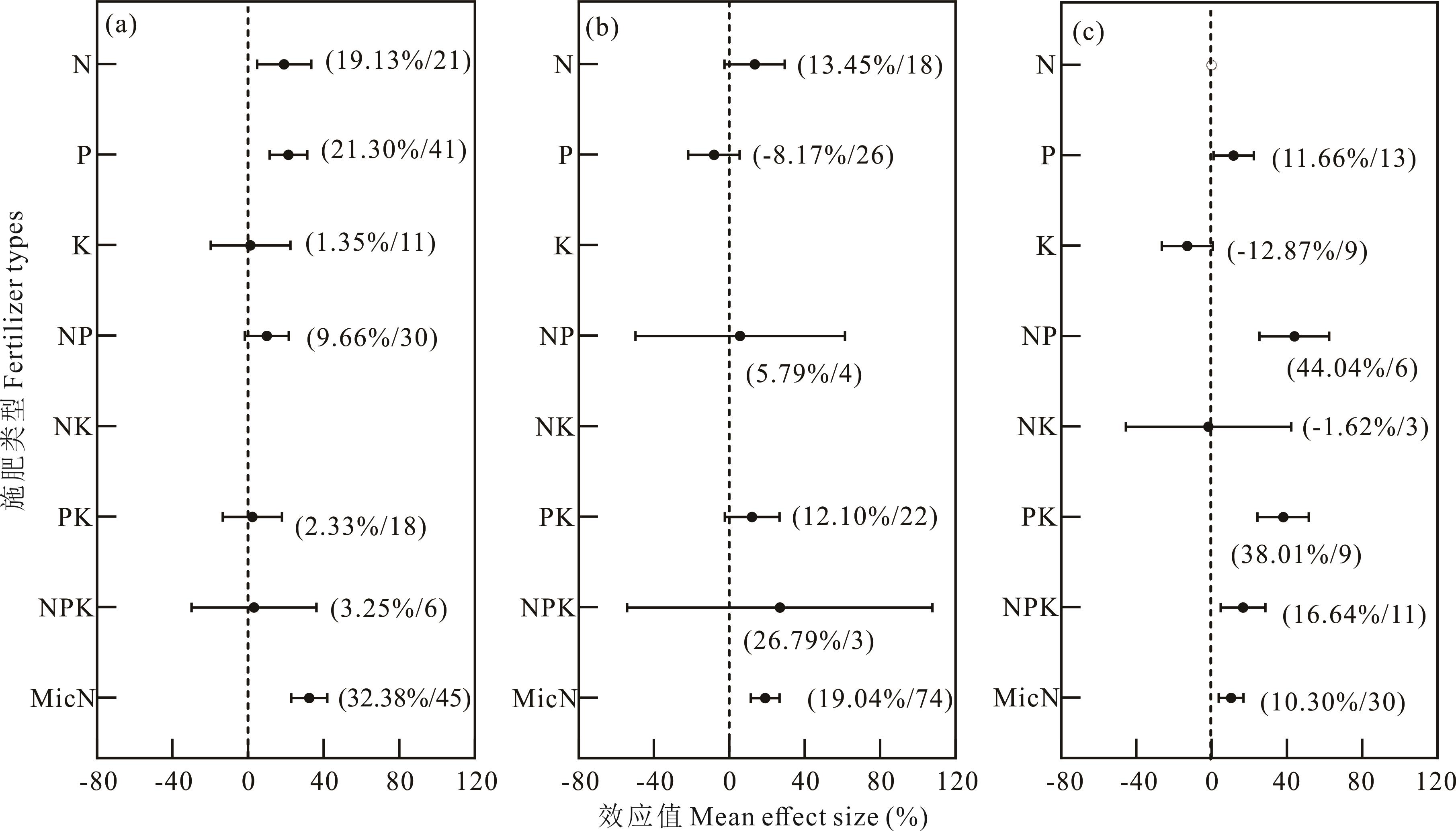
图3 不同年均降水量下施肥对苜蓿种子产量的影响a、b、c:年平均降水量≤200 mm、200~400 mm和>400 mm。a, b, c: mean annual precipitation ≤200 mm, 200-400 mm and >400 mm.
Fig.3 Effect of fertilization on alfalfa seed yield under different annual average precipitations
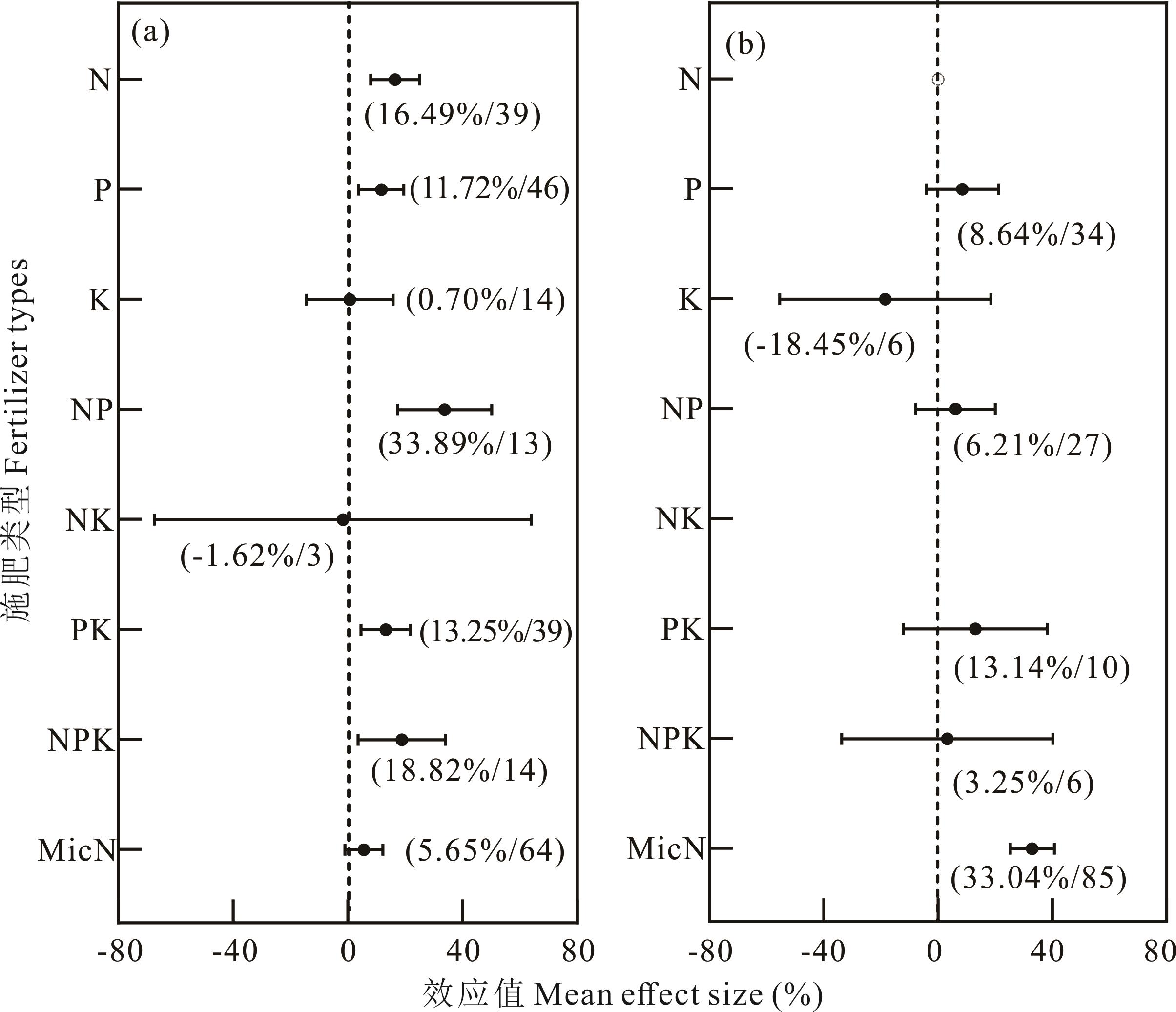
图4 施肥条件下不同年平均温度对苜蓿种子产量的影响a和b:年均温度≤7.5 ℃和>7.5 ℃。a and b: mean annual temperatures ≤7.5 ℃ and >7.5 ℃.
Fig.4 Effect of different mean annual temperatures under fertilization conditions on seed yield of alfalfa
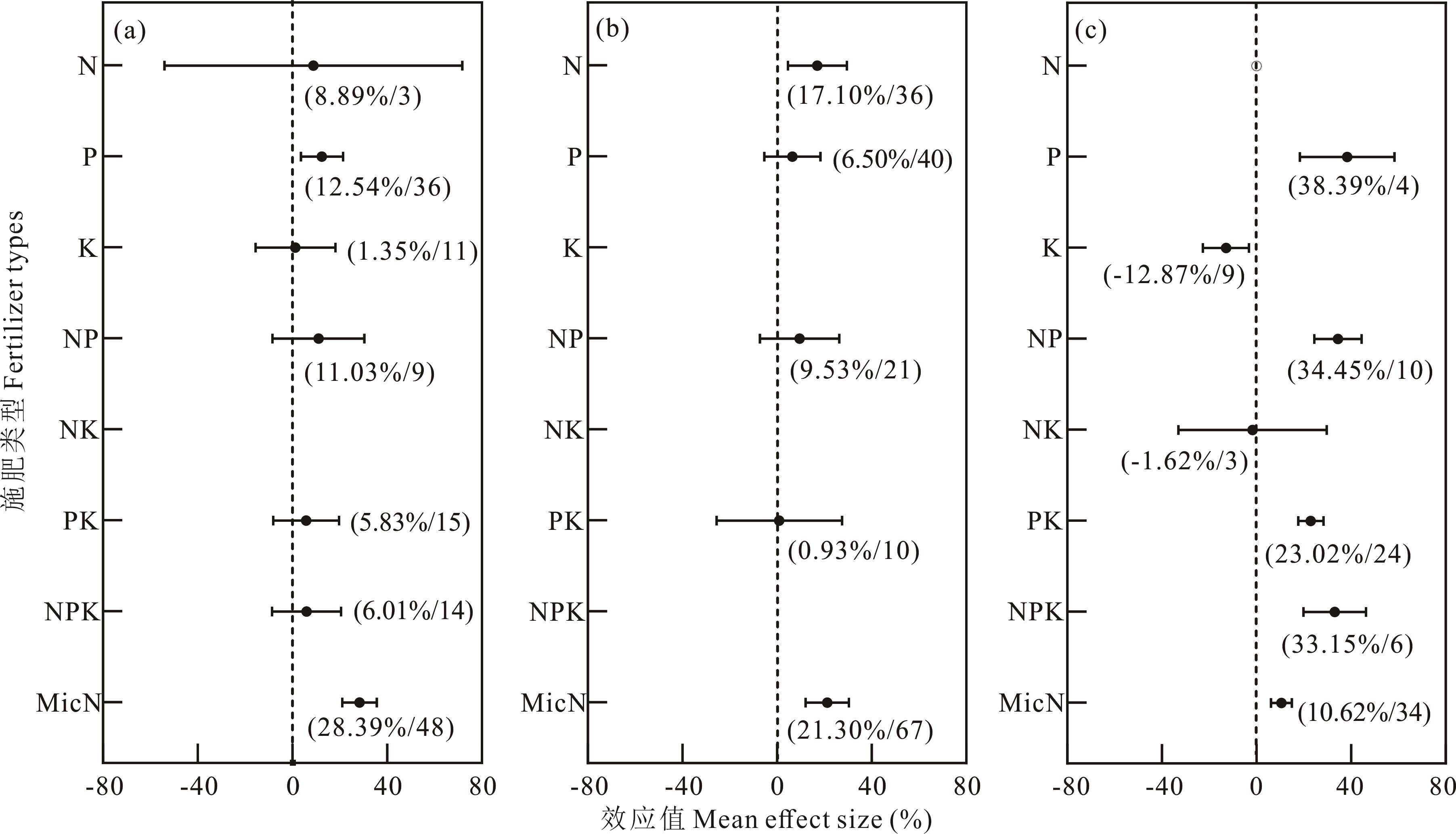
图5 施肥条件下不同土壤有机质含量对苜蓿种子产量的影响a、b、c:土壤有机质含量≤10 g·kg-1、10~20 g·kg-1和>20 g·kg-1。a, b, c: soil organic matter content ≤10 g·kg-1, 10-20 g·kg-1 and >20 g·kg-1.
Fig.5 Effect of different soil organic matter contents on seed yield of alfalfa under fertilization conditions
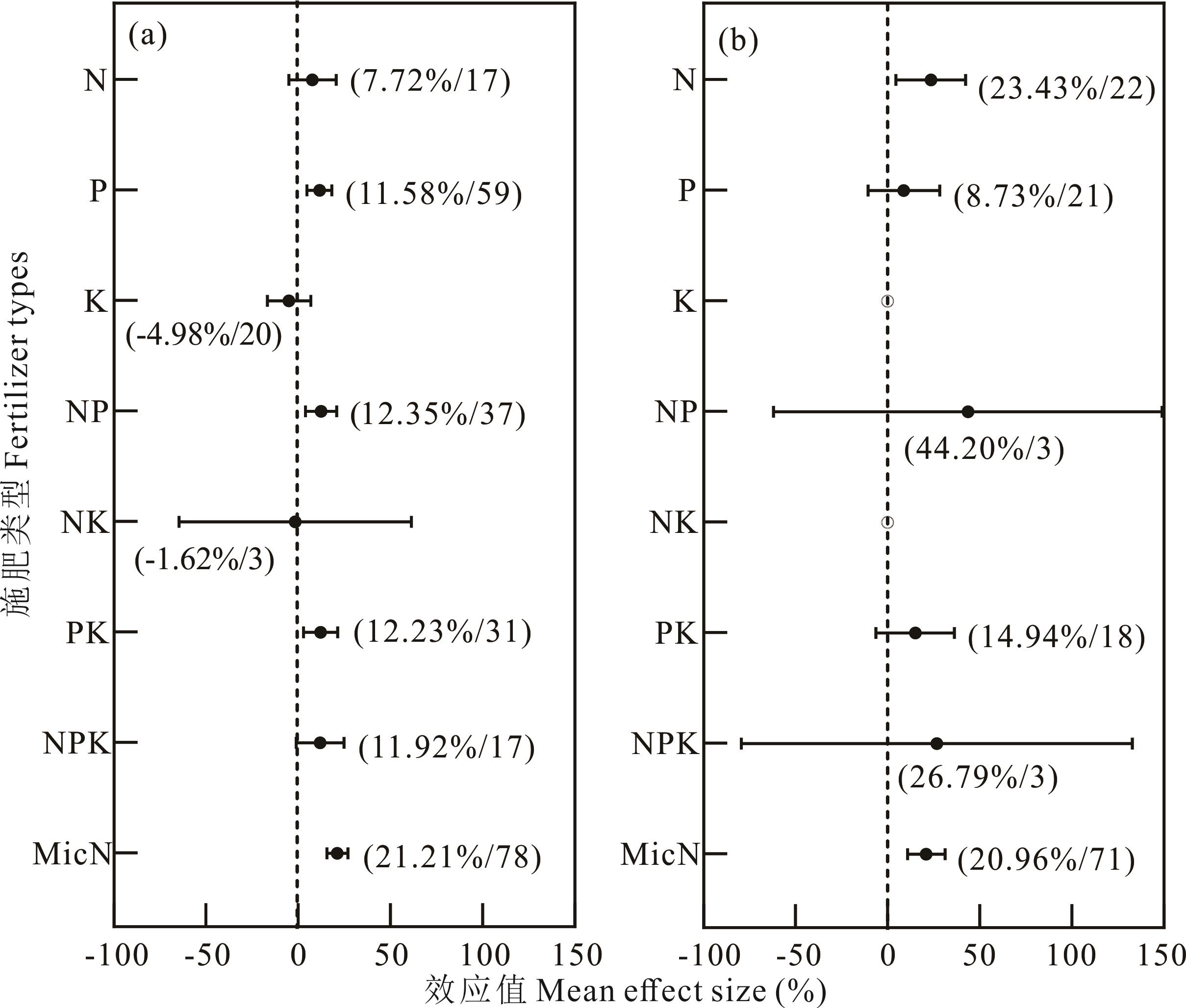
图6 施肥条件下不同土壤全氮含量对苜蓿种子产量的影响a、b:土壤全氮含量≤1 g·kg-1和>1 g·kg-1。a, b: soil total nitrogen content ≤1 g·kg-1 and >1 g·kg-1.
Fig.6 Effects of different soil total nitrogen contents on seed yield of alfalfa under fertilization conditions

图7 施肥条件下不同土壤速效养分含量对苜蓿种子产量的影响a、b:土壤碱解氮含量≤50 mg·kg-1和>50 mg·kg-1;c、d:土壤速效磷含量≤10 mg·kg-1和>10 mg·kg-1;e、f:土壤速效钾含量≤150 mg·kg-1和>150 mg·kg-1。a, b: soil alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content ≤50 mg·kg-1 and >50 mg·kg-1; c, d: soil available phosphorus content ≤10 mg·kg-1 and >10 mg·kg-1; e, f: soil available potassium content ≤150 mg·kg-1 and >150 mg·kg-1.
Fig.7 Effects of different soil quick nutrient contents on seed yield of alfalfa under fertilization conditions
| [1] | Chmelíková L, Wolfrum S, Schmid H, et al. Seasonal development of biomass yield in grass-legume mixtures on different soils and development of above- and belowground organs of Medicago sativa. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2015, 61(3): 329-346. |
| [2] | Hadidi M, Ibarz A, Pagan J. Optimisation and kinetic study of the ultrasonic-assisted extraction of total saponins from alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and its bioaccessibility using the response surface methodology. Food Chemistry, 2020, 309: 125786. |
| [3] | Zhou Y Z. Study on the extraction of spatial planting structure of alfalfa based on Sentinel-2 data. South Agricultural Machinery, 2024, 55(18): 62-65. |
| 周杨振. 基于Sentinel-2数据的苜蓿空间种植结构提取研究. 南方农机, 2024, 55(18): 62-65. | |
| [4] | Li C J, Guo Q, Wang Z X. Study on the demand of alfalfa grass import in China. China Feed, 2025(3): 145-150. |
| 李翠锦, 郭琦, 王姿璇. 我国苜蓿草进口需求研究. 中国饲料, 2025(3): 145-150. | |
| [5] | Wang X M, Zhang H, Song R, et al. Comparison of forage seed production between China and U.S.A. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(10): 2115-2125. |
| 王雪萌, 张涵, 宋瑞, 等. 中美牧草种子生产比较. 草地学报, 2021, 29(10): 2115-2125. | |
| [6] | Wang X L, Zhu L, Jiang P, et al. Analysis on the plant quarantine approval of forage seeds imported from abroad from 2009 to 2021 in China. Plant Quarantine, 2023, 37(6): 62-68. |
| 王晓亮, 朱莉, 姜培, 等. 2009-2021年从国外引进牧草种子检疫审批情况分析. 植物检疫, 2023, 37(6): 62-68. | |
| [7] | Mao X T. Effects of continuous fertilization on yield and quality of alfalfa and soil mineral nutrients under non-irrigated conditions. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 毛小涛. 连续施肥对旱作苜蓿产量品质及土壤养分的影响. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2017. | |
| [8] | Shan X H, Zhang Y L, Wang X G, et al. Effect of phosphorus fertilizer application rate on biomass accumulation and phosphorus absorption of alfalfa in planting year. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2024, 46(8): 63-71. |
| 单新河, 张运龙, 王显国, 等. 磷肥施用量对紫花苜蓿建植当年生物量累积和磷素吸收规律的影响. 中国草地学报, 2024, 46(8): 63-71. | |
| [9] | Tian X H, Du W H. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on seed yield and yield components of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2008(4): 16-20. |
| 田新会, 杜文华. 氮、磷、钾肥对紫花苜蓿种子产量及产量构成因素的影响. 中国草地学报, 2008(4): 16-20. | |
| [10] | Ju X F, Liu X P, Li G L, et al. Effect of different phosphorus and potassium fertilizer ratios on alfalfa seed yield. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2012(5): 85-87. |
| 鞠晓峰, 刘香萍, 李国良, 等. 不同磷、钾肥配比对紫花苜蓿种子产量的影响. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2012(5): 85-87. | |
| [11] | Ma X, Wang L L, Li W J, et al. Effects of different nitrogen levels on nitrogen fixation and seed production of alfalfa inoculated with rhizobia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(1): 95-102. |
| 马霞, 王丽丽, 李卫军, 等. 不同施氮水平下接种根瘤菌对苜蓿固氮效能及种子生产的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(1): 95-102. | |
| [12] | Luo Y Q, Hui D F, Zhang D Q. Elevated CO2 stimulates net accumulations of carbon and nitrogen in land ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Ecology, 2006, 87(1): 53-63. |
| [13] | Hedges L V, Gurevitch J, Curtis P S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology, 1999, 80(4): 1150-1156. |
| [14] | Geisseler D, Scow K M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms-A review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 75: 54-63. |
| [15] | Wang L L, Li Q, Coulter J A, et al. Winter wheat yield and water use efficiency response to organic fertilization in Northern China: A meta-analysis. Agricultural Water Management, 2020, 229: 105934. |
| [16] | Card N A. Applied meta-analysis for social science research. New York: Guilford Press, 2011. |
| [17] | Malhi S S, Goerzen D W. Improving yield in alfalfa seed stands with balanced fertilization. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2010, 33: 2157-2166. |
| [18] | Du W H. Regulations on vegetative and reproductive growth of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2005. |
| 杜文华. 紫花苜蓿营养生长与生殖生长的调控. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2005. | |
| [19] | Wan W F, Li Y J, Li H G. Yield and quality of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) in response to fertilizer application in China: A meta-analysis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 1051725. |
| [20] | Zhang W H, Zhou Y C, Dibley K E, et al. Nutrient loading of developing seeds. Functional Plant Biology, 2007, 34(4): 314-331. |
| [21] | Clarence M R, Marble V, Brown D, et al. Seed production practices. Agronomy Monographs Alfalfa and Alfalfa Improvement, 1988: 985-1021. |
| [22] | Craiu D, Florea A, Gaidanov I, et al. Experimental results with lucerne seed crops in the Danube plain. Probleme de Agrofitotehnie Teoretică şi Aplicată, 1983, 5(2): 171-183. |
| [23] | Vasileva V, Kostov O. Effect of mineral and organic fertilization of alfalfa on some seed yield characteristics, root biomass accumulation and soil humus content. Acta Agriculturae Serbica, 2015, 20(39): 51-65. |
| [24] | Jiao W T, Chen W P, Chang A C, et al. Environmental risks of trace elements associated with long-term phosphate fertilizers applications: a review. Environmental Pollution, 2012, 168: 44-53. |
| [25] | Du W H, Tian X H, Cao Z Z, et al. Effects of micronutrients on seed yield and yield components of alfalfa. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2009, 32(5): 809-820. |
| [26] | Chen T. Effect of irrigation and boron fertilization on seed yield and quality of new strains of alfalfa and sainfoin in Hexi region. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2023. |
| 陈涛. 灌溉与硼肥对河西地区紫花苜蓿和红豆草新品系种子产量及质量的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2023. | |
| [27] | Dordas C. Foliar boron application improves seed set, seed yield, and seed quality of alfalfa. Agronomy Journal, 2006, 98(4): 907-913. |
| [28] | Yang J, Sui X Q, Wang X Y, et al. Effect of combined application of nitrogen fertiliser and compound nitrophenol sodium on the physiological characteristics and seed yield of alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(5): 1471-1478. |
| 杨静, 隋晓青, 王鑫尧, 等. 氮肥与复硝酚钠复配施用对紫花苜蓿生理特性及种子产量的影响. 草地学报, 2024, 32(5): 1471-1478. | |
| [29] | Chen L L, Ren W, Mao P S, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on seed yield and nitrogen accumulation in alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(6): 98-104. |
| 陈玲玲, 任伟, 毛培胜, 等. 氮素对紫花苜蓿种子产量与氮累积动态变化的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 98-104. | |
| [30] | Zhu J Q, Lu H Z, Ma J, et al. Effects of N, P and K fertilizers on yield of alfalfa seed in Jiuquan City. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020(5): 8-14. |
| 朱建强, 路宏中, 马静, 等. 氮磷钾配施对酒泉市紫花苜蓿种子产量的影响. 甘肃农业科技, 2020(5): 8-14. | |
| [31] | Moir J, Jordan P, Moot D, et al. Phosphorus response and optimum pH ranges of twelve pasture legumes grown in an acid upland New Zealand soil under glasshouse conditions. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2016, 16(2): 438-460. |
| [32] | Xing L M. Effects of different phosphorus supply levels on the growth and functional diversity of rhizosphere microorganisms in alfalfa. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022. |
| 邢鏻木. 不同供磷水平对苜蓿生长及根际微生物功能多样性的影响. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2022. | |
| [33] | Sterner R W, Elser J J. Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2003. |
| [34] | Lu J X, Sun Y. Research progress on the effect of fertilization on seed yield of alfalfa. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2013(5): 133-137. |
| 陆继肖, 孙彦. 施肥对苜蓿种子产量影响的研究进展. 黑龙江农业科学, 2013(5): 133-137. | |
| [35] | Wang X G. Effects of density manipulation, cutting, fertilizer and growth regulator application on the characteristics related to alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield and quality. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2005. |
| 王显国. 密度调控、施肥、刈割等措施对紫花苜蓿种子产量和质量的影响. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2005. | |
| [36] | Johnson R, Vishwakarma K, Hossen M S, et al. Potassium in plants: growth regulation, signaling, and environmental stress tolerance. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2022, 172: 56-69. |
| [37] | Yang X Y, Xia T Y, Wu T. Potassium nutrient stress in plants: A review. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(18): 101-106. |
| 杨晓燕, 夏体渊, 吴甜. 植物钾营养胁迫研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(18): 101-106. | |
| [38] | Yang Z W, Shen Y Y, Xie T L, et al. Biological nitrogen fixation efficiency in soybean under different levels of nitrogen supply. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2009, 29(3): 574-579. |
| 杨子文, 沈禹颖, 谢田玲, 等. 外源供氮水平对大豆生物固氮效率的影响. 西北植物学报, 2009, 29(3): 574-579. | |
| [39] | Liu M G, Xu R, Yang H M. Response of alfalfa to soil moisture and effect of the irrigation. Journal of Southwest Minzu University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 45(1): 16-22. |
| 刘敏国, 许瑞, 杨惠敏. 紫花苜蓿的水分响应及灌溉效应. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 45(1): 16-22. | |
| [40] | Ren H Y, Xu Z W, Isbell F, et al. Exacerbated nitrogen limitation ends transient stimulation of grassland productivity by increased precipitation. Ecological Monographs, 2017, 87(3): 457-469. |
| [41] | Wen L. Effects of water deficit and nitrogen application on spring wheat growth and water and nitrogen use in Hexi region. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2019. |
| 闻磊. 水分亏缺和施氮对河西地区春小麦生长和水氮利用的影响. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. | |
| [42] | Athar M, Johnson D A. Nodulation, biomass production, and nitrogen fixation in alfalfa under drought. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 1996, 19(1): 185-199. |
| [43] | Elias E, Marklein A, Abatzoglou J T, et al. Vulnerability of field crops to midcentury temperature changes and yield effects in the Southwestern USA. Climatic Change, 2018, 148: 403-417. |
| [44] | Du W H, Tian X H, Cao Z Z. Influence of phosphorus,potassium and micro-nutrients on seed yield of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Grassland and Turf, 2006(6): 15-18. |
| 杜文华, 田新会, 曹致中. 施磷、钾肥及微肥对紫花苜蓿种子产量影响的研究进展. 草原与草坪, 2006(6): 15-18. | |
| [45] | Gossen B D, Ukrainetz H, Soroka J J. Effect of fertilizer on seed yield of alfalfa under irrigation in Saskatchewan. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 2004, 84(4): 1105-1108. |
| [46] | Witzgall K, Vidal A, Schubert D I, et al. Particulate organic matter as a functional soil component for persistent soil organic carbon. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 4115. |
| [47] | Ali S, Liu K, Ahmed W, et al. Nitrogen mineralization, soil microbial biomass and extracellular enzyme activities regulated by long-term N fertilizer inputs: A comparison study from upland and paddy soils in a red soil region of China. Agronomy, 2021, 11(10): 2057. |
| [48] | Tong Y S, Zhang C P, Yu Y, et al. Response of microbiological properties to short-term nitrogen addition in perennial alpine cultivated grassland. Environmental Science, 2024, 45(12): 7316-7325. |
| 童永尚, 张春平, 俞旸, 等. 多年生高寒栽培草地土壤微生物学特性对短期氮添加的响应. 环境科学, 2024, 45(12): 7316-7325. | |
| [49] | Liu Y L, Li Y, Zhang Y R, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on phosphatase activities in paddy and dryland of yellow soil. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2022, 53(4): 948-955. |
| 刘彦伶, 李渝, 张雅蓉, 等. 长期施肥对黄壤稻田和旱地土壤磷酸酶活性的影响. 土壤通报, 2022, 53(4): 948-955. |
| [1] | 陈丽娟, 高荣, 王建喜, 马晖玲. 紫花苜蓿与红豆草在不同生长时期缩合单宁合成差异的比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 221-236. |
| [2] | 张继元, 安海全, 潘靖一, 刘畅, 龙思思, 赵丽丽. 7个紫花苜蓿品种种子萌发及幼苗生长的抗旱性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 68-82. |
| [3] | 张颖, 贺善睦, 何傲蕾, 李昌宁, 姚拓. 微生物菌剂与有机钙蛋白配施对紫花苜蓿生长和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 25-39. |
| [4] | 俞鸿千, 马雪鹏, 曾翰国, 单晓艳, 李曼莉, 王占军. 地下滴灌时期和水量对紫花苜蓿种子生产的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 53-64. |
| [5] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [6] | 鲜燃, 邓雨, 付秋月, 蒋晶霞, 陶佳丽, 许涛, 朱慧森, 岑慧芳. 紫花苜蓿MsMYB86基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 162-172. |
| [7] | 刘沂欣, 隋晓青, 王鑫尧, 郎梦卿, 孙凌子寅, 吉尔尔格. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿的缓解作用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 206-214. |
| [8] | 张译尹, 王斌, 王腾飞, 兰剑, 胡海英. 苜蓿种子田间作小黑麦对饲草产量、水分利用及苜蓿种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 43-53. |
| [9] | 樊文娟, 宋建超, 张小娟, 盛宇航, 史金涛, 张龙骥, 鱼小军. 氮磷配施对甘肃省武威灌区扁蓿豆种子产量和质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 54-65. |
| [10] | 李文秀, 姚拓, 李昌宁, 贾倩民, 何傲蕾, 周杨. “凹凸棒-有机基质”菌肥载体最佳配比的筛选及对紫花苜蓿的促生效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 88-98. |
| [11] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [12] | 温小月, 赵颖, 王宝强, 王贤, 朱晓林, 王义真, 魏小红. 外源NO调控干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿AP2/ERFs基因的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 154-167. |
| [13] | 张英豪, 刘楚波, 周坤, 郭家存, 刘世鹏, 孙娈姿. 果草系统中枣树对不同方位紫花苜蓿和鸭茅生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 203-212. |
| [14] | 崔灿, 王梦琦, 赵琬璐, 刘新颖, 鉴晶晶, 严俊鑫. 胺鲜酯浸种对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 46-58. |
| [15] | 曾燕霞, 陈志龙, 尚继红, 沙晓弟, 吴娟, 陈彩锦. 太空诱变对PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿材料苗期生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 59-69. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||